Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
Addition and subtraction of fractions are discussed here with examples.
To add or subtract two or more fractions, proceed as under:
Step I: Convert the mixed fractions (if any.) or natural numbers to improper fraction.
Step II: Find the L.C.M of the denominators of the fractions and place the L.C.M below a horizontal bar.
Step III: The L.C.M is then divided by each denominator and the quotient is multiplied to the corresponding numerator. The results obtained are placed above the horizontal bar with proper sign (+) or (-) to obtain a single fraction.
Step IV: Reduce the fraction obtained to simplest form and then convert it into mixed form if needed.
In order to add or subtract like fractions, we add or subtract their numerators and retain the common denominator.
I. Addition and Subtraction of Like Fractions:
Working Rules for Addition and Subtraction of Like Fractions:
Step I: Add or subtract the numerators of the given fractions and keep the denominator as it is.
Step II: Reduce the fraction of its lowest term.
Step III: If the result is an improper fraction, convert it into a mixed fraction.
In short,
Sum or Difference of like fractions
= Sum of Difference of Numerators
Common denominator
Examples on Addition or Subtraction with Like Fractions:
1. Find the sum of
(i) \(\frac{6}{11}\) and \(\frac{9}{11}\)
(ii) 2\(\frac{3}{10}\) and 3\(\frac{1}{10}\)
Solution:
\(\frac{6}{11}\) + \(\frac{9}{11}\)
= \(\frac{6 + 9}{11}\)
= \(\frac{15}{11}\)
= 1\(\frac{4}{11}\)
(ii) 2\(\frac{3}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{1}{10}\)
= \(\frac{23}{10}\) + \(\frac{31}{10}\)
= \(\frac{23 + 31}{10}\)
= \(\frac{54}{10}\)
= \(\frac{27}{5}\)
= 5\(\frac{2}{5}\)
2. Subtract:
(i) \(\frac{8}{15}\) from \(\frac{13}{15}\)
(ii) 2\(\frac{4}{5}\) from 5\(\frac{3}{5}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{8}{15}\)
= \(\frac{13 - 8}{15}\)
= \(\frac{5}{15}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) 5\(\frac{3}{5}\) - 2\(\frac{4}{5}\)
= \(\frac{28}{5}\) - \(\frac{14}{5}\)
= \(\frac{28 - 14}{5}\)
= \(\frac{14}{5}\)
= 2\(\frac{4}{5}\)
More Examples on addition or subtraction with like fractions;
(i) \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\)
= \(\frac{5 + 2}{8}\)
= \(\frac{7}{8}\)
(ii) \(\frac{11}{15}\) – \(\frac{7}{15}\)
= \(\frac{11 - 7}{15}\)
= \(\frac{4}{15}\)
(iii) \(\frac{16}{5}\) – \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) – \(\frac{9}{5}\)
= \(\frac{16 - 3 + 2 - 9}{5}\)
= \(\frac{18 - 12}{5}\)
= \(\frac{6}{5}\)
(iv) 4\(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) – 4\(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 3 + 2}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) – \(\frac{4 × 3 + 1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{14}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) – \(\frac{13}{3}\)
= \(\frac{14 + 1 - 13}{3}\)
= \(\frac{15 - 13}{3}\)
= \(\frac{2}{3}\)
II. Addition and Subtraction of Unlike Fractions:
To add or subtract unlike fractions, we first convert them into like fractions and then add or subtract as usual.
Working Rules for Addition and Subtraction of Unlike Fractions:
In order to add and subtract unlike fractions, we follow the following steps:
STEP I: Obtain the fractions and their denominators.
STEP II: Find the LCM of the denominators.
STEP III: Convert each of the fraction into an equivalent fraction having its denominator equal to the Least Common Multiple (LCM) obtained in step II.
STEP IV: Add or subtract like fractions obtained in step III.
Examples on addition or subtraction with unlike fractions;
1. Add:
(i) \(\frac{7}{10}\) + \(\frac{2}{15}\)
(ii) 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) + 3\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac{7}{10}\) + \(\frac{2}{15}\)
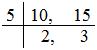
LCM of 10 and 15 is (5 × 2 × 3) = 30.
So, we convert the given fractions into equivalent fractions with denominator 30.
\(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{7 × 3}{10 × 3}\) = \(\frac{21}{30}\), and \(\frac{2}{15}\) = \(\frac{2 × 2}{15 × 2}\) = \(\frac{4}{30}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{7}{10}\) + \(\frac{2}{15}\)
= \(\frac{21}{30}\) + \(\frac{4}{30}\)
= \(\frac{21 + 4}{30}\)
=
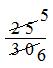
= \(\frac{5}{6}\)
(ii) 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) + 3\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 3 + 2}{3}\) + \(\frac{3 × 2 + 1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{8}{3}\) + \(\frac{7}{2}\)
= \(\frac{8 × 2}{3 × 2}\) + \(\frac{7 × 3}{2 × 3}\); [Since least common multiple (LCM) of 3 and 2 is 6; so, convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with denominator 6]
= \(\frac{16}{6}\) + \(\frac{21}{6}\)
= \(\frac{16 + 21}{6}\)
= \(\frac{37}{6}\)
= 6\(\frac{1}{6}\)
2. Simplify:
(i) \(\frac{15}{16}\) – \(\frac{11}{12}\)
(ii) \(\frac{11}{15}\) – \(\frac{7}{20}\)
(i) \(\frac{15}{16}\) – \(\frac{11}{12}\)
Least common multiple (LCM) of 16 and 12 = (4 × 4 × 3) = 48.
= \(\frac{15 × 3}{16 × 3}\) – \(\frac{11 × 4}{12 × 4}\)
[Converting each fraction to an equivalent fraction with denominator 48]
= \(\frac{45}{48}\) – \(\frac{44}{48}\)
= \(\frac{45 - 44}{48}\)
= \(\frac{1}{48}\)
(ii) \(\frac{11}{15}\) – \(\frac{7}{20}\)
Least common multiple (LCM) of 15 and 12 = 5 × 3 × 4 = 60
= \(\frac{11 × 4}{15 × 4}\) – \(\frac{7 × 3}{20 × 3}\)
[Converting each fraction to an equivalent fraction with denominator 60]
= \(\frac{44}{60}\) – \(\frac{21}{60}\)
= \(\frac{44 - 21}{60}\)
= \(\frac{23}{60}\)
Combination of Addition and Subtraction of Fractions:
3. Simplify: 4\(\frac{5}{6}\) – 2\(\frac{3}{8}\) + 3\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Solution:
4\(\frac{5}{6}\) – 2\(\frac{3}{8}\) + 3\(\frac{7}{12}\)
= \(\frac{6 × 4 + 5}{6}\) – \(\frac{2 × 8 + 3}{8}\) + \(\frac{3 × 12 + 7}{12}\)
= \(\frac{29}{6}\) – \(\frac{19}{8}\) + \(\frac{43}{12}\)
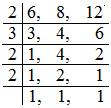
= \(\frac{29 × 4}{6 × 4}\) – \(\frac{19 × 3}{8 × 3}\) + \(\frac{43 × 2}{12 × 2}\); [Since, LCM of 6, 8, 12 is 2 × 3 × 2 × 2 = 24]
= \(\frac{116}{24}\) – \(\frac{57}{24}\) + \(\frac{86}{24}\)
= \(\frac{116 - 57 + 86}{24}\)
= \(\frac{202 - 57}{24}\)
= \(\frac{145}{24}\)
4. Simplify the fraction:
(i) 2 – \(\frac{3}{5}\) (ii) 4 + \(\frac{7}{8}\) (iii) \(\frac{9}{11}\) – \(\frac{4}{15}\) (iv) 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) – 3\(\frac{5}{8}\)
(i) 2 – \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Solution:
2 – \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{2}{1}\) – \(\frac{3}{5}\); [Since, 2 = \(\frac{2}{1}\)]
= \(\frac{2 × 5}{1 × 5}\) – \(\frac{3 × 1}{5 × 1}\); [Since, LCM of 1 and 5 is 5]
= \(\frac{10}{5}\) - \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{10 - 3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{7}{5}\)
(ii) 4 + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Solution:
4 + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
= \(\frac{4}{1}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) [Since, 4 = \(\frac{4}{1}\) ]
= \(\frac{4 × 8}{1 × 8}\) + \(\frac{7 × 1}{8 × 1}\); [Since, LCM of 1 and 8 is 8]
= \(\frac{32}{8}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
= \(\frac{32 + 7}{8}\)
= \(\frac{39}{8}\)
(iii) \(\frac{9}{11}\) – \(\frac{4}{15}\)
Solution:
\(\frac{9}{11}\) – \(\frac{4}{15}\)
LCM of 11 and 15 is 11 × 15 = 165.
= \(\frac{9 × 15}{11 × 15}\) - \(\frac{4 × 11}{15 × 11}\)
= \(\frac{135}{165}\) – \(\frac{44}{165}\)
= \(\frac{135 - 44}{165}\)
= \(\frac{91}{165}\)
(iv) 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) – 3\(\frac{5}{8}\)
Solution:
8\(\frac{1}{2}\) – 3\(\frac{5}{8}\)
= \(\frac{17}{2}\) – \(\frac{29}{8}\)
= \(\frac{17 × 4}{2 × 4}\) – \(\frac{29 × 1}{8 × 1}\); [Since, LCM of 2 and 8 is 8]
= \(\frac{68}{8}\) – \(\frac{29}{8}\)
= \(\frac{68 - 29}{8}\)
= \(\frac{39}{8}\)
= 4\(\frac{7}{8}\)
5. Simplify: 4\(\frac{2}{3}\) – 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{6}\).
Solution:
4\(\frac{2}{3}\) – 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{6}\).
= \(\frac{14}{3}\) – \(\frac{13}{4}\) + \(\frac{13}{6}\)
= \(\frac{14 × 4}{3 × 4}\) – \(\frac{13 × 3}{14 × 3}\) + \(\frac{13 × 2}{6 × 2}\)
[Since, LCM of 3, 4 and 6 is 12, so we convert each fraction into an equivalent fraction with denominator 12]
= \(\frac{56}{12}\) – \(\frac{39}{12}\) + \(\frac{26}{12}\)
= \(\frac{56 - 39 + 26}{12}\)
= \(\frac{82 - 39}{12}\)
= \(\frac{43}{12}\)
= 3\(\frac{7}{12}\)
More Examples on Addition and Subtraction of Fractions:
6. Add \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Solution:
The LCM of the denominators 8 and 12 is 24.
We convert the fractions into equivalent fractions with denominator 24.
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{3 × 3}{8 × 3}\) = \(\frac{9}{24}\) and \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5 × 2}{12 × 2}\) = \(\frac{10}{24}\)
\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{9}{24}\) + \(\frac{10}{24}\)
= \(\frac{9 + 10}{24}\)
= \(\frac{19}{24}\)
7. Add 2\(\frac{1}{8}\), 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\frac{7}{16}\)
Solution:
We have 2\(\frac{1}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{7}{16}\)
= \(\frac{17}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{2}\) + \(\frac{7}{16}\); (convert mixed fractions to improper fractions)
= \(\frac{17 × 2}{8 × 2}\) + \(\frac{5 × 8}{2 × 8}\) + \(\frac{7 × 1}{16 × 1}\); (Since, LCM of 8, 2 and 16=16)
= \(\frac{34}{16}\) + \(\frac{40}{16}\) + \(\frac{7}{16}\)
= \(\frac{34 + 40 + 7}{16}\)
= \(\frac{81}{16}\)
= 5\(\frac{1}{16}\).
8. Subtract \(\frac{4}{5}\) from \(\frac{13}{15}\)
Solution:
LCM of 15 and 5 is 15.
Now,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{4 × 3}{5 × 3}\) = \(\frac{12}{15}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{12}{15}\)
= \(\frac{13 - 12}{15}\)
= \(\frac{1}{15}\).
9. Find 6\(\frac{1}{5}\) - 3\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution:
6\(\frac{1}{5}\) - 3\(\frac{2}{3}\)
= \(\frac{31}{5}\) - \(\frac{11}{3}\)
= \(\frac{31 × 3}{5 × 3}\) - \(\frac{11 × 5}{3 × 5}\); [Since, LCM of 5 and 3 = 15]
= \(\frac{93}{15}\) - \(\frac{55}{15}\)
= \(\frac{93 - 55}{15}\)
= \(\frac{38}{15}\)
= 2\(\frac{8}{15}\)
10. Simplify 6\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Solution:
6\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2\(\frac{2}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{13}{2}\) + \(\frac{8}{3}\) - \(\frac{1}{4}\); [Converting mixed fractions into improper fractions]
= \(\frac{13 × 6}{2 × 6}\) + \(\frac{8 × 4}{3 × 4}\) - \(\frac{1 × 3}{4 × 3}\); [Since, LCM of 2, 3 and 4 = 12]
= \(\frac{78}{12}\) + \(\frac{32}{12}\) - \(\frac{3}{12}\)
= \(\frac{78 + 32 - 3}{12}\)
= \(\frac{110 - 3}{12}\)
= \(\frac{107}{12}\)
= 8\(\frac{11}{12}\)
Addition of Proper Fractions:
1. Add the following unlike fractions:
(i) \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
(ii) \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
We first change the given unlike fractions to like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 2 and 6, which is 6.
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 3}{2 × 3}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) and
\(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{1 × 1}{6 × 1}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\).
Now \(\frac{3}{6}\) and \(\frac{1}{6}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, \(\frac{3}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{3 + 1}{6}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\).
(ii) \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
We first change the given unlike fractions to like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 6 and 4, which is 12.
Therefore, \(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{5 × 2}{6 × 2}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\) and
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 × 3}{4 × 3}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\).
Now \(\frac{10}{12}\) and \(\frac{9}{12}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, \(\frac{10}{12}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{10 + 9}{12}\) = \(\frac{19}{12}\) = 1\(\frac{7}{12}\).
Subtraction of Proper Fractions:
1. Find the difference:
(i) \(\frac{11}{12}\) - \(\frac{7}{18}\)
(ii) \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{11}{20}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac{11}{12}\) - \(\frac{7}{18}\)
We first change the given unlike fractions into like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 12 and 18, which is 36.
Therefore, \(\frac{11}{12}\) = \(\frac{11 × 3}{12 × 3}\) = \(\frac{33}{36}\) and
\(\frac{7}{18}\) = \(\frac{7 × 2}{18 × 2}\) = \(\frac{14}{36}\).
Now \(\frac{33}{36}\) and \(\frac{14}{36}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, \(\frac{11}{12}\) - \(\frac{7}{18}\) = \(\frac{33}{36}\) - \(\frac{14}{36}\) = \(\frac{33 - 14}{36}\) = \(\frac{19}{36}\).
(ii) \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{11}{20}\)
We first change the fractions into like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 15 and 20, which is 60.
Therefore, \(\frac{13}{15}\) = \(\frac{13 × 4}{15 × 4}\) = \(\frac{52}{60}\) and
\(\frac{11}{20}\) = \(\frac{11 × 3}{20 × 3}\) = \(\frac{33}{60}\).
Now \(\frac{52}{60}\) and \(\frac{33}{60}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, \(\frac{13}{15}\) - \(\frac{11}{20}\) = \(\frac{52}{60}\) - \(\frac{33}{60}\) = \(\frac{52 - 33}{60}\) = \(\frac{19}{60}\).
Addition of Mixed Fractions:
1. Add 3\(\frac{1}{5}\) and 2\(\frac{1}{10}\)
Solution:
3\(\frac{1}{5}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{10}\)
We first convert the given mixed fractions into improper fractions.
Therefore, 3\(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{3 × 5 + 1}{5}\) = \(\frac{15 + 1}{5}\) = \(\frac{16}{5}\) and
2\(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{2 × 10 + 1}{10}\) = \(\frac{20 + 1}{10}\) = \(\frac{21}{10}\)
Now we see that \(\frac{16}{5}\) and \(\frac{21}{10}\) are unlike fractions.
So, we convert \(\frac{16}{5}\) and \(\frac{21}{10}\) into like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 5 and 10, which is 10.
Therefore, \(\frac{16}{5}\) = \(\frac{16 × 2}{5 × 2}\) = \(\frac{32}{10}\) and
\(\frac{21}{10}\) = \(\frac{21 × 1}{10 × 1}\) = \(\frac{21}{10}\).
Now \(\frac{32}{10}\) and \(\frac{21}{109}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, 3\(\frac{1}{5}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{16}{5}\) + \(\frac{21}{10}\) = \(\frac{32}{10}\) + \(\frac{21}{10}\) = \(\frac{32 + 21}{10}\) = \(\frac{53}{10}\) = 5\(\frac{3}{10}\).
Subtraction of Mixed Fractions:
1. Subtract 1\(\frac{7}{15}\) from 2\(\frac{5}{9}\)
Solution:
2\(\frac{5}{9}\) - 1\(\frac{7}{15}\)
We first convert the given mixed fractions into improper fractions.
Therefore, 2\(\frac{5}{9}\) = \(\frac{2 × 9 + 5}{9}\) = \(\frac{18 + 5}{9}\) = \(\frac{23}{9}\) and
1\(\frac{7}{15}\) = \(\frac{1 × 15 + 7}{15}\) = \(\frac{15 + 7}{15}\) = \(\frac{22}{15}\)
Now we see that \(\frac{23}{9}\) and \(\frac{22}{15}\) are unlike fractions.
So, we convert \(\frac{23}{9}\) and \(\frac{22}{15}\) into like fractions.
So, take the LCM of the denominators 9 and 15, which is 45.
Therefore, \(\frac{23}{9}\) = \(\frac{23 × 5}{9 × 5}\) = \(\frac{115}{45}\) and
\(\frac{22}{15}\) = \(\frac{22 × 3}{15 × 3}\) = \(\frac{66}{45}\).
Now \(\frac{115}{45}\) and \(\frac{66}{45}\) are like fractions.
Therefore, 2\(\frac{5}{9}\) - 1\(\frac{7}{15}\) = \(\frac{23}{9}\) - \(\frac{22}{15}\) = \(\frac{115}{45}\) - \(\frac{66}{45}\) = \(\frac{115 - 66}{45}\) = \(\frac{49}{45}\) = 1\(\frac{4}{45}\).
Word Problems on Addition and subtraction of fractions:
1. Ron solved \(\frac{2}{7}\) part of an exercise while Shelly solved \(\frac{4}{5}\) of it. Who solved less?
Solution:
In order to know who solved less part of the exercise, we will compare \(\frac{2}{7}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\)
LCM of denominators (i.e., 7 and 5) = 7 × 5 = 35
Converting each fraction in to an equivalent fraction having 35 as its denominator, we have
\(\frac{2}{7}\) = \(\frac{2 × 5}{7 × 5}\) = \(\frac{10}{35}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{4 × 7}{5 × 7}\) = \(\frac{28}{35}\)
Since, 10 < 28
Therefore, \(\frac{10}{35}\) < \(\frac{28}{35}\) ⟹ \(\frac{2}{7}\) < \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Hence, Ron solved lesser part than Shelly.
2. Jack finished coloring a picture in \(\frac{7}{12}\) hour. Victor finished coloring the same picture in \(\frac{3}{4}\) hour. Who worked longer? By what fraction was it longer?
Solution:
In order to know who worked longer, we will compare fractions \(\frac{7}{12}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\).
LCM of 12 and 4 = 12
Converting each fraction into an equivalent fraction with 12 as denominator
\(\frac{7}{12}\) = \(\frac{7 × 1}{12 × 1}\) = \(\frac{7}{12}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 × 3}{4 × 3}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Since, 7 < 9
Therefore, \(\frac{7}{12}\) < \(\frac{9}{12}\) ⟹ \(\frac{7}{12}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Thus, Victor finished coloring in longer time.
Now, \(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{7}{12}\)
= \(\frac{9}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{12}\)
= \(\frac{9 - 7}{12}\)
= \(\frac{2}{12}\)
= \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Hence, Victor finished coloring in \(\frac{1}{6}\) hour more time than Jack.
3. Sarah purchased 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) kg apples and 4\(\frac{3}{4}\) kg oranges. What is the total weight of fruits purchased by her?
Solution:
Total weight of the fruits purchased by Sarah is 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) kg + 4\(\frac{3}{4}\) kg.
Now, 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 4\(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{7}{2}\) + \(\frac{19}{4}\)
= \(\frac{7 × 2}{2 × 2}\) + \(\frac{19 × 1}{4 × 1}\)
= \(\frac{14}{4}\) + \(\frac{19}{4}\)
= \(\frac{14 + 19}{4}\)
= \(\frac{33}{4}\)
= 8\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, total weight is 8\(\frac{1}{4}\) kg.
4. Rachel ate \(\frac{3}{5}\) part of an apple and the remaining apple was eaten by her brother Shyla. How much part of the apple did Shyla eat? Who had the larger share? By how much?
Solution:
We have, Part of an apple eaten by Rachel = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Therefore, part of an apple eaten by Shyla = 1 - \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{5}{5}\) – \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{5 - 3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Clearly, \(\frac{3}{5}\) > \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So, Rachel had the larger share.
Now,
\(\frac{3}{5}\) - \(\frac{2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{3 - 2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Therefore, Rachel had \(\frac{1}{5}\) part more than Shyla.
5. Sam wants to put a picture in a frame. The picture is 7\(\frac{3}{5}\) cm wide. To fit in the frame the picture cannot be more than 7\(\frac{3}{10}\) cm wide. How much the picture should be trimmed?
Solution:
Actual width of the picture = 7\(\frac{3}{5}\) cm = (\(\frac{38}{5}\) cm
Required width of the picture = 7\(\frac{3}{10}\) cm = \(\frac{73}{10}\) cm
Therefore, extra width = (\(\frac{38}{5}\) – \(\frac{73}{10}\)) cm
= \(\frac{38 × 2}{5 × 2}\) – \(\frac{73 × 1}{10 × 1}\) cm
= \(\frac{76}{10}\) – \(\frac{73}{10}\) cm
= \(\frac{76 - 73}{10}\) cm
= \(\frac{3}{10}\) cm
Hence, \(\frac{3}{10}\) cm width of the picture should be trimmed.
6. What should be added to 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) to get 4\(\frac{2}{5}\)?
Solution:
To get the required number, we should subtract 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) from 4\(\frac{2}{5}\).
We get:
4\(\frac{2}{5}\) - 2\(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 5 + 2}{5}\) - \(\frac{2 × 5 + 1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{20 + 2}{5}\) - \(\frac{10 + 1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{22}{5}\) - \(\frac{11}{5}\)
= \(\frac{22 - 11}{5}\)
= \(\frac{11}{5}\)
= 2\(\frac{1}{5}\)
Hence, 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) is added to 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) to get 4\(\frac{2}{5}\).
7. The sum of two fractions is \(\frac{23}{27}\). If one of the fractions is \(\frac{4}{9}\) find the other.
Solution:
To get the required number, we should subtract \(\frac{4}{9}\) from \(\frac{23}{27}\).
We get:
\(\frac{23}{27}\) - \(\frac{4}{9}\)
= \(\frac{23}{27}\) - \(\frac{4 × 3}{9 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{23}{27}\) - \(\frac{12}{27}\)
= \(\frac{23 - 12}{27}\)
= \(\frac{11}{27}\)
Hence, \(\frac{11}{27}\) is the other number.
1. How do you add and subtract like fractions?
1. How do you add and subtract like fractions?
Answer:
To find the sum or difference of two fractions that have the same denominator (i.e., like fractions), we add or subtract their numerators and retain the common denominator. Thus:
Sum or difference of like fractions = \(\frac{\textrm{Sum or Difference of Numerators}}{\textrm{Common Denominator}}\)
For Example:
(i) Add: \(\frac{7}{9}\) + \(\frac{16}{9}\) + \(\frac{11}{9}\)
= \(\frac{7 + 16 + 11}{9}\)
= \(\frac{34}{9}\)
= 3\(\frac{7}{9}\)
(ii) Subtract: \(\frac{6}{8}\) from \(\frac{12}{8}\)
= \(\frac{12}{8}\) - \(\frac{6}{8}\)
= \(\frac{12 - 6}{8}\)
= \(\frac{6}{8}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Note: ✍️ Reduce the answer to the lowest terms.
✍️ If the answer is an improper fraction, convert it into mixed fraction.
2. How do you add or subtract unlike fractions?
2. How do you add or subtract unlike fractions?
Answer:
To find the sum or difference of two unlike fractions, we first change the fractions into equivalent like fractions by finding LCM of denominators and then proceed same as in like fractions.
For Example:
Find sum or difference:
(i) \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(ii) \(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Solution:
(i) We have, \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
The LCM of denominators 5 and 8 is 40.
Now converting each fraction into equivalent like fraction, we get:
\(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{1 × 8}{5 × 8}\) = \(\frac{8}{40}\)
and
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{3 × 5}{8 × 5}\) = \(\frac{15}{40}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
= \(\frac{8}{40}\) + \(\frac{15}{40}\)
= \(\frac{8 + 15}{40}\)
= \(\frac{23}{40}\).
(ii) We have, \(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{3}{10}\)
The LCM of denominators 4 and 10 is 20.
Now converting each fraction into equivalent like fraction, we get:
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 × 5}{4 × 5}\) = \(\frac{15}{20}\)
and
\(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{3 × 2}{10 × 2}\) = \(\frac{6}{20}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{3}{4}\) - \(\frac{3}{10}\)
= \(\frac{15}{20}\) - \(\frac{6}{20}\)
= \(\frac{15 - 6}{20}\)
= \(\frac{9}{20}\).
Note:
To add or subtract mixed fractions:
✍️ first, convert the mixed fractions into improper fractions.
✍️ then, convert the improper fractions into equivalent like fractions.
✍️ then, proceed as done before in case of like fractions.
● Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
● Fractions - Worksheets
Worksheet on Multiplication of Fractions
Worksheet on Division of Fractions
From Addition and Subtraction of Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.