Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Construction of a Circle
A circle is a collection of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant.
Centre: The fixed point in the plane which is equidistant from every point on the boundary of a circle is called centre.
In figure, O is the centre of the circle.
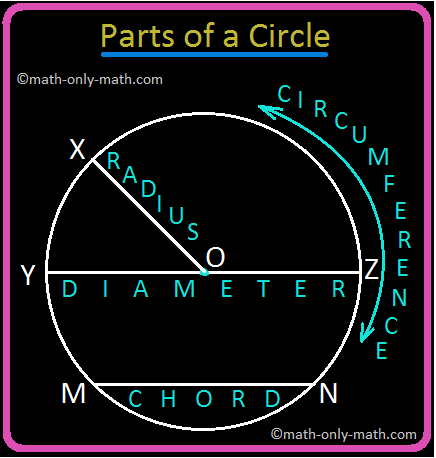
Radius: The fixed distance between the centre and any point on the boundary of the circle is called radius.
In figure, OX is a radius.
Chord: A line segment joining any two points on a circle is called a chord of the circle.
In figure, MN is a chord.
Diameter: A chord that passes through the centre of a circle is called diameter of the circle.
In figure, YZ is a diameter. The length of a diameter = 2 × radius.
In a circle, diameter is the longest chord.
Construction of a Circle when the Length of its Radius is Given:
Working Rules for Construction of a Circle:
Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be put on a mark say 3 cm (Let the radius of the circle be 3 cm).
Step II: Mark a point with pencil where we want the centre of the circle: Let it be O.
Step III: Place the pointer of the compass on O which we have marked in step II.
Step IV: Turn the compass around the point O to get the required circle.
Constructing a Circle:
We draw a circle with the help of a pair of compasses, provided in the geometry box and a fine pointed pencil.
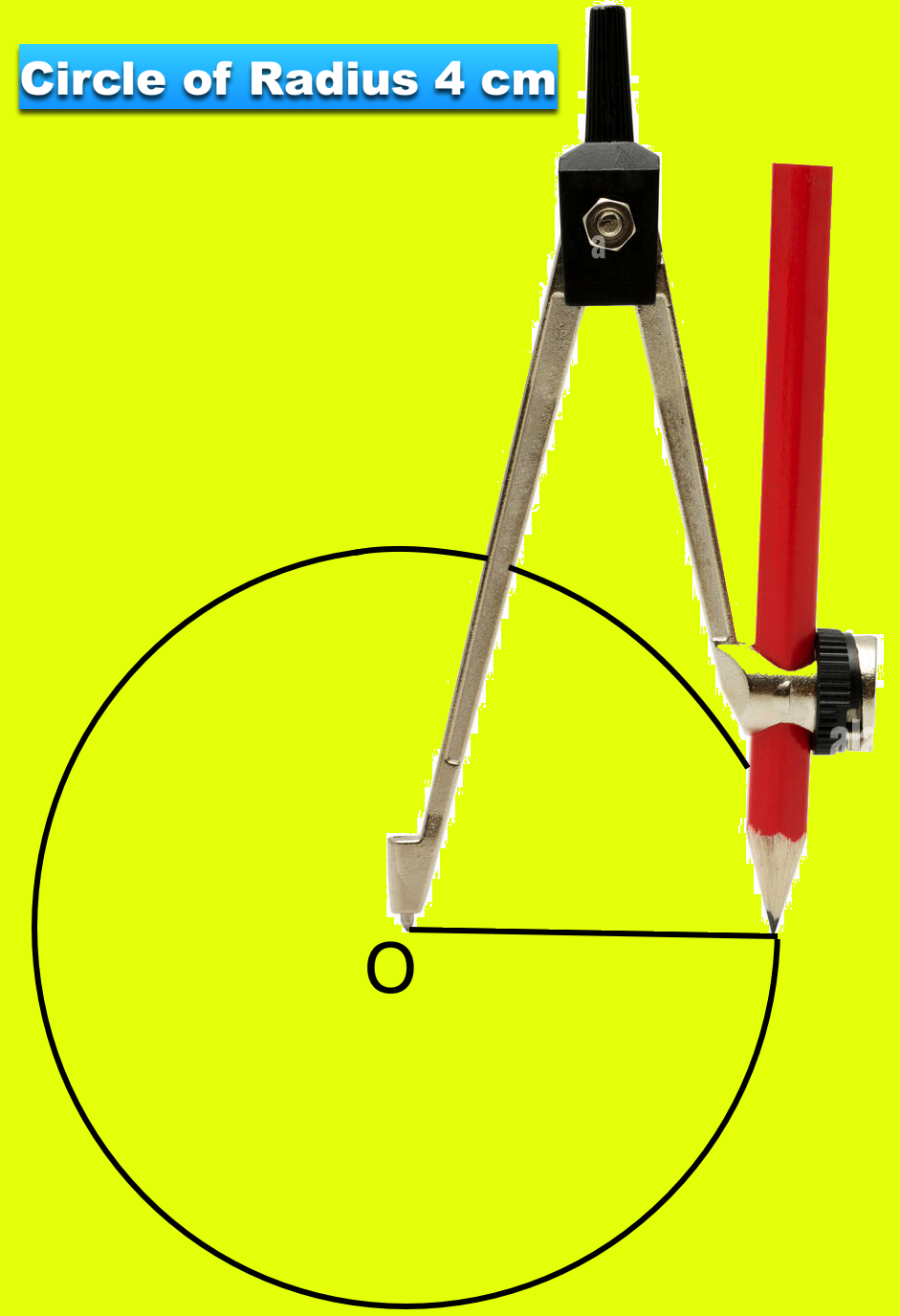
Let us draw a circle of radius 4 cm. We observe the following steps.
Step I: We expand the two arms of a pair of compasses and take the measure of 4 cm on the scale by placing pointed end at zero and the other end having a pencil at 4 cm, mark on the scale as shown in the figure.
Step II: We take a convenient point O on a piece of paper.
Step III: We fix the pointed end of the pair of compasses at O and move the pencil point around holding the pair of compasses firmly at the top. We get the desired round shape called a circle.
Example on Construction of a Circle:
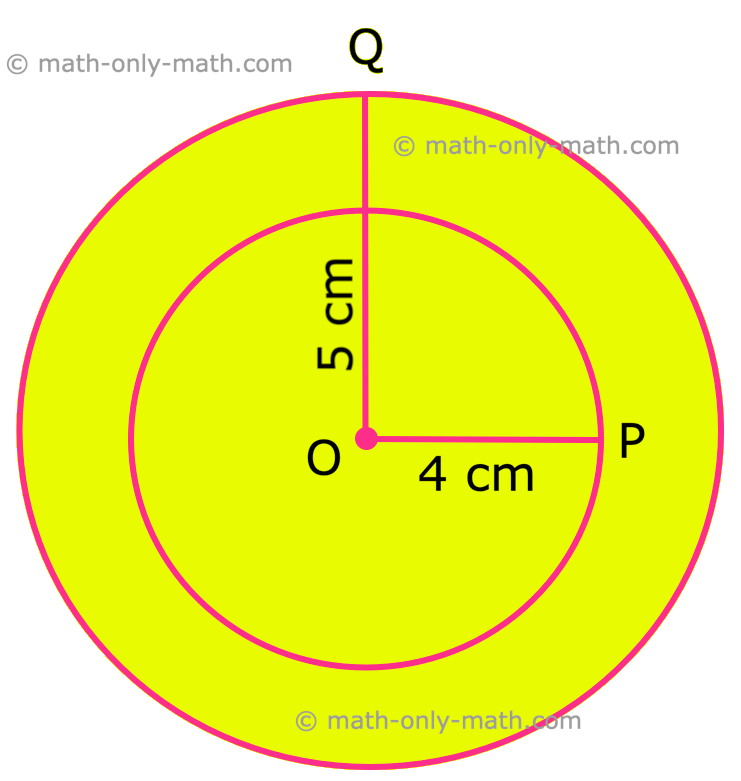
1. Draw two circle of radii 4 cm and 5 cm with same centre O.
I. Open the compass by putting the pointer on initial point of a scale and by opening the pencil-end upto 5 cm.
II. Marka point O with pencil and consider it as centre of the circle.
III. Place the pointer of the compass on O.
IV. Turn the compass around O to get the circle of radius 5 cm.
V. With the help of same above steps, draw an another circle of radius 4 cm having the same O as centre.
Solved Example on Circle:
1. Find the radius of circle whose diameter is 28 cm.
Solution:
Radius of a circle = \(\frac{\textrm{Diameter of the circle}}{\textrm{2}}\)
= \(\frac{28}{2}\) cm
= 14 cm
Worksheet on Construction of a Circle:
1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) on Circle:
Tick (✔) the correct option.
(i) The radius of a circle of diameter 20 cm is
(a) 8 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) 4.0 cm
(d) 4.5 cm
(ii) Find the diameter of the circle when radius is
(a) 3.8 cm
(b) 7.3 cm
(c) 2.9 cm
(d) 4.8 cm
(iii) O is the centre of a circle, and its radius is 5 cm. Where does P lie, when
(i) OP = 5.2 cm?
(ii) OP = 5cm?
(iii) OP = 4.8 cm?
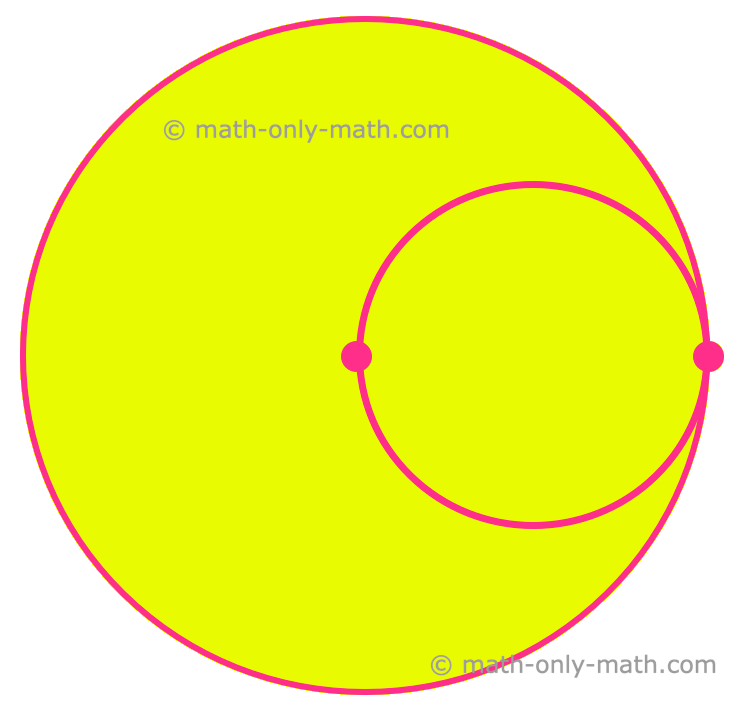
4. Draw two circles one having radius 6 cm and other having 3 cm as shown in the following figure such that the inner circle passes through centre of the other circle.
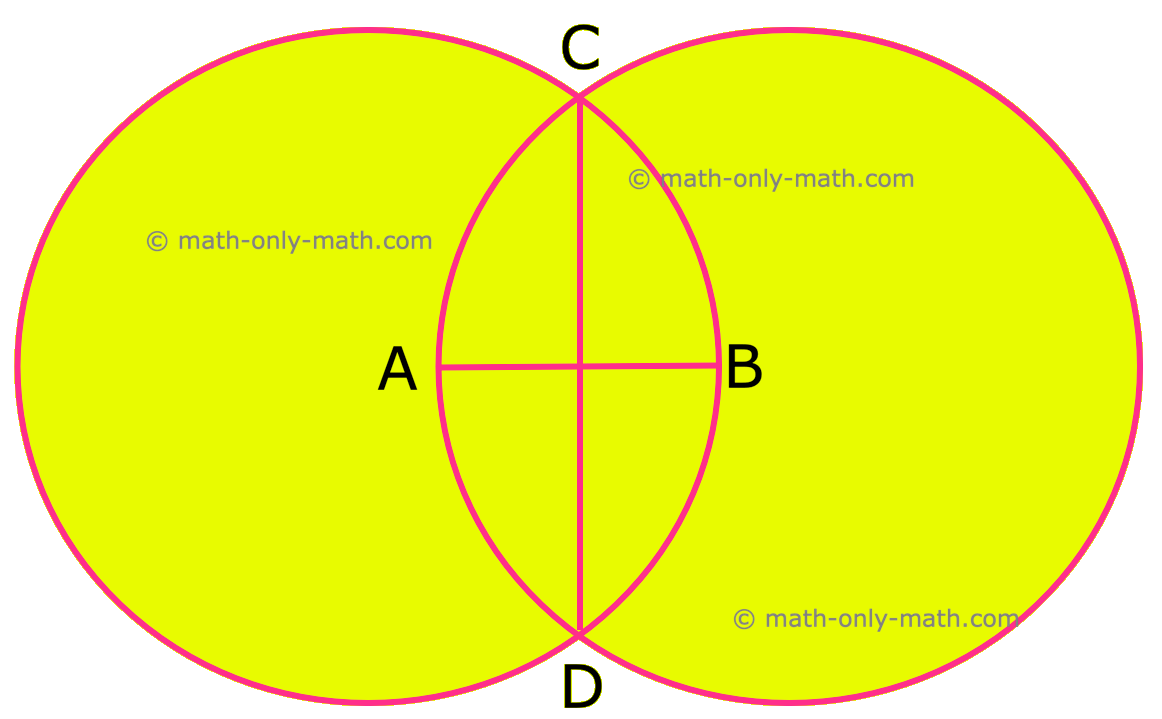
5. Draw two circles of equal radii with centres A and B such that each one of them passes through the centre of the other. Check whether AB ⊥ CD.
6. With the same centre O, draw three circles of radii 2.5 cm, 3.5 cm and 4.5 cm.
From Construction of a Circle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.