Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Addition of Unlike Fractions
We will learn how to solve addition of unlike fractions.
In order to add unlike fractions, first we convert them as like fractions with same denominator in each fraction with the help of method explained earlier and then we add the fractions.
Let us consider some of the examples of adding unlike fractions:
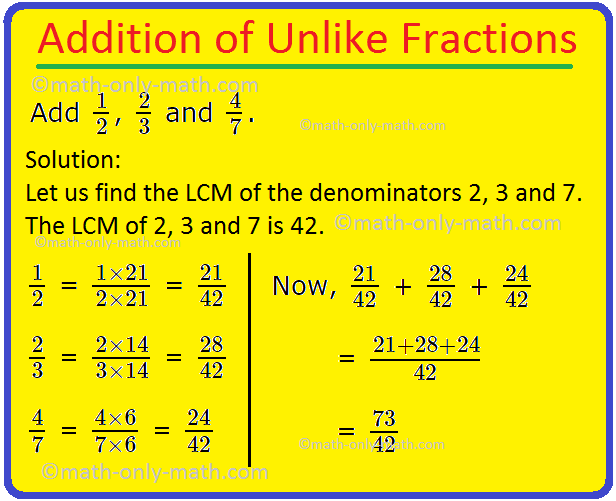
1. Add \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{4}{7}\).
Solution:
Let us find the LCM of the denominators 2, 3 and 7.
The LCM of 2, 3 and 7 is 42.
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 21}{2 × 21}\) = \(\frac{21}{42}\)
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{2 × 14}{3 × 14}\) = \(\frac{28}{42}\)
\(\frac{4}{7}\) = \(\frac{4 × 6}{7 × 6}\) = \(\frac{24}{42}\)
Therefore, we get the like fractions \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{4}{7}\).
Now, \(\frac{21}{42}\) + \(\frac{28}{42}\) + \(\frac{24}{42}\)
= \(\frac{21 + 28 + 24}{42}\)
= \(\frac{73}{42}\)
2. Add \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Solution:
The L.C.M. of the denominators 8 and 10 is 40.
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{7 × 5}{8 × 5}\) = \(\frac{35}{40}\), (because 40 ÷ 8 = 5)
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{9 × 4}{10 × 4}\) = \(\frac{36}{40}\), (because 40 ÷ 10 = 4)
Thus, \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{10}\)
= \(\frac{35}{40}\) + \(\frac{36}{40}\)
= \(\frac{35 + 36}{40}\)
= \(\frac{71}{40}\)
= 1\(\frac{31}{40}\)
3. Add \(\frac{1}{6}\) and \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Solution:
Let L.C.M. of the denominators 6 and 12 is 12.
\(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{1 × 2}{6 × 2}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\), (because 12 ÷ 6 = 2)
\(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5 × 1}{12 × 1}\) = \(\frac{5}{12}\), (because 12 ÷ 12 = 1)
Thus, \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\)
= \(\frac{2}{12}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\)
= \(\frac{2 + 5}{12}\)
= \(\frac{7}{12}\)
4. Add \(\frac{2}{3}\), \(\frac{1}{15}\) and \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Solution:
The L.C.M. of the denominators 3, 15 and 6 is 30.
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{2 × 10}{3 × 10}\) = \(\frac{20}{30}\), (because 30 ÷ 3 = 10)
\(\frac{1}{15}\) = \(\frac{1 × 2}{15 × 2}\) = \(\frac{2}{30}\), (because 30 ÷ 15 = 2)
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{5 × 5}{6 × 5}\) = \(\frac{25}{30}\), (because 30 ÷ 6 = 5)
Thus, \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{15}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\)
= \(\frac{20}{30}\) + \(\frac{2}{30}\) + \(\frac{25}{30}\)
= \(\frac{20 + 2 + 25}{30}\)
= \(\frac{47}{30}\)
= 1\(\frac{17}{30}\)
Adding Fractions Using Butterfly Method 🦋 Video
More examples on Addition of Unlike Fractions (Fractions having Different Denominators)
5. Add \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
|
Solution: First Method: Step I: Find the L.C.M. of the denominators 6 and 4. L.C.M. of 6 and 4 = 2 × 3 × 2 =12 |
Step II:Write the equivalent fractions of \(\frac{1}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\) with denominator 12.
\(\frac{1 × 2}{6 × 2}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
\(\frac{3 × 3}{4 × 3}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Step III:Add the equivalent fractions
\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{2}{12}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\)
= \(\frac{2 + 9}{12}\)
= \(\frac{11}{12}\)
Add \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Second Method:
|
\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{(12 ÷ 6) × 1 + (12 ÷ 4) × 3}{12}\) = \(\frac{(2 × 1) + (3 × 3}{12}\) = \(\frac{2 + 9}{12}\) = \(\frac{11}{12}\) |
Steps: Divide 12 by I denominator. Multiply the quotient with I numerator. Divide 12 by II denominator. Multiply the quotient with II numerator. |
|
6. Add \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{4}\) + \(\frac{6}{16}\) Solution: L.C.M. of 8, 4, 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 16 \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{4}\) + \(\frac{6}{16}\) = \(\frac{(16 ÷ 8) × 3 + (16 ÷ 4) × 2 + (16 ÷ 16) × 6}{16}\) = \(\frac{(2 × 3) + (4 × 2) + (1 × 6)}{16}\) = \(\frac{6 + 8 + 6}{16}\) = \(\frac{20}{16}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{4}\) |
Addition of Mixed Numbers
7. Add 2\(\frac{2}{6}\) + 5\(\frac{1}{3}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Solution:
First Method:
Separate the whole numbers and proper fractions.
2\(\frac{2}{6}\) + 5\(\frac{1}{3}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{5}\) = (2 + 5 + 1) + \(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\)
= 8 + \(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\)
L.C.M. of 6, 3 and 5 is 30.
= 8 + \(\frac{(30 ÷ 6) × 2 + (30 ÷ 3) × 1 + (30 ÷ 5) × 4}{30}\)
= 8 + \(\frac{(5 × 2) + (10 × 1) + (6 × 4)}{30}\)
= 8 + \(\frac{10 + 10 + 24}{30}\)
= 8 + \(\frac{44}{30}\)
= 8 + \(\frac{22}{15}\)
= 8 + 1\(\frac{7}{15}\)
Second Method:
Add 2\(\frac{2}{6}\) + 5\(\frac{1}{3}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Convert the mixed number into improper fractions and find the sum
2\(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{(2 × 6) + 2}{6}\) = \(\frac{14}{6}\)
5\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{(5 × 3) + 1}{3}\) = \(\frac{16}{3}\)
1\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{(1 × 5) + 4}{5}\) = \(\frac{9}{5}\)
Therefore, 2\(\frac{2}{6}\) + 5\(\frac{1}{3}\) + 1\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{14}{6}\) + \(\frac{16}{3}\) + \(\frac{9}{5}\)
= \(\frac{14 × 5}{6 × 5}\) + \(\frac{16 × 10}{3 × 10}\) + \(\frac{9 × 6}{5 × 6}\)
= \(\frac{70}{30}\) + \(\frac{160}{30}\) + \(\frac{54}{30}\)
= \(\frac{70 + 160 + 54}{30}\)
= \(\frac{284}{30}\)
= \(\frac{142}{15}\)
= 9\(\frac{7}{15}\)
8. Add \(\frac{2}{6}\), 4 and \(\frac{7}{12}\)
|
Solution: 4 = \(\frac{4}{1}\) \(\frac{2}{6}\) + 4 + \(\frac{7}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{4}{1}\) + \(\frac{7}{12}\) L.C.M. of 6, 1, 12 is 12
= \(\frac{(2 × 2) + (12 × 4) + (1 × 7)}{12}\) = \(\frac{4 + 48 + 7}{12}\) = \(\frac{59}{12}\) = 4\(\frac{11}{12}\) |
To add unlike fractions, we first convert them into like fractions. In order to make a common denominator we find the LCM of all different denominators of the given fractions and then make them equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
Word Problems on Addition of Unlike Fractions:
1. On Monday Michael read \(\frac{5}{16}\) of the book. On Wednesday he reads \(\frac{4}{8}\) of the book. What fraction of the book has Michael read?
Solution:
On Monday Michael read \(\frac{5}{16}\) of the book.
On Wednesday he reads \(\frac{4}{8}\) of the book.
Now add the two fractions
\(\frac{5}{16}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Let us find the LCM of the denominators 16 and 8.
The LCM of 16 and 8 is 16.
\(\frac{5}{16}\) = \(\frac{5 × 1}{16 × 1}\) = \(\frac{5}{16}\)
\(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{4 × 2}{8 × 2}\) = \(\frac{8}{16}\)
Therefore, we get the like fractions \(\frac{5}{16}\) and \(\frac{8}{16}\).
Now, \(\frac{5}{16}\) + \(\frac{8}{16}\)
= \(\frac{5 + 8}{16}\)
= \(\frac{13}{16}\)
Therefore, Michael read in two days \(\frac{13}{16}\) of the book.
2. Sarah ate \(\frac{1}{3}\) part of the pizza and her sister ate \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the pizza. What fraction of the pizza was eaten by both sisters?
Solution:
Sarah ate \(\frac{1}{3}\) part of the pizza.
Her sister ate \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the pizza.
Now add the two fractions
\(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Let us find the LCM of the denominators 3 and 2.
The LCM of 3 and 2 is 6.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{1 × 2}{3 × 2}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 3}{2 × 3}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Therefore, we get the like fractions \(\frac{2}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{6}\).
Now, \(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{6}\)
= \(\frac{2 + 3}{6}\)
= \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{5}{6}\) of the pizza was eaten by both sisters.
3. Catherine is preparing for her final exam. She study \(\frac{9}{22}\) hours on Wednesday and \(\frac{5}{11}\) hours on Sunday. How many hours she studied in two days?
Solution:
Catherine study \(\frac{9}{22}\) hours on Wednesday.
Again, she study \(\frac{5}{11}\) hours on Sunday.
Now add the two fractions
\(\frac{9}{22}\) + \(\frac{5}{11}\)
Let us find the LCM of the denominators 22 and 11.
The LCM of 22 and 11 is 22.
\(\frac{9}{22}\) = \(\frac{9 × 1}{22 × 1}\) = \(\frac{9}{22}\)
\(\frac{5}{11}\) = \(\frac{5 × 2}{11 × 2}\) = \(\frac{10}{22}\)
Therefore, we get the like fractions \(\frac{9}{22}\) and \(\frac{10}{22}\).
Now, \(\frac{9}{22}\) + \(\frac{10}{22}\)
= \(\frac{9 + 10}{22}\)
= \(\frac{19}{22}\)
Therefore, Catherine studied a total \(\frac{9}{22}\) hours in two days.
Questions and Answers Addition of Unlike Fractions:
1. Add the following Unlike Fractions:
(i) \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\)
(ii) \(\frac{1}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{6}{7}\)
(iii) \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{4}{10}\)
(iv) \(\frac{3}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{6}{11}\)
(v) 3\(\frac{5}{8}\) + 4\(\frac{1}{6}\) + 4\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Answer:
1. (i) 1\(\frac{7}{12}\)
(ii) 1\(\frac{2}{3}\)
(iii) 2\(\frac{13}{120}\)
(iv) 1\(\frac{144}{385}\)
(v) 12\(\frac{3}{8}\)
Related Concept
- Fraction of a Whole Numbers
- Representation of a Fraction
- Equivalent Fractions
- Properties of Equivalent Fractions
- Like and Unlike Fractions
- Comparison of Like Fractions
- Comparison of Fractions having the same Numerator
- Types of Fractions
- Changing Fractions
- Conversion of Fractions into Fractions having Same Denominator
- Conversion of a Fraction into its Smallest and Simplest Form
- Addition of Fractions having the Same Denominator
- Subtraction of Fractions having the Same Denominator
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions on the Fraction Number Line
From Addition of Unlike Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
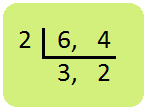
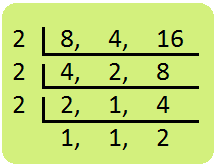
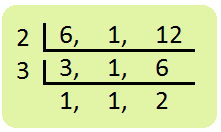


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.