Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Signs of Trigonometrical Ratios
Here we will discuss about the signs of trigonometrical ratios.
Let a rotating line \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) rotates about O in the anti-clockwise direction or clockwise direction. Suppose starting from the rotating line \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) as the initial position \(\overrightarrow{OX}\) take ∠XOA = θ. Take a point B on \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) and a line is drawn which is \(\overline{BC}\) perpendicular to \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) (or \(\overrightarrow{OX'}\)). Therefore, by the definition of trigonometrical ratios of the angle θ of the right-angled triangle OBC are:
|
sin θ = CB/OB = opposite side/hypotenuse; cos θ = OC/OB = adjacent side/hypotenuse; tan θ = CB/OC = opposite side/adjacent side;
csc θ = OB/CB = hypotenuse/opposite side sec θ = OB/OC = hypotenuse/adjacent side; cot θ = OC/CB = adjacent side/opposite side |
According to the value of θ the final arm \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) would be in the first quadrant or second quadrant or third quadrant or fourth quadrant:
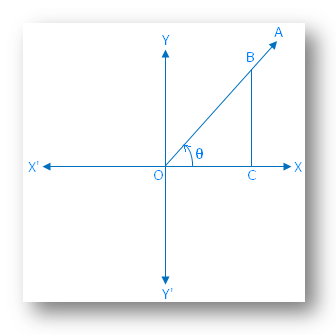
Case 1: When the final arm \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) lies in the first quadrant
According to the trigonometric rules, we get
OC is positive,
CB is positive and
OB is positive.
Therefore, according to the definitions of trigonometrical ratios the values of all trigonometrical ratios i.e. sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, csc θ, sec θ and cot θ are positive.
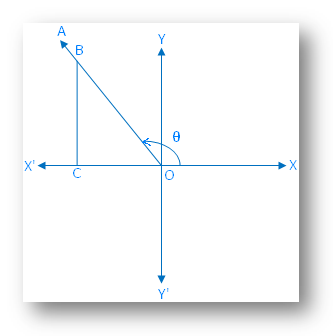
Case 2: When the final arm \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) lies in the second quadrant.
According to the trigonometric rules, we get
OC is negative,
CB is positive and
OB is positive.
Therefore, according to the definitions of trigonometrical ratios the values of sin θ and csc θ are positive and the other trigonometrical ratios i.e. cos θ, tan θ, sec θ and cot θ are negative.
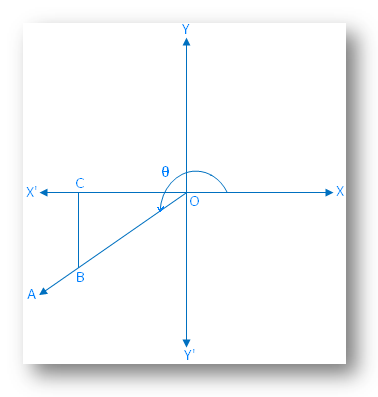
Case 3: When the final arm \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) lies in the third quadrant.
According to the trigonometric rules, we get
OC is negative;
CB is negative and
OB is positive.
Therefore, according to the definitions of trigonometrical ratios the values of tan θ and cot Ѳ are positive and the other trigonometrical ratios i.e. sin θ, cos θ, sec θ and csc θ are negative.
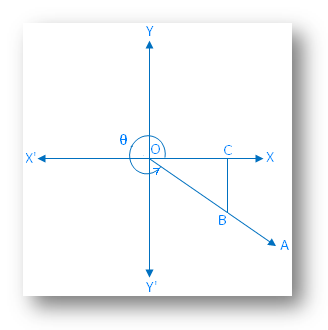
Case 4: When the final arm \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) lies in the fourth quadrant.
According to the trigonometric rules, we get
OC is positive;
CB is negative and
OB is positive.
Therefore, according to the definitions of trigonometrical ratios the values of cos θ and sec θ are positive and the other trigonometrical ratios i.e. sin θ, tan θ, csc θ and cot θ are negative.
● Trigonometric Functions
- Basic Trigonometric Ratios and Their Names
- Restrictions of Trigonometrical Ratios
- Reciprocal Relations of Trigonometric Ratios
- Quotient Relations of Trigonometric Ratios
- Limit of Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometrical Identity
- Problems on Trigonometric Identities
- Elimination of Trigonometric Ratios
- Eliminate Theta between the equations
- Problems on Eliminate Theta
- Trig Ratio Problems
- Proving Trigonometric Ratios
- Trig Ratios Proving Problems
- Verify Trigonometric Identities
- Trigonometrical Ratios of 0°
- Trigonometrical Ratios of 30°
- Trigonometrical Ratios of 45°
- Trigonometrical Ratios of 60°
- Trigonometrical Ratios of 90°
- Trigonometrical Ratios Table
- Problems on Trigonometric Ratio of Standard Angle
- Trigonometrical Ratios of Complementary Angles
- Rules of Trigonometric Signs
- Signs of Trigonometrical Ratios
- All Sin Tan Cos Rule
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (- θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (90° + θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (90° - θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (180° + θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (180° - θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (270° + θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (270° - θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (360° + θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of (360° - θ)
- Trigonometrical Ratios of any Angle
- Trigonometrical Ratios of some Particular Angles
- Trigonometric Ratios of an Angle
- Trigonometric Functions of any Angles
- Problems on Trigonometric Ratios of an Angle
- Problems on Signs of Trigonometrical Ratios
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Signs of Trigonometrical Ratios to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.