Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Practical Geometry
We have learnt the technique of measuring line segments and comparing two line segments by observation, by tracing and by using a divider.
In practical geometry, we study geometrical constructions.
The word 'construction' in geometry is used for drawing a correct and accurate figure from the given measurements. In this chapter, we shall learn how to draw some plane figures using the instruments; ruler, set-square, protractor, compass.
Let us first know something about these geometrical instruments.
I: Ruler/Straight-Edge/Scale:
The straight-edge is graduated into centimeters along one edge and inches along the other edge.
It is used to draw line segments and measure their length.
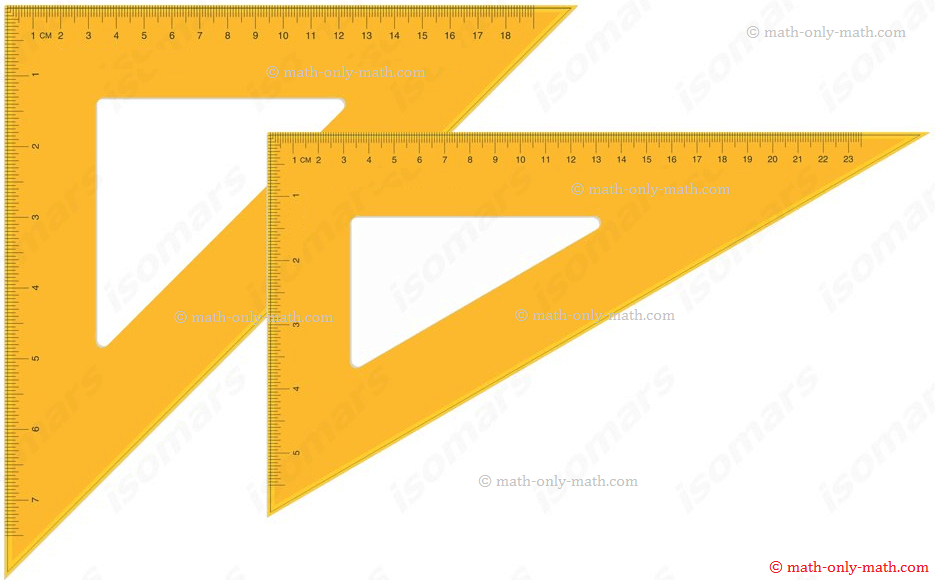
II: Set-Squares:
A pair of set-squares has two instruments (triangular in shape) in the geometry-box.
In one, the angles are 30°, 90°, 60° and in the other, the angles are 45°, 45°, 90°.
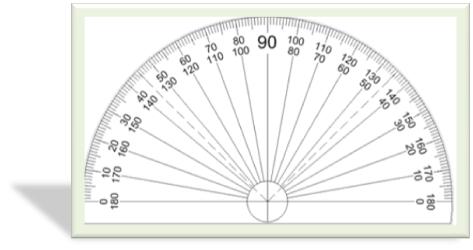
III: Protractor:
To measure the number of degrees in an angle, an instrument called protractor is used.
It is graduated into 180 equal divisions; each division represents one unit measure of an angle, called a degree. Thus, the protractor is marked from 0 degree up to 180 degrees (i.e. 0° to 180°) in both directions and the straight edge of the protractor lies along the line segment joining the 0° mark and 180° mark.
IV: Compass:
A compass has a pointer (i.e. metal-end) on one end and a pencil holder on the other.
It is used to mark off equal lengths, but does not measure them. It is also used to draw arcs and circles.
V: Divider:
A divider has a pair of pointers. It is used to compare lengths.
8th Grade Math Practice
From Practical Geometry to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.