Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Properties of Triangle
We will discuss here about some of the properties of triangle.
I. Angle Sum Property of a Triangle:
Relation between the measures of three angles of a triangle.
The sum of three angles of every triangle is 180°.
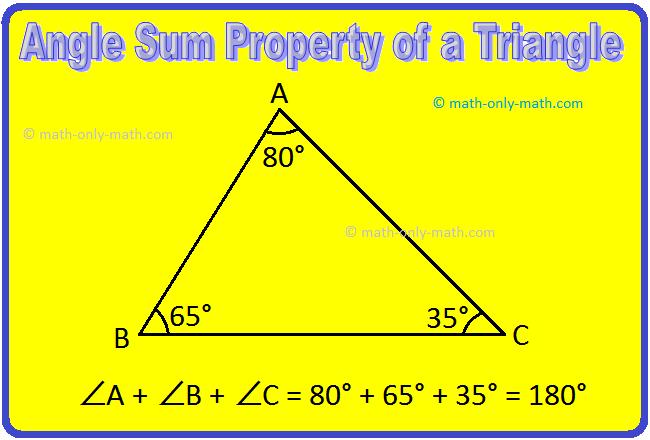
In ∆ABC, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°,
|
Draw three triangles on your not book. Name them as ∆PQR, ∆ABC and ∆LMN. With the help of protector measure all the angles the angles and find them: In ∆ABC ∠ABC + ∠BCA + ∠CAB = 180°
In ∆PQR ∠PQR + ∠QRP + ∠RPQ = 180° In ∆LMN ∠LMN + ∠MNL + ∠NLM = 180° |
Here, we observe that in each case, the sum of the measures of three angles of a triangle is 180°.
In the given figure, ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 90° and ∠C = 30°.
We see ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 60° + 90° + 30° = 180°.
Hence, the sum of the three angles of a triangle is equals to 180°.
Note: If two angles of a triangle are given, we can easily find out its third angle.
Solved Examples on Angle Sum Property of a Triangle:
1. In a right triangle, if one angle is 50°, find its third angle.
Solution:
∆ PQR is a right triangle, that is, one angle is right angle.
Given, ∠PQR = 90°
∠QPR = 50°
Therefore, ∠QRP = 180° - (∠Q + ∠ P)
= 180° - (90° + 50°)
= 180° - 140°
∠R = 40°
2. PQR is an equilateral triangle. Find the measure of its each angle.
Solution:
|
PQR is an equilateral triangle. ∠P = ∠Q = ∠R According to the angle sum property of a triangle, we get ∠P + ∠Q + ∠R = 180° ⟹ ∠P + ∠P + ∠P = 180°; [Since, ∠P = ∠Q = ∠R] ⟹ 3 ∠P = 180° ⟹ ∠P = \(\frac{180°}{3}\) ⟹ ∠P = 60° Thus, ∠P= ∠Q= ∠R = 60° |
Therefore, each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°.
3. Two angles of a triangle are 83° and 36°. Find the third angle.
Solution:
The sum of two given angles of the triangle = 83° + 36° = 119°
The sum of all the three angles of the triangle = 180°
So, the third angle = 180° - the sum of two angles
= 180° - 119°
= 61°
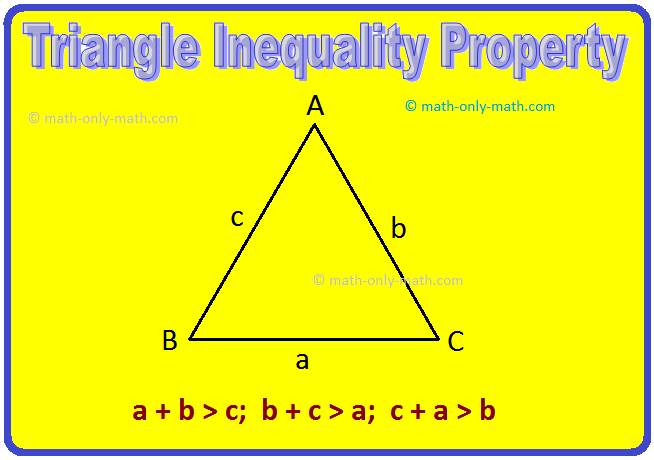
II. Triangle Inequality Property:
Triangle inequality property is the relation between lengths of the side of a triangle.
∆ABC has three sides namely AB, BC and CA.
For a shorter notation, the length of the side opposite to the vertex A is written as 'a'
i.e., a = BC
Similarly, b = CA and c = AB
If we measure the lengths of a, b and c, we find the following relation:
a + b > c
b + c > a
c + a > b
Now, we have the following:
The sum of any two sides in a triangle is greater than the third side.
Solved Examples on Triangle Inequality Property:
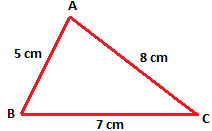
1. Draw a ∆ABC. Measure the length of its three sides.
Let the lengths of the three sides be AB = 5 cm, BC = 7 cm, AC = 8 cm.
Now add the lengths of any two sides compare this sum with the lengths of the third side.
(i) AB + BC = 5 cm + 7 cm = 12 cm
Since 12 cm > 8 cm
Therefore, (AB + BC) > AC
(ii) BC + CA = 7 cm + 8 cm = 15 cm
Since 15 cm > 5 cm
Therefore, (BC + CA) > AB
(iii) CA + AB = 8 cm + 5 cm = 13 cm
Since 13 cm > 7 cm
Therefore, (CA + AB) > BC
In the below figure we can see in each case, if we add up any two sides of the ∆, the sum is more than its third side.
Thus, we conclude that the sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Solved Examples on Triangle Inequality Property:
1. Is it possible to have a triangle whose sides are 5 cm, 6 cm and 4 cm?
Solution:
The lengths of the sides are 5 cm, 6 cm, 4 cm,
(a) 5 cm + 6 cm > 4 cm.
(b) 6 cm + 4 cm > 5 cm.
(c) 5 cm + 4 cm > 6 cm.
Hence, a triangle with these sides is possible.
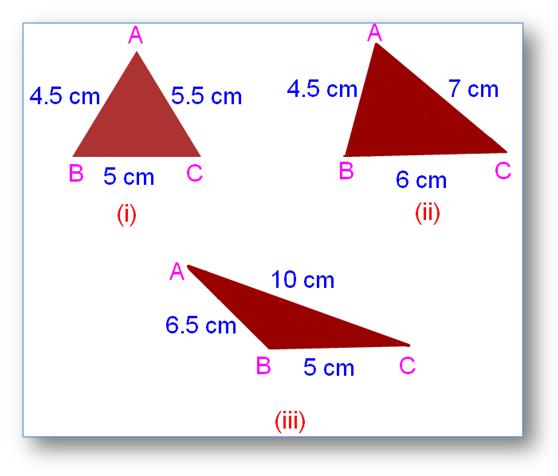
2. Which of the following can be the possible lengths (in cm) of a triangle?
(i) 3, 5, 3
(ii) 4, 3, 8
Solution:
(i) Since 3 + 5 (i.e., 8) > 3, 5 + 3 (i.e., 8) > 3 and 3 + 3 (i.e., 6) > 5, therefore 3, 5, 3 (in cm) can be the lengths of the sides of a triangle.
(ii) Since 4 + 3 (i.e., 7) < 8, therefore 4, 3, 8 (in cm) cannot be the lengths of the sides of a triangle.
3. The lengths of three line segments AB, BC and AC are as follows
(i) 3 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm
(ii) 4 cm, 4 cm, 9 cm.
(iii) 2 cm, 4 cm, 8-cm
(iv) 5 cm, 2 cm, 8 cm
In which of the above cases, you can construct a A ABC and in which you cannot and why?
Solution:
(i) The three sides are AB = 3 cm, BC = 5 cm and AC = 6 cm.
Now we see,
AB + BC > AC as 3 cm + 5 cm > 6 cm
AB + AC > BC as 3 cm + 6 cm > 5 cm
BC + AC > AB as 5 cm + 6 cm > 3 cm
So, we can construct the triangle ∆ ABC
(ii) AB = 4 cm, BC = 4 cm, AC = 9 cm
Here, we see, AB + BC < AC
i.e., 4 cm + 4 cm = 8 cm < 9 cm
So, the construction of triangle ABC is not possible.
(iii) AB = 2 cm, BC = 4 cm and AC = 8cm
Here, we see, AB + BC < AC
ie, 2 cm + 4 cm = 6 cm < 8 cm
So, the construction of ∆ ABC is not possible.
(iv) AB = 5 cm, BC = 2 cm, AC = 8 cm
Here, we see, AB + BC < AC
i.e., 5 cm + 2 cm = 7cm < 8 cm
So, the construction of triangle ABC is not possible.
III. Properties of Exterior Angles and Interior Opposite Angles of a Triangle:
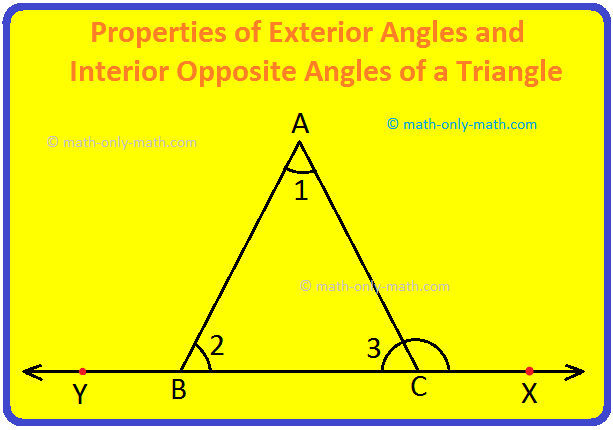
Consider a triangle ABC. Produce its side BC to X.
∠ACX is called an exterior angle of ∆ABC at C.
Similarly, produce side CB to Y, then ∠ABY is an exterior angle of ∆ABC at B.
Now, ∠ACB i.e., ∠3 is called the interior adjacent angle for ∠ACX at C, whereas ∠CBA and ∠CAB are called interior opposite angles for ∠ACX at C.
Similarly, ∠ABC i.e., ∠2 is called the interior adjacent angle for ∠ABY and ∠ACB, BAC are the interior opposite angles for ∠ABY.
Let us find a relation between the exterior angle and its interior opposite angles of a ∆ABC shown in the above figure.
In ∆ABC, Also, ∠1 + ∠ 2+ ∠3 = 180 deg; [Angle Sum Property]
Also, ∠ACB + ∠ACX = 180°; [Linear Pair]
⟹ ∠3 + ∠ACX = 180°
⟹ ∠3 + ∠ACX = ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3; (Since, 1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 180°)
⟹ ∠ACX = ∠1 + ∠2
Thus, exterior ∠ACX = sum of its two interior opposite angles, where ∠1 (= angle A) and ∠2 (= angle B) are the two interior opposite angles of the exterior ∠ACX
Similarly, exterior ∠ABY = ∠1 + ∠3
i.e. exterior ∠ABY = sum of its two interior opposite angles
Now, we have the following:
1. In a triangle, an exterior angle is equal to the sum of its two interior opposite angles.
2. In a triangle, an exterior angle is greater than either of the two interior opposite angles.
1. What is the angle sum property of a triangle?
1. What is the angle sum property of a triangle?
Answer:
The sum of all the angles of a triangle is always 180°. You can draw any number of triangles and measure their angles. You will find, the sum of the angles of each triangle is 180°.
2. What is a triangle inequality property?
2. What is a triangle inequality property?
Answer:
The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
You can draw any number of triangles and measure their sides. In each case, you will find, the sum of the lengths of any two sides of the triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
To Construct a Triangle whose Three Sides are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Sides and the included Angles are given.
To Construct a Triangle when Two of its Angles and the included Side are given.
To Construct a Right Triangle when its Hypotenuse and One Side are given.
Worksheet on Construction of Triangles.
5th Grade Math Problems
From Properties of Triangle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.