Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Fractions in Descending Order
We will discuss here how to arrange the fractions in descending order.
Solved examples for arranging in descending order:
1. Arrange the following fractions \(\frac{5}{6}\), \(\frac{7}{10}\), \(\frac{11}{20}\) in descending order.
First we find the L.C.M. of the denominators of the fractions to make the denominators same.
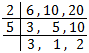
L.C.M. of 6, 10 and 20 = 2 × 5 × 3 × 1 × 2 = 60
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{5 × 10}{6 × 10}\) = \(\frac{50}{60}\) (because 60 ÷ 6 = 10)
\(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{7 × 6}{10 × 6}\) = \(\frac{42}{60}\) (because 60 ÷ 10 = 6)
\(\frac{11}{20}\) = \(\frac{11 × 3}{20 × 3}\) = \(\frac{33}{60}\) (because 60 ÷ 20 = 3)
Now we compare the like fractions \(\frac{50}{60}\), \(\frac{42}{60}\) and \(\frac{33}{60}\)
Comparing numerators, we find that 50 > 42 > 33.
Therefore, \(\frac{50}{60}\) > \(\frac{42}{60}\) > \(\frac{33}{60}\) or \(\frac{5}{6}\) > \(\frac{7}{10}\) > \(\frac{11}{20}\)
The descending order of the fractions is \(\frac{5}{6}\), \(\frac{7}{10}\), \(\frac{11}{20}\).
2. Arrange the following fractions \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{7}{8}\), \(\frac{5}{12}\) in
descending order.
First we find the L.C.M. of the denominators of the fractions to make the denominators same.
L.C.M. of 2, 4, 8 and 12 = 24
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 12}{2 × 12}\) = \(\frac{12}{24}\) (because 24 ÷ 2 = 12)
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 × 6}{4 × 6}\) = \(\frac{18}{24}\) (because 24 ÷ 10 = 6)
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{7 × 3}{8 × 3}\) = \(\frac{21}{24}\) (because 24 ÷ 20 = 3)
\(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5 × 2}{12 × 2}\) = \(\frac{10}{24}\) (because 24 ÷ 20 = 3)
Now we compare the like fractions \(\frac{12}{24}\), \(\frac{18}{24}\), \(\frac{21}{24}\) and \(\frac{10}{24}\).
Comparing numerators, we find that 21 > 18 > 12 > 10.
Therefore, \(\frac{21}{24}\) > \(\frac{18}{24}\) > \(\frac{12}{24}\) > \(\frac{10}{24}\) or \(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{3}{4}\) > \(\frac{1}{2}\) > \(\frac{5}{12}\)
The descending order of the fractions is \(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{3}{4}\) > \(\frac{1}{2}\) > \(\frac{5}{12}\).
3. Arrange the following fractions in descending order of magnitude.
|
\(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{5}{8}\), \(\frac{4}{6}\), \(\frac{2}{9}\) L.C.M. of 4, 8, 6 and 9 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 2 × 3 = 72 |
|
\(\frac{3 × 18}{4 × 18}\) = \(\frac{54}{72}\) Therefore, \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{54}{72}\) |
\(\frac{5 × 9}{8 × 9}\) = \(\frac{45}{72}\) Therefore, \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{45}{72}\) |
|
\(\frac{4 × 12}{6 × 12}\) = \(\frac{48}{72}\) Therefore, \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{48}{72}\) |
\(\frac{2 × 8}{9 × 8}\) = \(\frac{16}{72}\) Therefore, \(\frac{2}{9}\) = \(\frac{16}{72}\) |
Descending order: \(\frac{54}{72}\), \(\frac{48}{72}\), \(\frac{45}{72}\), \(\frac{16}{72}\)
i.e., \(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{4}{6}\), \(\frac{5}{8}\), \(\frac{2}{9}\)
4. Arrange the following fractions in descending order of magnitude.
4\(\frac{1}{2}\), 3\(\frac{1}{2}\), 5\(\frac{1}{4}\), 1\(\frac{1}{6}\), 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Observe the whole numbers.
4, 3, 5, 1, 2
1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5
Therefore, descending order: 5\(\frac{1}{4}\), 4\(\frac{1}{2}\), 3\(\frac{1}{2}\), 2\(\frac{1}{4}\), 1\(\frac{1}{6}\)
5. Arrange the following fractions in descending order of magnitude.
3\(\frac{1}{4}\), 3\(\frac{1}{2}\), 2\(\frac{1}{6}\), 4\(\frac{1}{4}\), 8\(\frac{1}{9}\)
Observe the whole numbers.
3, 3, 2, 4, 8
Since the whole number part of 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) and 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) are same, compare them.
Which is bigger? 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) or 3\(\frac{1}{2}\)? \(\frac{1}{4}\) or \(\frac{1}{2}\)?
L.C.M. of 4, 2 = 4
\(\frac{1 × 1}{4 × 1}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) \(\frac{1 × 2}{2 × 2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Therefore, 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) = 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) = 3\(\frac{2}{4}\)
Therefore, 3\(\frac{2}{4}\) > 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) i.e., 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) > 3\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Therefore, descending order: 8\(\frac{1}{9}\), 4\(\frac{3}{4}\), 3\(\frac{1}{2}\), 3\(\frac{1}{4}\), 2\(\frac{1}{6}\)
Worksheet on Fractions in Descending Order:
Comparison of Like Fractions:
1. Arrange the given fractions in descending order:
(i) \(\frac{7}{27}\), \(\frac{10}{27}\), \(\frac{18}{27}\), \(\frac{21}{27}\)
(ii) \(\frac{15}{39}\), \(\frac{7}{39}\), \(\frac{10}{39}\), \(\frac{26}{39}\)
Answers:
1. (i) \(\frac{21}{27}\), \(\frac{18}{27}\), \(\frac{10}{27}\), \(\frac{7}{27}\)
(ii) \(\frac{26}{39}\), \(\frac{15}{39}\), \(\frac{10}{39}\), \(\frac{7}{39}\)
2. Arrange the following fractions in descending order of magnitude:
(i) \(\frac{5}{23}\), \(\frac{12}{23}\), \(\frac{4}{23}\), \(\frac{17}{23}\), \(\frac{45}{23}\), \(\frac{36}{23}\)
(ii) \(\frac{13}{17}\), \(\frac{12}{17}\), \(\frac{11}{17}\), \(\frac{16}{17}\)
Answers:
2. (i) \(\frac{45}{23}\), \(\frac{36}{23}\), \(\frac{17}{23}\), \(\frac{12}{23}\), \(\frac{5}{23}\)
(ii) \(\frac{16}{17}\) > \(\frac{13}{17}\) > \(\frac{12}{17}\) > \(\frac{11}{17}\)
Comparison of Unlike Fractions:
3. Arrange the following fractions in descending order:
(i) \(\frac{1}{6}\), \(\frac{5}{12}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\), \(\frac{5}{18}\)
(ii) \(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\), \(\frac{4}{3}\), \(\frac{6}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(iⅲ) \(\frac{3}{6}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{5}\), \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(iv) \(\frac{4}{7}\), \(\frac{6}{7}\), \(\frac{3}{14}\), \(\frac{5}{21}\)
Answers:
3. (1) \(\frac{2}{3}\) > \(\frac{5}{12}\) > \(\frac{5}{18}\) > \(\frac{1}{6}\)
(ii) \(\frac{6}{4}\) > \(\frac{4}{3}\) > \(\frac{3}{4}\) > \(\frac{2}{3}\) > \(\frac{1}{2}\) > \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(iⅲ) \(\frac{3}{4}\) > \(\frac{3}{5}\) > \(\frac{3}{6}\) > \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(iv) \(\frac{6}{7}\) > \(\frac{4}{7}\) > \(\frac{5}{21}\) > \(\frac{3}{14}\)
Related Concept
● Representation of a Fraction
● Properties of Equivalent Fractions
● Comparison of Like Fractions
● Comparison of Fractions having the same Numerator
● Conversion of Fractions into Fractions having Same Denominator
● Conversion of a Fraction into its Smallest and Simplest Form
● Addition of Fractions having the Same Denominator
● Subtraction of Fractions having the Same Denominator
● Addition and Subtraction of Fractions on the Fraction Number Line
4th Grade Math Activities
From Fractions in Descending Order to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.