Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Division of Fractions
In division of fractions or dividing fractions requires inverting the divisor, and then proceed the steps as in multiplication.
Reciprocal of a Fraction:
Two fractions are said to be the reciprocal or multiplicative inverse of each other, if their product is 1.
For example:
(i) 3/4 and 4/3 are the reciprocals of each other, because 3/4 × 4/3 = 1.
(ii) The reciprocal of 1/7 is 7/1 i.e.; 7, because 1/7 × 7/1 = 1
(iii) The reciprocal of 1/9 is 9, because 1/9 × 9 = 1
(iv) The reciprocal of 2³/₅ i.e., 13/5 is 5/13, because 2³/₅ × 5/13 = 1.
Reciprocal of 0 does not exist because division by zero is not possible.
Therefore, the reciprocal of a non-zero fraction a/b is the fraction b/a.
Division of fractions:
The division of a fraction a/b by a non-zero fraction c/d is defined as the product of a/b with the multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of c/d.
i.e. a/b ÷ c/d = a/b × d/c
How to divide fractions explain with examples?
There are 3 steps to divide fractions:
Step I: Turn over the second fraction (the one you want to divide by) upside-down (this is now a reciprocal).
Step II: Multiply the first fraction by that reciprocal.
Step III: Simplify the fraction (if possible to its lowest form) .
For example:
(i) 3/5 ÷ 5/9
[Step I: Turn over the second fraction upside-down (it becomes a reciprocal): 5/9 becomes 9/5.]
= 3/5 × 9/5
[Step II: Multiply the first fraction by that reciprocal: (3 × 9)/(5 × 5)]
= 27/25
[Step III: Is not required here since, we cannot simplify]
(ii) 2/3 ÷ 8
[Step I: Turn over the second fraction upside-down (it becomes a reciprocal): 8 = 8/1 becomes 1/8.]
= 2/3 × 1/8
= (2 × 1)/(3 × 8) [Step II: Multiply the first fraction by that reciprocal]
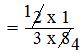
[Step III: Simplify the fraction]
= 1/12
(iii) 4 ÷ 6/7
[Step I: Turn over the second fraction upside-down (it becomes a reciprocal): 6/7 becomes 7/6.]
= 4/1 × 7/6
= (4 × 7)/(1 × 6) [Step II: Multiply the first fraction by that reciprocal]
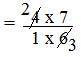
[Step III: Simplify the fraction]
= 14/3
= 4²/₃
(iv) 4²/₃ ÷ 3¹/₂
= 14/3 ÷ 7/2
[Step I: Turn over the second fraction upside-down (it becomes a reciprocal): 7/2 becomes 2/7.]
= 14/3 × 2/7
= (14 × 2)/(3 × 7) [Step II: Multiply the first fraction by that reciprocal]
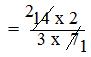
[Step III: Simplify the fraction]
= 4/3
Examples on division of fractions are explained here step by step:
1. Divide the fractions:
(i) 5/9 by 2/3
(ii) 28 by 7/4
(iii) 36 by 6²/₃
(iv) 14/9 by 11
Solution:
(i) 5/9 ÷ 2/3
= 5/9 × 3/2
= (5 × 3)/(9 × 2)
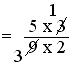
= (5 × 1)/(3 × 2)
= 5/6
(ii) 28 ÷ 7/4
= 28/1 ÷ 7/4
= 28/1 × 4/7
= (28 × 4)/(1 × 7)
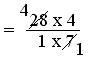
= (4 × 4)/(1 × 1)
= 16/1
(iii) 36 ÷ 6²/₃
= 36 ÷ 20/3
= 36/1 ÷ 20/3
= 36/1 × 3/20
= (36 × 3)/(1 × 20)
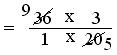
= (9 × 3)/(1 × 5)
= 27/5
= 5²/₅
(iv) 14/9 ÷ 11
= 14/9 ÷ 11/1
= 14/9 × 1/11
= (14 × 1)/(9 × 11)
= 14/99
2. Simplify the fractions:
(i) 4/9 ÷ 2/ 3
(ii) 1⁴/₇ ÷ 5/7
(iii) 3³/₇ ÷ 8/21
(iv) 15³/₅ ÷ 1²³/₄₉
Solution:
(i) 4/9 ÷ 2/3
= 4/9 × 3/2
= (4 × 3)/(9 × 2)
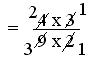
= (2 × 1)/(3 × 1)
= 2/3
(ii) 1⁴/₇ ÷ 5/7
= 11/7 × 7/5
= (11 × 7)/(7 × 5)
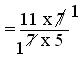
= 11/5
(iii) 3³/₇ ÷ 8/21
= 24/7 ÷ 8/21
= 24/7 × 21/8
= (24 × 21)/(7 × 8)
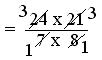
= (3 × 3)/(1 × 1)
= 9
(iv) 15³/₇ ÷ 1²³/₄₉
= 108/ 7 ÷ 72/49
= 108/7 × 49/72
= (108 × 49)/(7 × 72)
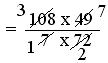
= (3 × 7)/(1 × 2)
= 21/2
3. Simplify the dividing fractions:
(i) (16/5 ÷ 8/20) + (15/5 + 3/35)
(ii) (3/2 ÷ 4/5) + (9/5 × 10/3)
Solution:
(i) (16/5 ÷ 8/20) + (15/5 + 3/35)
= (16/5 × 20/8) + (15/5 × 35/3)
= (16 × 20)/(5 × 8) + (15 × 35)/(5 × 3)
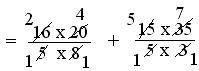
= (3 × 7)/(1 × 2)
= 21/2
3. Simplify the dividing fractions:
(i) (16/5 ÷ 8/20) + (15/5 + 3/35)
(ii) (3/2 ÷ 4/5) + (9/5 × 10/3)
Solution:
(i) (16/5 ÷ 8/20) + (15/5 + 3/35)
= (16/5 × 20/8) + (15/5 × 35/3)
= (16 × 20)/(5 × 8) + (15 × 35)/(5 × 3)
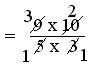
= 15/8 + 6/1
= 15/8 + (6 × 8)/(1 × 8)
= 15/8 + 48/8
= (15 + 48)/8
= 63/8
= 7⁷/₈
Examples on word problems on division of fractions:
1. The cost of 5²/₅ kg of sugar is $ 101¹/₄, find its cost per kg.
Solution:
Cost of 5²/₅ kg of sugar kg of sugar = $ 101¹/₄
Cost of 27/5 kg of sugar = $ 405/4
Cost of 1 kg of sugar
= $ (405/4 ÷ 27/5)
= $ (405/4) × (5/27)
= $ (405 × 5)/(4 × 27)
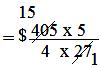
= $ 75/4
= $ 18³/₄
Hence, the cost of 1 kg of sugar is $ 18³/₄.
2. The product of two numbers is 20⁵/₇. If one of the numbers is 6²/₃, find the other.
Solution:
Product of two numbers = 20⁵/₇ = 145/7
One of the numbers is = 6²/₃ = 20/3
The other number = (Product of the numbers ÷ One of the numbers)
= 145 /7 ÷ 3/20
= 145/7 × 3/20
= (145 × 3)/ (7 × 20)
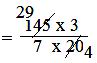
= (29 × 3)/(7 × 4)
= 87/28
= 3³/₂₈
Hence, the other number is 3³/₂₈.
3. By what number should 5⁵/₆ be multiplied to get 3¹/₃?
Solution:
Product of two numbers = 3¹/₃ =10/3
One of the numbers = 5⁵/₆ = 35/6
The other number = Product of the numbers ÷ One of the numbers
The other number = 10/3 ÷ 35/6
= 10/3 × 6/35
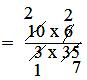
= (2 × 2)/(1 × 7)
= 4/7
Hence, required number is 4/7.
4. If the cost of a notebook is $ 8³/₄, how many notebooks can be purchased for $ 131¹/₄?
Solution:
Cost of one note book = $ 8³/₄ = $ 35/4
Total amount $ 131¹/₄ = $ 525/4
Therefore, number of notebooks = total amount/cost of one note book
= 525/4 ÷ 35/4
= 525/4 × 4/35
= (525 × 4)/(4 × 35)
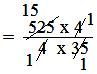
= 15
Hence, 15 notebooks can be purchased for $ 131¹/₄
5. A bucket contains 24³/₄ litres of water. How many 3/4 litre jugs can be filled from the bucket to get it emptied?
Solution:
Volume of water in the bucket = 24³/₄ litres = 99/4litres
Capacity of jug = 3/4 litre
Therefore, number of jugs that can be filled to get the bucket emptied
= 99/4 ÷ 3/4
= 99/4 × 4/3
= (99 × 4)/(4 × 3)
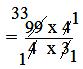
= 33
Hence, 33 jugs of 3/4 litre can be filled to get the bucket emptied.
● Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
● Fractions - Worksheets
Worksheet on Multiplication of Fractions
Worksheet on Division of Fractions
7th Grade Math Problems
From Division of Fractions to HOMEPAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.