Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Measuring an Angle by a Protractor
In measuring an angle by a protractor, first we need to know what a protractor is.
Protractor:
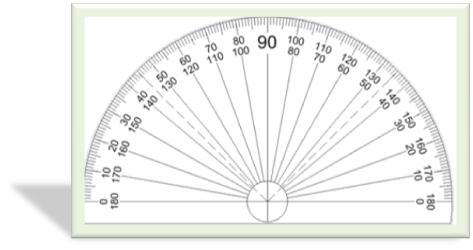
We measure the size of an angle by using protractor. The protractor is in the shape of a semicircle. The semicircle is divided into 180 equal parts which show angle measurements from 0° to 180°.
The protractor has two sets of measurements. The marking on the inner circle is 0° to 180° in the opposite direction to the markings on the outer circle.
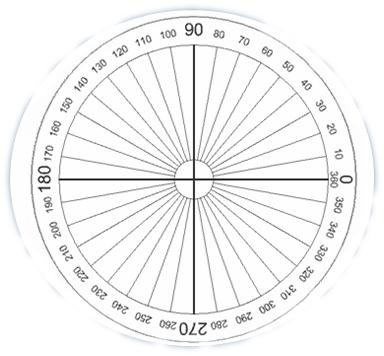
It is an instrument for measuring or constructing an angle of a given measure. It is a circular or semicircular piece of metal or plastic.
It is a circular protractor which is marked in degrees from 0° to 360° from left as shown in adjoining figure.
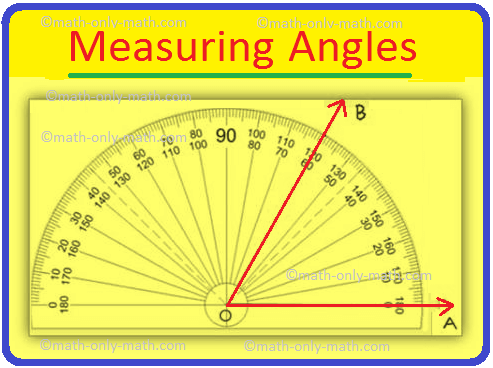
To measure an angle ABC, we place the mid point of the
protractor on the vertex O of the angle. The base OA arm falls along with the base
line of the protractor as shown in the figure below. The
angle is measures on the protractor counting from 0 up to the point where the
arm OB lies. In the above figure ∠AOB = 60°. The
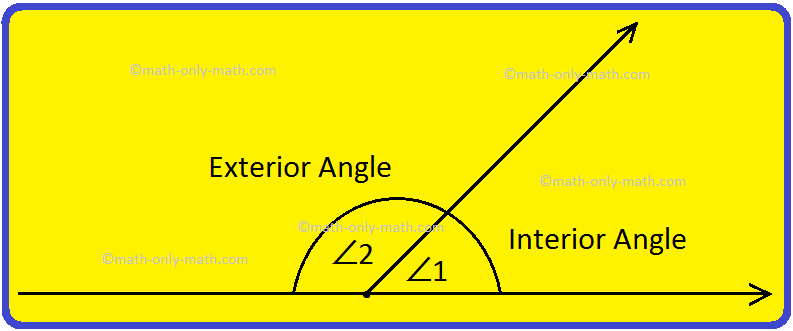
angle which is formed outside is known as the exterior angle. In the above figure ∠2 is the exterior angle and ∠1 is known
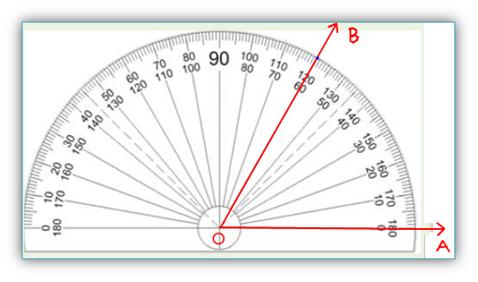
as interior angle. For Example: 1. Use your protractor to draw 60°. The centre O of the piece is also the midpoint of its base line. In order to measure ∠AOB, place the protractor in such a way that its centre is exactly on the vertex O of the angle, the base line lies along the arm OA. We need to read the mark through which the arm OB passes, starting from O on the side A, as we observe in the above figure. The centre O of the piece is also the midpoint of its base line. In order to measure ∠AOB, place the protractor in such a way that its centre is exactly on the vertex O of the angle, the base line lies along the arm OA. We need to read the mark through which the arm OB passes, starting from O on the side A, as we observe in the above figure. ● Angle. Interior and Exterior of an Angle. Measuring an Angle by a Protractor. Construction of Angles by using Compass. Geometry Practice Test on angles. 5th Grade Geometry Page Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information
about Math Only Math.
Use this Google Search to find what you need.
It is a semicircular protractor which is marked in degrees from 0° to 180° from left as shown in adjoining figure.
Thus we find ∠ AOB = 60°.
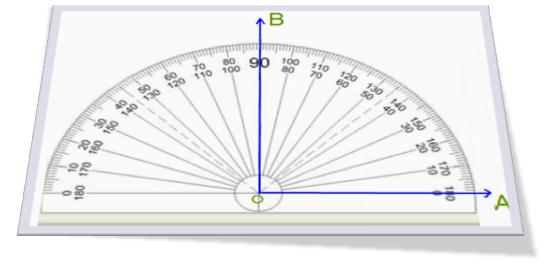
2. Use your protractor to draw 90°.
Thus we find ∠ AOB = 90°.
5th Grade Math Problems
From Measuring an Angle by a Protractor to HOME PAGE


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.