Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Subtraction of Unlike Fractions
We will learn how to solve subtraction of unlike fractions. In order to subtract unlike fractions first we convert them as like fractions.
To subtract unlike fractions, we first convert them into like fractions. In order to make a common denominator, we find LCM of all the different denominators of given fractions and then make them equivalent fractions with a common denominators.
Subtracting Unlike Fractions Using Butterfly Method Video:
Let us consider some of the examples of subtracting unlike fractions:
1. Subtract 1/10 from 2/5.
Solution:
2/5 - 1/10
The L.C.M. of the denominators 10 and 5 is 10.
2/5 = (2 × 2)/(5 × 2) = 4/10, (because 10 ÷ 5 = 2)
1/10 = (1 × 1)/(10 × 1) = 1/10, (because 10 ÷ 10 = 1)
Thus, 2/5 - 1/10
= 4/10 - 1/10
= (4 - 1)/10
= 3/10
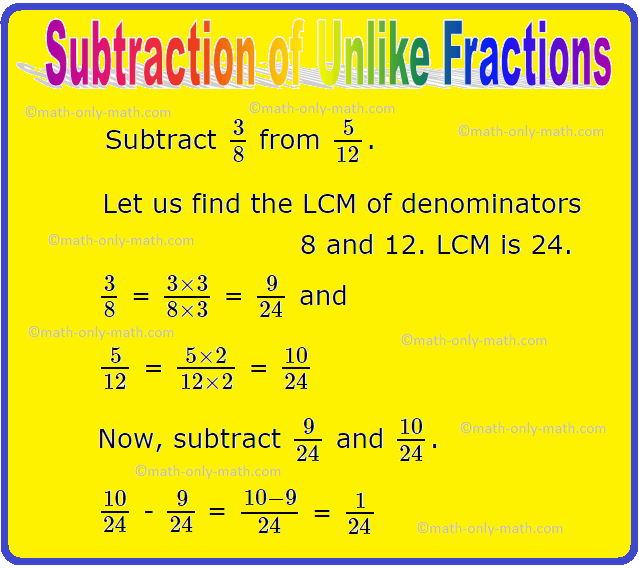
2. Subtract \(\frac{3}{8}\) from \(\frac{5}{12}\).
Solution:
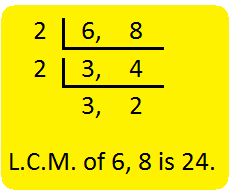
Let us find the LCM of denominators 8 and 12. LCM is 24.
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{3 × 3}{8 × 3}\) = \(\frac{9}{24}\) and
\(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5 × 2}{12 × 2}\) = \(\frac{10}{24}\)
Now, subtract \(\frac{9}{24}\) and \(\frac{10}{24}\).
\(\frac{10}{24}\) - \(\frac{9}{24}\)
= \(\frac{10 - 9}{24}\)
= \(\frac{1}{24}\)
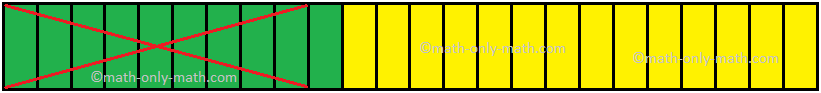
Let us illustrate the above example pictorially as shown below.
The whole strip above has 24 equal parts. The fraction \(\frac{5}{12}\) is equal to \(\frac{10}{24}\). So the shaded portion represents \(\frac{10}{24}\). We take away \(\frac{3}{8}\) or \(\frac{9}{24}\) of the above strip. The remaining part represents \(\frac{1}{24}\) of the whole strip.
3. Subtract 4/9 from 5/7.
Solution:
5/7 - 4/9
The L.C.M. of the denominators 9 and 7 is 63.
5/7 = (5 × 9)/(7 × 9) = 45/63, (because 63 ÷ 7 = 9)
4/9 = (4 × 7)/(9 × 7) = 28/63, (because 63 ÷ 9 = 7)
Thus, 5/7 - 4/9
= 45/63 - 28/63
= (45 - 28)/63
= 17/63
4. Subtract 5/8 from 1.
Solution:
1 - 5/8
= 1/1 - 5/8
The L.C.M. of the denominators 1 and 8 is 8.
1/1 = (1 × 8)/(1 × 8) = 8/8, (because 8 ÷ 1 = 8)
5/8 = (5 × 1)/(8 × 1) = 5/8, (because 8 ÷ 8 = 1)
Thus, 1/1 - 5/8
= 8/8 - 5/8
= (8 - 5)/8
= 3/8
5. Subtract 19/36 from 23/24.
Solution:
23/24 - 19/36
The L.C.M. of the denominators 24 and 36 is 72.
23/24 = (23 × 3)/(24 × 3) = 69/72, (because 72 ÷ 24 = 3)
19/36 = (19 × 2)/(36 × 2) = 38/72, (because 72 ÷ 36 = 2)
Thus, 23/24 - 19/36
= 69/72 - 38/72
= (69 - 38)/72
= 31/72
6. Subtract 9/35 from 3/7.
Solution:
3/7 - 9/35
The L.C.M. of the denominators 7 and 35 is 35.
3/7 = (3 × 5)/(7 × 5) = 15/35, (because 35 ÷ 7 = 5)
9/35 = (9 × 1)/(35 × 1) = 9/35, (because 35 ÷ 35 = 1)
Thus, 3/7 - 9/35
= 15/35 - 9/35
= (15 - 9)/35
= 6/35
7. Subtract \(\frac{2}{5}\) from 7.
Solution:
\(\frac{7}{1}\) - \(\frac{2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{7 × 5 - 2 × 1}{5}\) LCM of 1 and 5 is 5
= \(\frac{35 -2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{33}{5}\)
= 6\(\frac{3}{5}\)
Hence, 7 - \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 6\(\frac{3}{5}\)
Note: We write the whole number in the fraction form by keeping 1 in the denominator.
Subtraction of Fractions having the Different Denominator:
|
8. Subtract \(\frac{2}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\) [\(\frac{2 × 4}{3 × 4}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\)] \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{12}\) [\(\frac{1 × 3}{4 × 3}\) = \(\frac{3}{12}\)] \(\frac{2}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\) - \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{8 - 3}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{12}\) |
Method 1: Step I: Find the L.C.M. of the denominators 3 and 4. L.C.M. of 3 and 4 is 12 Step II: Write the equivalent fractions of \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\) with denominator 12. Step III: Subtract Step IV: Write the difference in lowest terms. |
|
9. Subtract \(\frac{5}{6}\) - \(\frac{1}{8}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) - \(\frac{1}{8}\) = \(\frac{(24 ÷ 6) × 5 – (24 ÷ 8) × 1}{24}\) = \(\frac{(4 × 5) – (3 × 1)}{24}\) = \(\frac{20 - 3}{24}\) = \(\frac{17}{24}\) |
Method 2: |
Subtraction of Mixed Numbers:
|
Method I: Subtract 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) = (8 – 3) + [\(\frac{1}{2}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\)] = 5 + [\(\frac{1}{2}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\)] = 5 + [\(\frac{2}{4}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\)] = 5 + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 5\(\frac{1}{4}\) |
Method II: Subtract 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) L.C.M. of 4 and 2 is 4. 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{17}{2}\) - \(\frac{13}{4}\) = \(\frac{34}{4}\) - \(\frac{13}{4}\) = \(\frac{34 - 13}{4}\)] = \(\frac{21}{4}\) = 5\(\frac{1}{4}\) |
2. What is 1\(\frac{4}{5}\) less than 4\(\frac{1}{2}\)?
Find 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 1\(\frac{4}{5}\)
4\(\frac{1}{2}\) - 1\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{9}{2}\) - \(\frac{9}{5}\) L.C.M. of 2 and 5 is 10.
= \(\frac{45}{10}\) - \(\frac{18}{10}\)
= \(\frac{45 - 18}{10}\)
= \(\frac{27}{10}\)
= 2\(\frac{7}{10}\)
Questions and Answers on Subtraction of Unlike Fractions:
1. Find the difference:
(i) \(\frac{3}{8}\) - \(\frac{1}{8}\)
(ii) \(\frac{17}{23}\) - \(\frac{6}{23}\)
(iii) \(\frac{1}{2}\) - \(\frac{3}{16}\)
(iv) \(\frac{5}{14}\) - \(\frac{2}{7}\)
(v) \(\frac{5}{6}\) - \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(vi) \(\frac{2}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{5}\)
(vii) 5 - \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(viii) 2 - \(\frac{15}{21}\)
(ix) 4\(\frac{2}{3}\) - 2
Answers:
1. (i) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(ii) \(\frac{11}{23}\)
(iii) \(\frac{5}{16}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{14}\)
(v) \(\frac{1}{12}\)
(vi) \(\frac{7}{15}\)
(vii) \(\frac{17}{4}\)
(viii) \(\frac{27}{21}\)
(ix) 2\(\frac{2}{3}\)
2. Subtract the following Unlike Fractions:
(i) \(\frac{4}{7}\) - \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(iii) 8 - \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(iv) 1\(\frac{5}{6}\) - 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(v) 4\(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(vi) 2\(\frac{1}{3}\) - 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(vii) 13\(\frac{4}{7}\) - 6
(viii) 7\(\frac{2}{5}\) - 3\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(ix) \(\frac{9}{2}\) - 4
(x) \(\frac{2}{5}\) - \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Answer:
2. (i) \(\frac{5}{21}\)
(ii) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(iii) 7\(\frac{1}{3}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(v) 4\(\frac{1}{4}\)
(vi) \(\frac{5}{6}\)
(vii) 7\(\frac{4}{7}\)
(viii) 3\(\frac{9}{10}\)
(ix) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(x) \(\frac{1}{10}\)
● Related Concepts
- Fraction of a Whole Numbers
- Representation of a Fraction
- Equivalent Fractions
- Properties of Equivalent Fractions
- Finding Equivalent Fractions
- Reducing the Equivalent Fractions
- Verification of Equivalent Fractions
- Finding a Fraction of a Whole Number
- Like and Unlike Fractions
- Comparison of Like Fractions
- Comparison of Fractions having the same Numerator
- Comparison of Unlike Fractions
- Fractions in Ascending Order
- Fractions in Descending Order
- Types of Fractions
- Changing Fractions
- Conversion of Fractions into Fractions having Same Denominator
- Conversion of a Fraction into its Smallest and Simplest Form
- Addition of Fractions having the Same Denominator
- Addition of Unlike Fractions
- Addition of Mixed Fractions
- Word Problems on Addition of Mixed Fractions
- Worksheet on Word Problems on Addition of Mixed Fractions
- Subtraction of Fractions having the Same Denominator
- Subtraction of Unlike Fractions
- Subtraction of Mixed Fractions
- Word Problems on Subtraction of Mixed Fractions
- Worksheet on Word Problems on subtraction of Mixed Fractions
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions on the Fraction Number Line
- Word Problems on Multiplication of Mixed Fractions
- Worksheet on Word Problems on Multiplication of Mixed Fractions
- Multiplying Fractions
- Dividing Fractions
- Word Problems on Division of Mixed Fractions
- Worksheet on Word Problems on Division of Mixed Fractions
From Subtraction of Unlike Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.