Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
5th Grade Circle
In our daily life, we see many things which have a circular shape. For example, one-rupee, two-rupees and five-rupees coins, bangles and wheels, etc. They form a circle.
A circle is the set of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant.
The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is known as the radius of the circle.
Full moon is the example of a circle.
Interior and Exterior of a Circle:
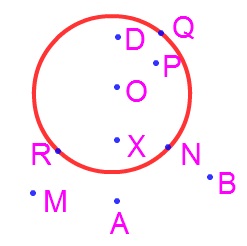
A Circle has an interior as well as an exterior region as shown in the below figure.
Here the points A, B and M lie in the exterior of the circle.
The points D, P and X lies in the interior of the circle.
The point R, Q, N lie on the circle.
The centre O of the circle always lies in the interior of the circle.
Consider a circle with centre O and radius r.
(i) The part of the plane consisting of the point A, for which OA < r, is called the interior of the circle.
(ii) The part of the plane consisting of the point B, for which OB = r, is the circle itself.
(iii) The part of the plane consisting of the point C, for which OC > r, is called the exterior of the circle.
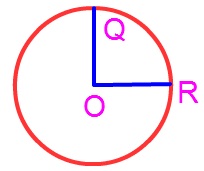
1. What is the centre of the circle?
Solution:
The point P at which we place the needle end of the compass and move the pencil around is the center of the circle.
The centre of a circle lies in its interior.
2. What is the circumference of the circle?
Solution:
The length of the boundary of the circle is its circumference.
In other words, it is the perimeter of the circle.
3. What is the radius of the circle?
Solution:
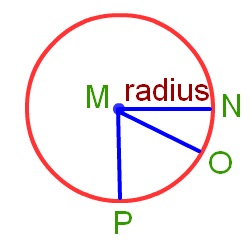
The line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is called the radius of the circle.
Take any point N on the circle and joint it with the centre M. The line segment MN is the radius of the circle.
Note:
MN = MO = MP → (Radii)
All the radii of a circle are equal in length. We can draw as many radii as we want. MN = MO = MP → (Radii)
All the radii of a circle are equal in length. We can draw as many radii as we want.
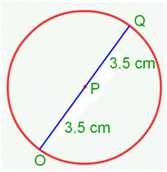
4. What is the diameter of the circle?
Solution:
Let us produce the radius PQ to meet another point O on the circle. We get a line segment OQ with its end points O & Q on the circle. It passes through the centre P.
Such a line segment is called a diameter.
The length of a diameter of a circle is twice the length of the radius of the circle.
OP = 3.5 cm
PQ = 3.5 cm
OQ = 3.5 cm + 3.5 cm
Therefore, OQ = 7.0 cm
5. What is the chord of the circle?
Solution:
The line segment joining any two points on the circle is the chord of the circle. The end points A and B of line segment AB lie on the circle.
So, AB is the chord of the circle.
Chords of a circle may or may not be equal in length. Diameter of a circle is the longest chord.
6. What is the arc of the circle?
Solution:
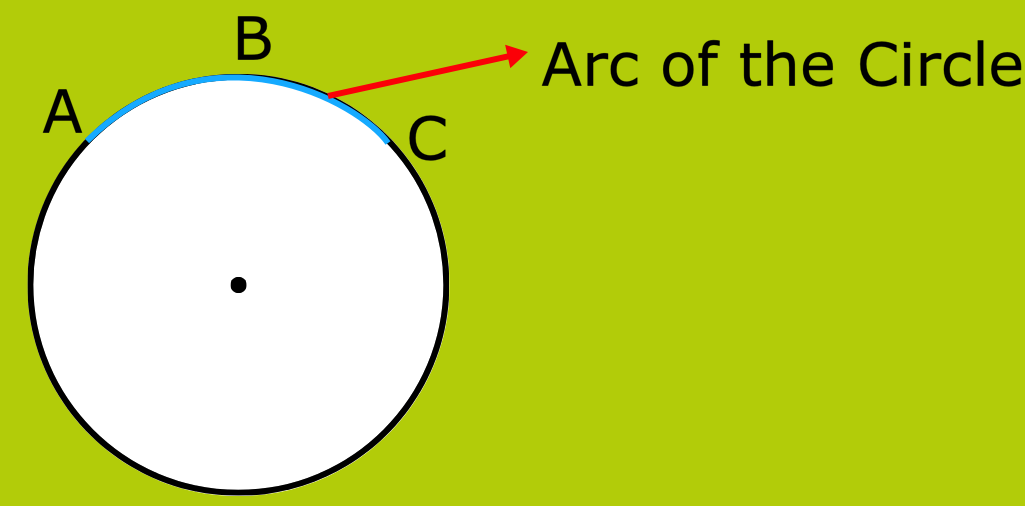
Any part of a circle is called an arc of the circle. An arc is usually named by 3 points.
ACB is an arc of the given circle.
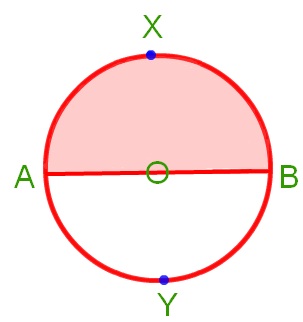
7. What is semi circle?
Solution:
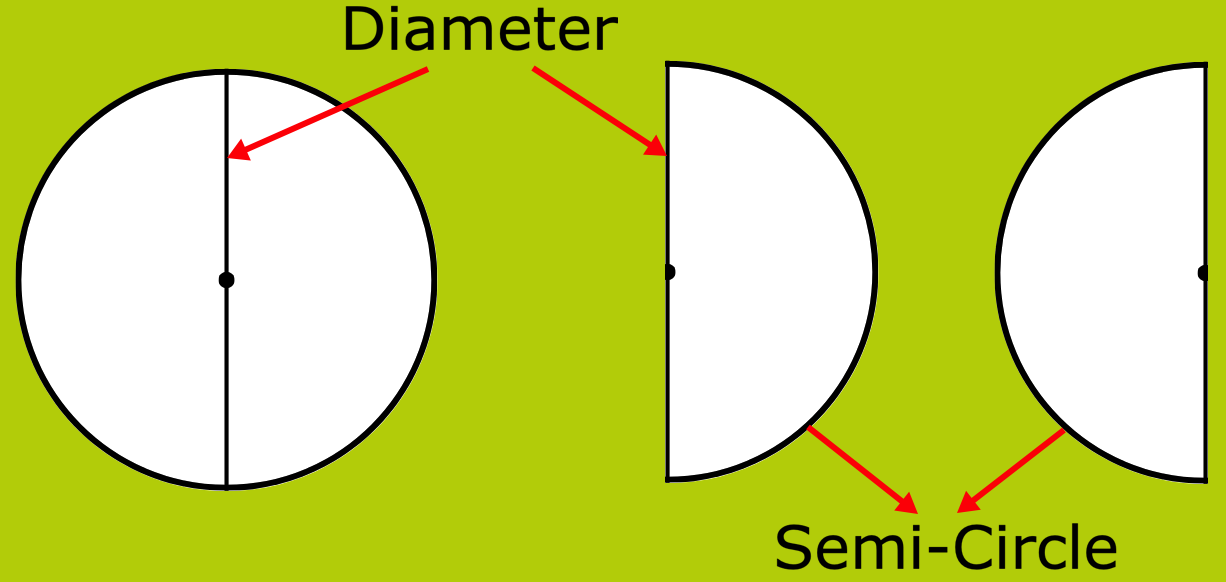
The end points of a diameter of a circle divide the circle into two parts; each part is called a semi-circular region.
AXB and AYB are two semi circles.
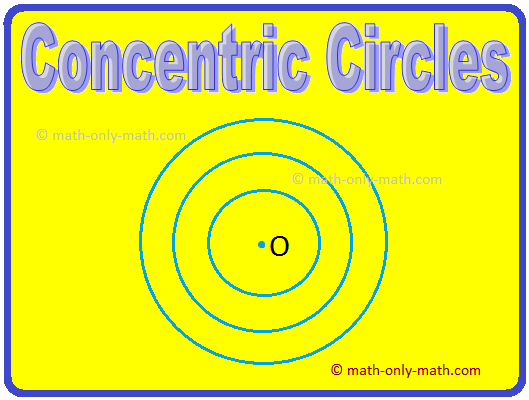
8. What are Concentric Circles?
Two or more circles with the same centre are called concentric circles.
In the above figure, three concentric circles with same centre O are drawn.
Math Only Math is based on the premise that children do not make a distinction between play and work and learn best when learning becomes play and play becomes learning.
However, suggestions for further improvement, from all quarters would be greatly appreciated.
Questions & Answers on 5th Grade Circle
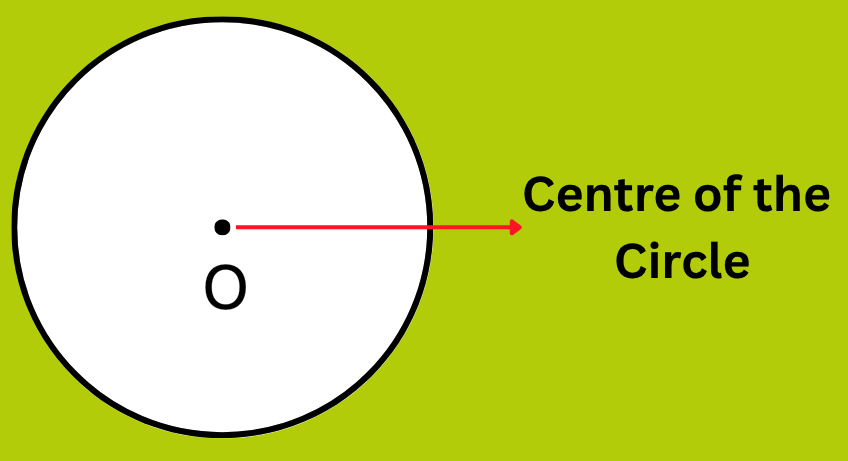
1. What is the Definition of Circle in Maths?
1. What is the Definition of Circle in Maths?
Answer:
A circle is a closed plane curve figure whose each point is at a equal distance from a fixed point called the centre of the circle.
For Example: O is the centre of circle in the given figure below. A circle is represented by O.
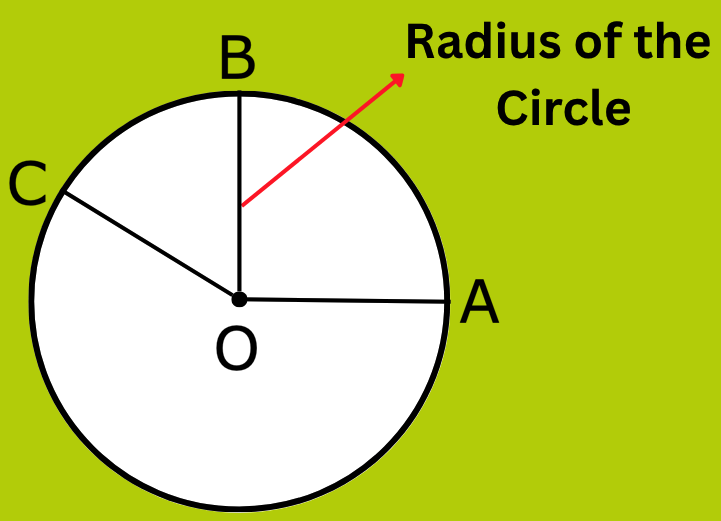
2. What is the Radius of a Circle in Maths?
Answer:
A line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is called the radius.
For Example: OA is the radius of the circle. OA, OB and OC are the radii of the circle in the figure below OA = OB = OC. (Radii is the plural of radius)
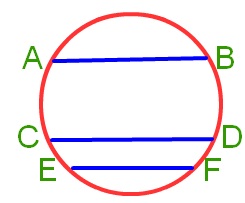
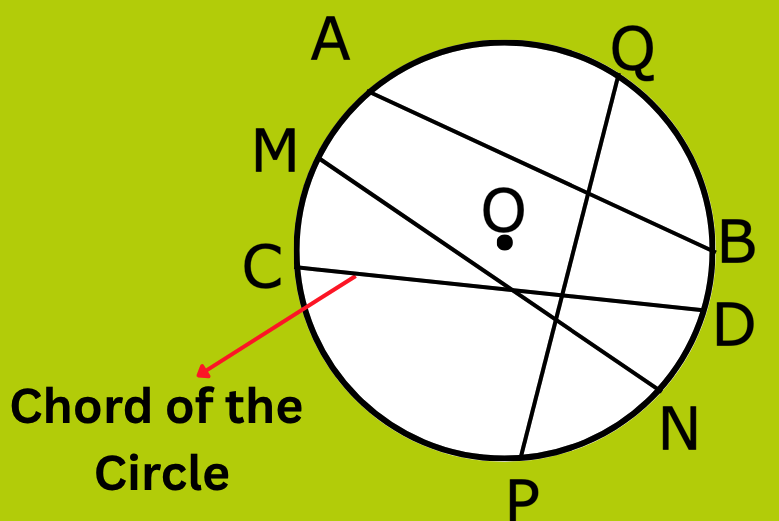
3. What is the Chord of a Circle in Maths?
Answer:
A chord is a line segment whose end points lie on a circle A chord may or may not pass through the centre of the circle.
In the figure below, AB, CD, MN and PQ are the chords of the circle.
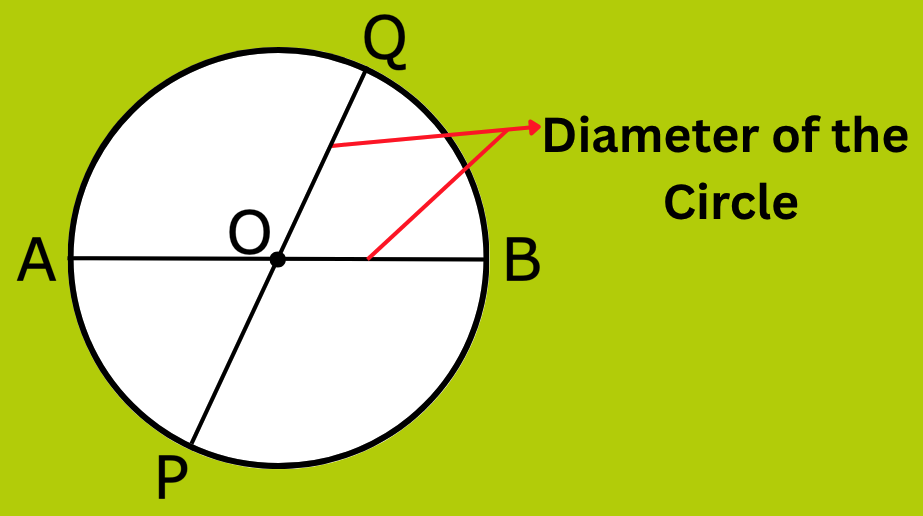
4. What is the Diameter of a Circle in Maths?
Answer:
If the chord of a circle passes through the centre, it is called the diameter of the circle.
We can also say, Diameter is a line segment whose two end points lie on the circle and it passes through the centre in the figure below, AB and PQ are the diameters of the circle which pass through its centre O. A diameter is the longest chord of a circle
Remember:
Diameter = 2 x Radius of the Circle
5. What is the Semi-Circle in Maths?
Answer:
The diameter of a circle divides the circle in two equal parts. Each half of the circle is called a semi-circle.
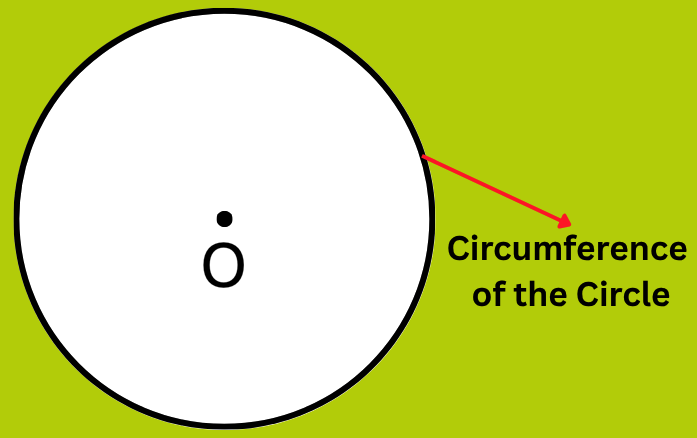
6. What is the Circumference of the Circle in Maths?
Answer:
The length of the circle is called its circumference. We cannot measure the length of a circle with the help of a scale. We measure it with the help of a thread. We first wrap the thread round the circle and then measure the length of the thread which is the circumference of the given circle.
7. What is the Arc of the Circle in Maths?
Answer:
A part of the circumference is called the arc of a circle.
Here in the figure below, ABC is an arc.
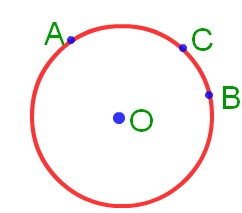
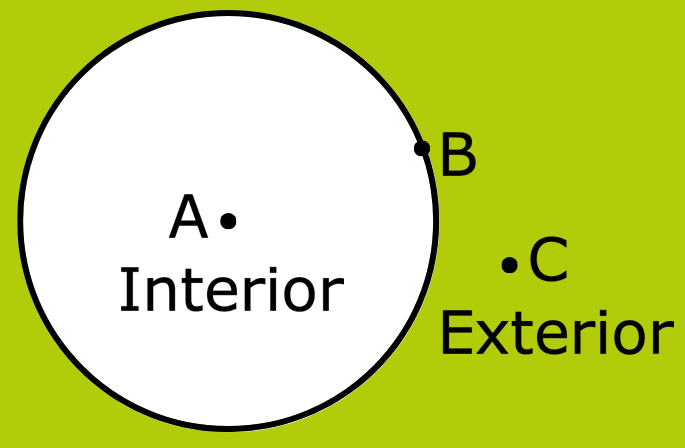
8. What is Interior and Exterior of a Circle in Maths?
Answer:
A circle divides the plane into three parts.
(i) Interior of the circle
(ii) Exterior of the circle
(iii) Circle itself
In the given figure below, point A lies in the interior of the circle. Point C lies in the exterior of the circle, and point B lies on the circle.
All the above are the Parts of a Circle or Terms Related to the Circle.
● Circle
Relation between Diameter Radius and Circumference.
5th Grade Geometry Page
5th Grade Math Problems
From 5th Grade Circle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.