Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Geometry
Geometry is one of the oldest and main branches of mathematics. Measurement of the earth is the exact meaning of the word ‘Geometry’. The geometry began when men felt the need to measure their lands while buying and selling. Various shapes and figures with which we deal in geometry are called geometrical figures. In 5th grade geometry, we learn about the construction of geometrical figures and study their basic properties. Thus, one can say that geometry is the science of properties and relations of figures.
We will learn about some basic concepts and terms in geometry.
In geometry terms namely point, line and plane form the foundation of geometry. These terms point, line and plane are cannot be precisely defined. However we give examples to illustrate the meaning of these terms. Geometry is all about describing shapes and their properties.
We have already learned about points, line segments, rays, straight lines, angles etc. Hence, we will revise these terms in brief.
Geometry is a science in which we study some properties and relations of points, lines, planes and solids in space.
Let us recall and review some of the concepts we developed earlier.
Point, Line, Line Segment, Ray and Straight Line:
|
Point: A circle of zero radius is known as point. Point is simply a dot (.) A point has no length, no breadth or no height (thickness). A point is represented by a dot (.) Points are named with capital letters A, B, C, D, etc. |
Collinear Points: The points lying on the same straight line are called collinear points. Points A, B, C, D, E are collinear points because all of them are lying on the same straight line.
Non-Collinear Points: The points which are not on the same straight line are called non Collinear Points. Points A, B, C and D are non collinear points because all of them are not on the same straight line.
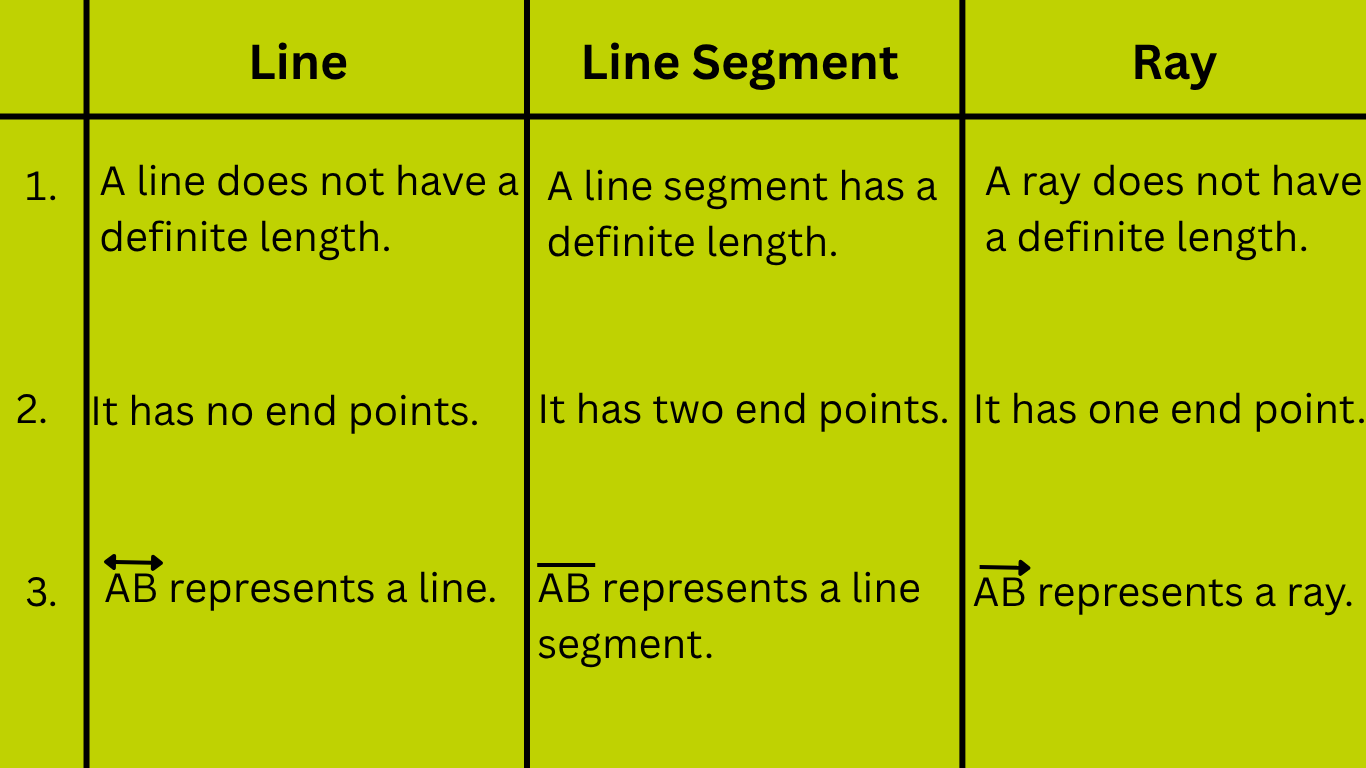
Line: Points join together to form a line.
A line has no end points.
Given below is line MN.
A line represented by two points on it.
Line MN = \(\overleftrightarrow{MN}\)
The two arrows show that it extends indefinitely to both directions.
|
Line Segment: A line segment is a part of a line. It has two end points. The given figure shows a line segment AB. It has two end points A and B. Every line segment has a definite measure which is equal to its length. A line segment is represented with the two end points. Line segment AB = AB |
|
Ray: A ray has an end point on one side and it extends indefinitely on the other side. Given below is a ray ST. A ray is represented by the end point and another point on it. The given figure shows ray AB. The symbol for the ray AB is \(\overrightarrow{AB}\). It has one end point. It can be extended to any length in the direction of B from A. |
|
Straight Line: The given figure shows a straight line AB. The symbol for the straight line AB is \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\). It has no end points. |
|
Plane: A plane is a flat surface. A plane extends in all the four directions infinitely endlessly in length and breadth. |
A plane cannot be drawn on a piece of paper. It has no boundary and what we draw on a paper is a part of a plane only but not the plane itself. Table top, wall, roof of the room etc. are the examples of the part of the plane.
In short, a plane is a flat surface like a table top, a book etc. The plane can be extended in all the directions. So, a part of plane can only be represented on a sheet of paper. Points and lines lie on a plane. It is named by marking three points on it.
Hence, flat shapes like lines; circles and triangles that can be drawn on a flat surface for example on a piece of paper are called plane geometry.
The three dimensional objects like cubes, cuboids, prisms, cylinder and pyramids are called solid geometry.
Questions and Answers on Geometry:
I. How many line segments are needed to draw:
(i) a rectangle
(ii) a square
(iii) a cube
(iv) a triangle
Answers:
I. (i) 4
(ii) 4
(iii) 12
(iv) 3
1. What is a Point in Math?
1. What is a Point in Math?
Answer: A point shows a definite position. It has no length, width or thickness. It has no shape and size. It is represented by a dot (.) and named by a capital letter such as A, B, C, P, Q, R, etc.
Remember, points that lie on a straight line are called collinear points. Those which are not on the same straight line are called non-collinear points.
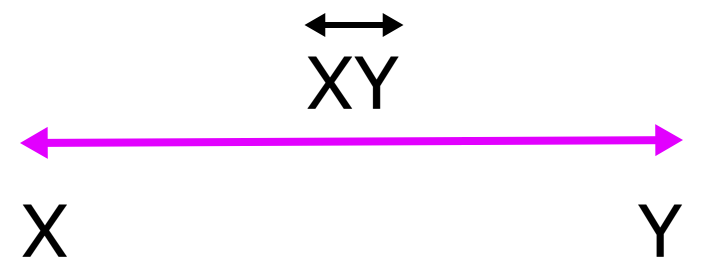
2. What is a Line in Math?
Answer:
A line has no fixed length and end points. A line can be extended indefinitely in any direction. We represent a line as \(\overleftrightarrow{XY}\).
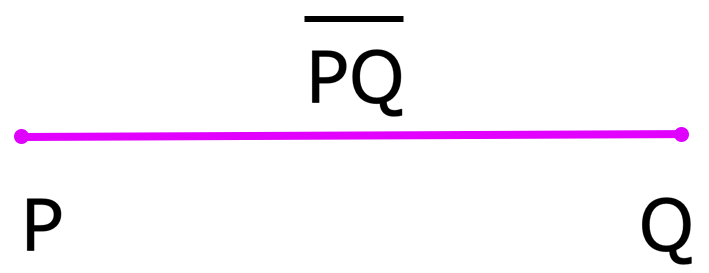
3. What is a Line Segment in Math?
Answer:
A part of a line is known as line segment. If we join two points P and Q which lie on a line we get a line segment PQ. The points P and Q are the end points of the line segment. It has a definite length. We can represent it as \(\overline{PQ}\).
3. What is a Ray in Math?
Answer:
A ray is a part of a line which has a definite starting point but goes indefinitely in another direction. It is represented by AB. A is its starting point.
4. What is the difference between line, line segment and ray?
Answer:
● Angle.
Interior and Exterior of an Angle.
Measuring an Angle by a Protractor.
Construction of Angles by using Compass.
Geometry Practice Test on angles.
To Construct a Triangle whose Three Sides are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Sides and the included Angles are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Angles and the included Side are given.
To Construct a Right Triangle when its Hypotenuse and One Side are given.
Worksheet on Construction of Triangles.
● Circle
Relation between Diameter Radius and Circumference.
Construction of Perpendicular Lines by using a Protractor.
Sum of Angles of a Quadrilateral.
Practice Test on Quadrilaterals.
● Area.
To find Area of a Rectangle when Length and Breadth are of Different Units.
To find Length or Breadth when Area of a Rectangle is given.
To find Cost of Painting or Tilling when Area and Cost per Unit is given.
To find the Number of Bricks or Tiles when Area of Path and Brick is given.
Word Problems on Area of a Rectangle
Word Problems on Area of a Square
Worksheet on Area of a Square and Rectangle
Worksheet on Area of Regular Figures
● Volume.
Worksheet on Volume of a Cube and Cuboid
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.