Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Parallel Lines
In parallel lines when two lines do not intersect each other at any point even if they are extended to infinity.
What are parallel lines in geometry?
Two lines which do not intersect each other at any point even if extended to infinity are called parallel lines.
The lines that always keep the same distance between them are parallel lines. These lines will never meet or intersect each other. There can be more than two lines parallel to each other. We have seen parallel lines on the zebra crossing while crossing the road.
Definition of Parallel Lines:
When two lines do not intersect each other and they have no point in common, they are called parallel lines.
For example:
The opposite edges of a ruler, rail lines, cross-bars of the window, etc. are parallel lines.
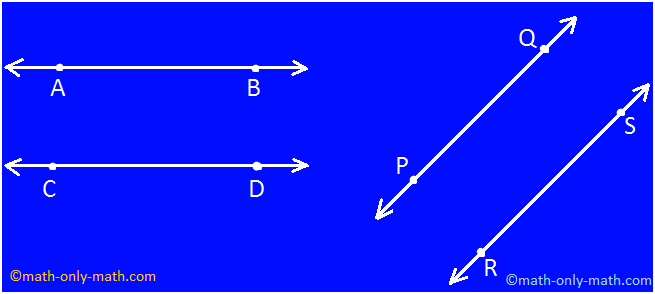
Some more examples of parallel lines are shown below.
In the figures given below line AB is parallel to CD and line PQ is parallel to RS.
Thus, two lines are parallel if;
(i) they lie on the same plane.
(ii) they do not have any common point in between.
(iii) the distance between these two lines always remains same everywhere.
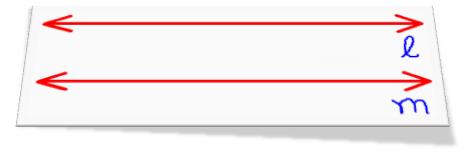
Line ℓ and m are parallel are parallel to each other.
The symbol for parallel lines is ||,
therefore, ℓ || m.
Two rays are parallel if the corresponding lines determined by them are parallel.
Two segments are parallel if the corresponding lines determined by them are parallel.
Parallel lines do not meet even if they ere extended indefinitely on the either side. There can be more than two lines parallel to each other.
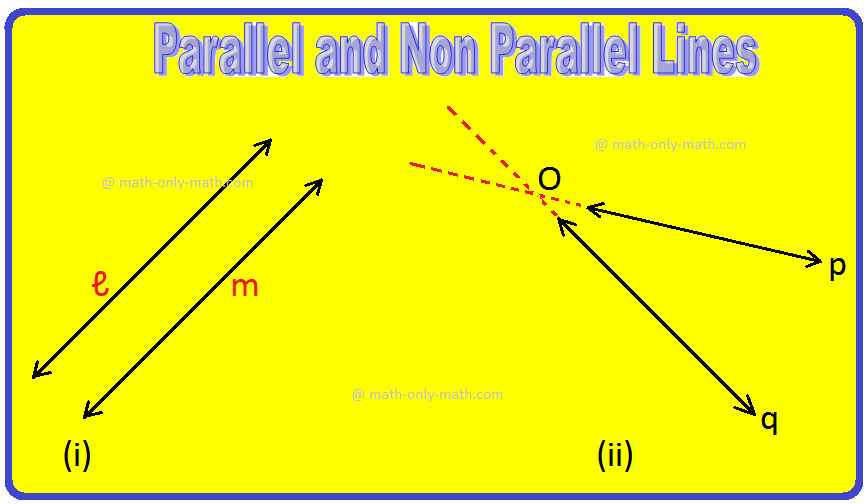
In figure (i) ℓ is parallel to m. We also write it as ℓ ∥ m.
In figure (ii), the lines p and q do not intersect. But on extending these lines, they meet at a point O. So, these are not parallel lines. From our daily life, we can say that the two rails of a railway line, the two edges of a ruler, etc., are examples of 'parallel lines'.
Working Rules to Draw Parallel Lines:
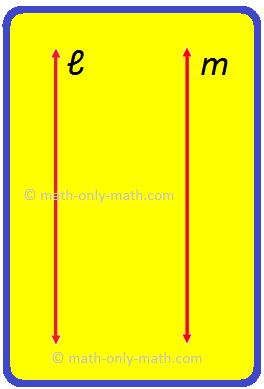
Step I: Draw two lines ℓ and m in such a way that when these two lines are extended in either direction, they do not meet at any point. There is no common point.
Step II: These lines are parallel lines. We write them as ℓ || m.
Drawing Parallel Lines with Set Squares:
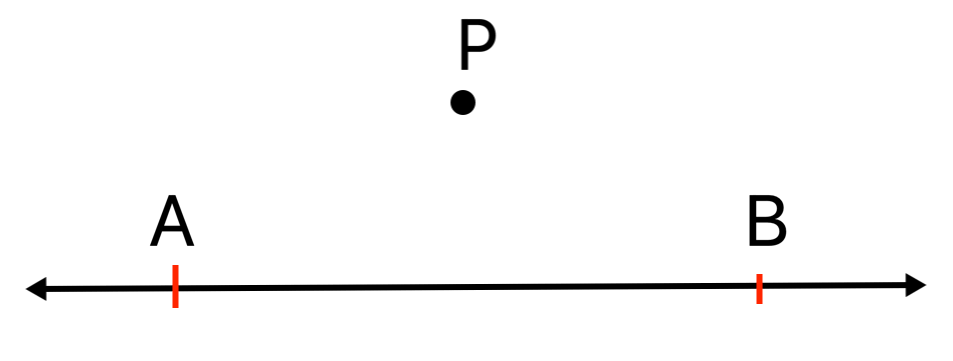
Draw a line segment through P which is parallel to \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\).
Procedure:
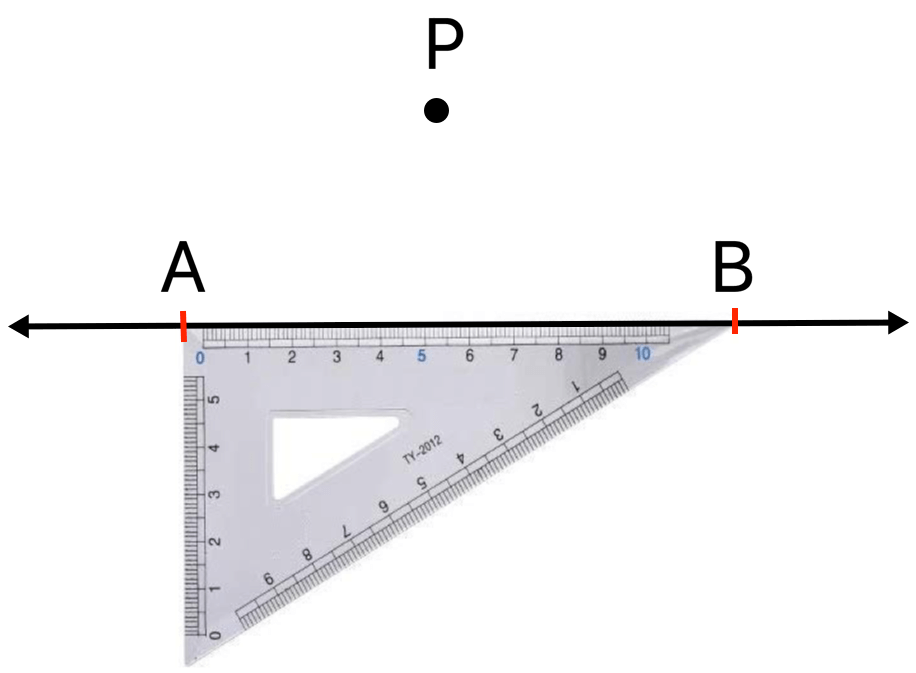
Step I: Place one edge of the two smaller edges of any set square along \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\).
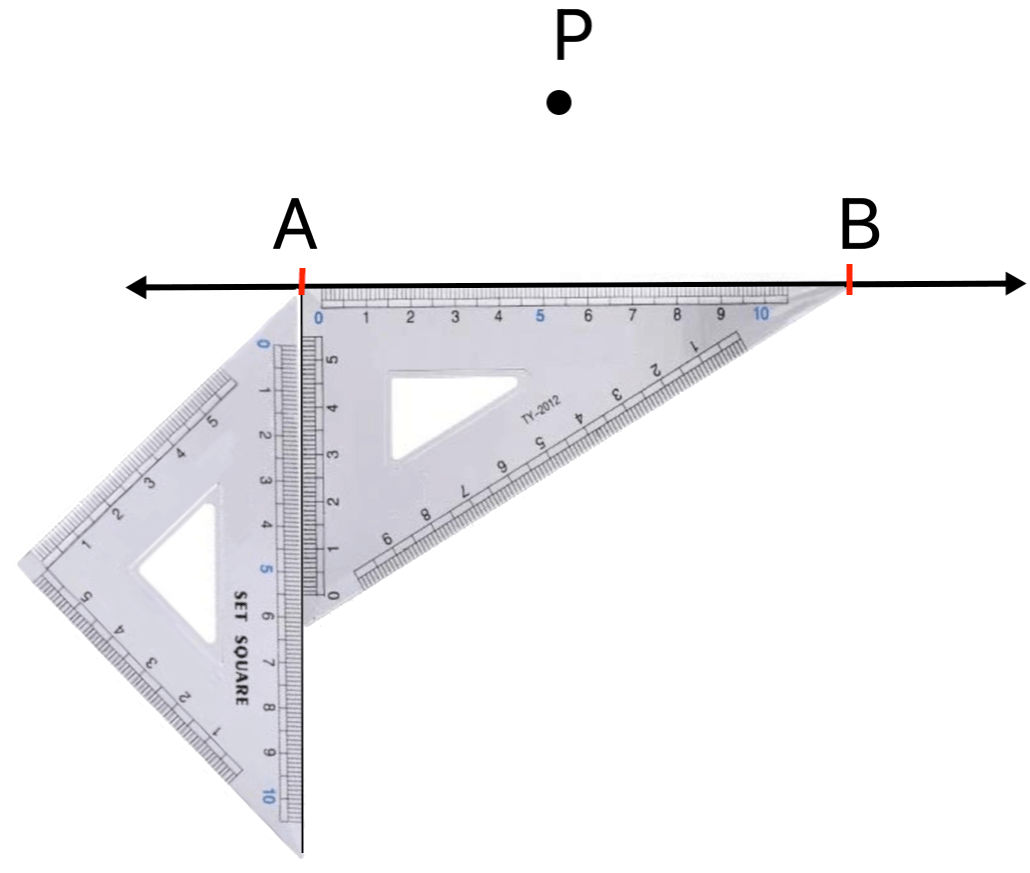
Step II: Place the longest edge of the other set square along the free side of the first set square.
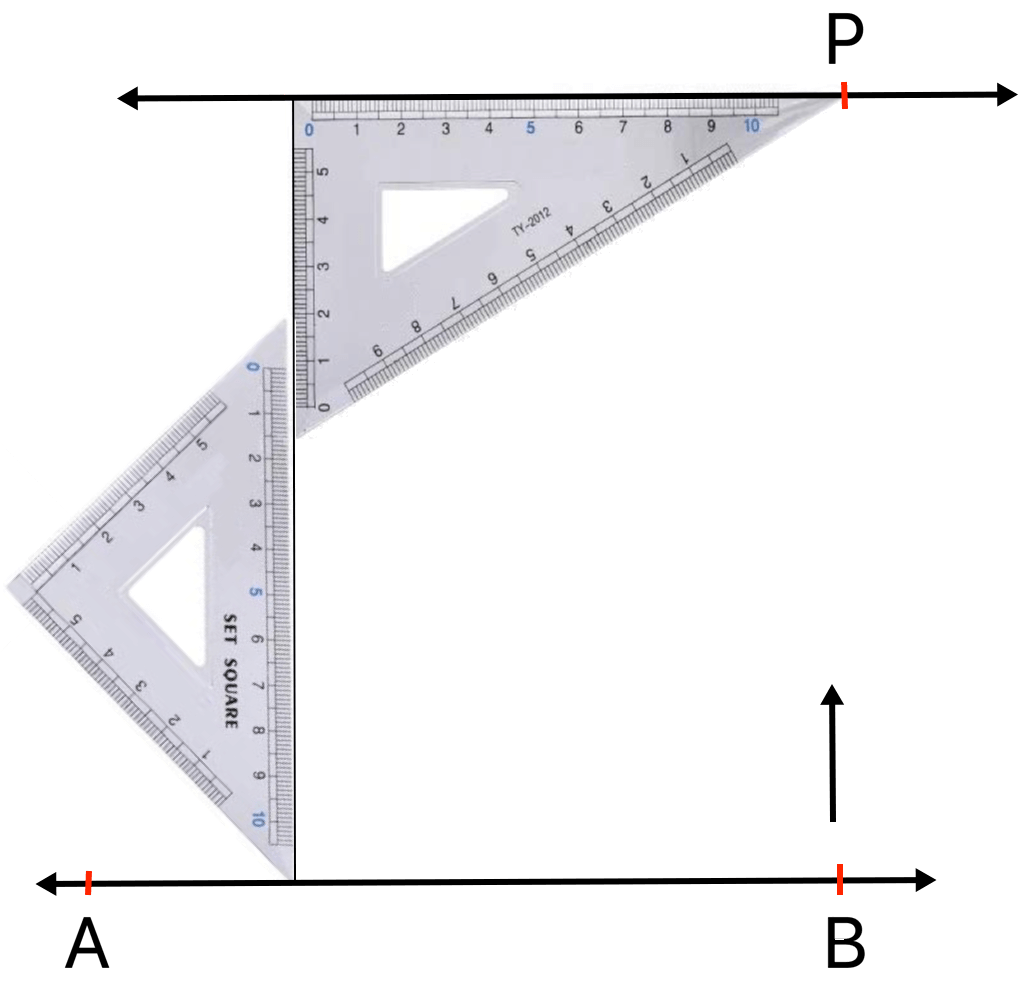
Step III: Press the second set square in position and slide the first set square until its edge passes through P. The direction of the slide is shown by an arrow.
Step IV: Draw the line through P with the help of the edge passing through P. While drawing this line, the first set square must be pressed in position.
Activity:
Step I: Take a rectangular sheet of paper.
Step II: Fold it half so that one part may cover the other part completely.
Step III: Fold it again in the same manner.
Step IV: Now unfold it to get three creases. These creases are parallel to one another.
Solved Problems on Parallel Lines:
|
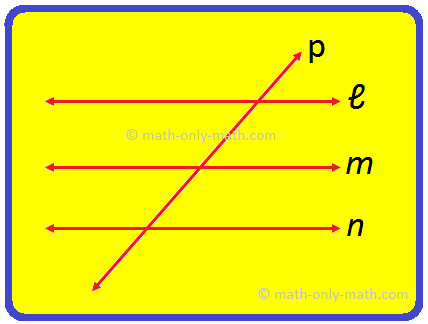
1. In the given figure, find: (i) all the lines with names. (ii) all pairs of parallel lines. Solution: (i) Lines: ℓ, m, n, p (ii) All pairs of parallel lines are (a) ℓ, m or, ℓ ∥ m (b) m, n or m ∥ n (c) ℓ, n or ℓ ∥ n |
Worksheet on Parallel Lines:
1. Draw the following:
(i) Draw a line segment AB. Mark a point C above it. Draw a line segment through C parallel to AB.
(ii) Draw a line segment AB of suitable length. Mark a point P above it. Draw PQ perpendicular to AB using set squares.
(iii) Draw a vertical line segment AB. Mark a point H on its right side. Draw a line segment through H parallel to AB.
(iv) Draw a line segment EF. Mark a point G below it. Draw a line segment through G parallel to EF.
Construction of Perpendicular Lines by using a Protractor.
Sum of Angles of a Quadrilateral.
Practice Test on Quadrilaterals.
5th Grade Geometry Page
5th Grade Math Problems
From Parallel Lines to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.