Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Classification of Angles
Angles can be classified according to their degree measures.
i.e, classification of angles on the basis of their degree measures are given below:
Acute Angle:
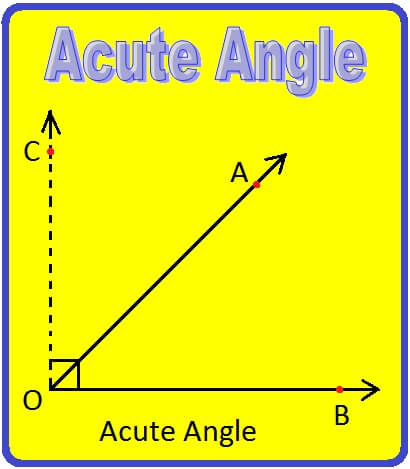
An angle whose measure is more than 0° but less than 90° is called an acute angle.
Definition of Acute Angle:
An angle measuring less than 90" is called an acute angle.
Angles having magnitudes 30°, 40°, 60° are all acute angles.
Examples of Acute Angle:
(i) Angles between two adjacent edges of scissors, etc.
(ii) Sun-rays make acute angle with the ground in the morning.
Right Angle:
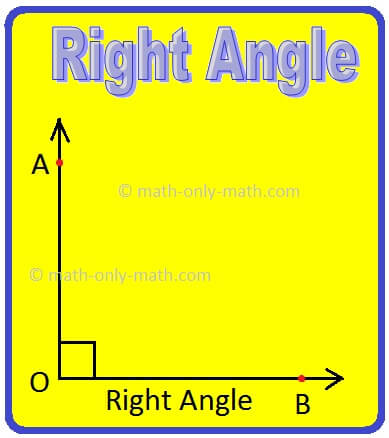
An angle whose measure is equal to 90° is called a right angle.
Definition of Right Angle:
An angle measuring 90° is called a right angle.
The arms of a right angle are perpendicular to each other.
In figure below, ∠AOB is a right angle.
Examples of Right Angle:
Corner of a room and Pillar on a ground form right angles.
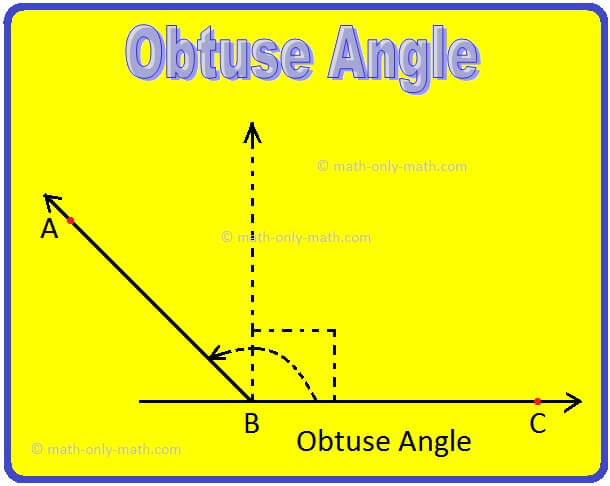
Obtuse Angle:
An angle whose measure is more than 90° but less than 180° is called an obtuse angle.
Definition of Obtuse Angle:
An angle greater than a right angle but less than two right angles is called an obtuse angle.
Its measure is more than 90° but less than 180°.
Examples of Right Angle:
Two adjacent sides of a microphone set, two edges of a book reading desk and two edges of the roof of a house form obtuse angles.
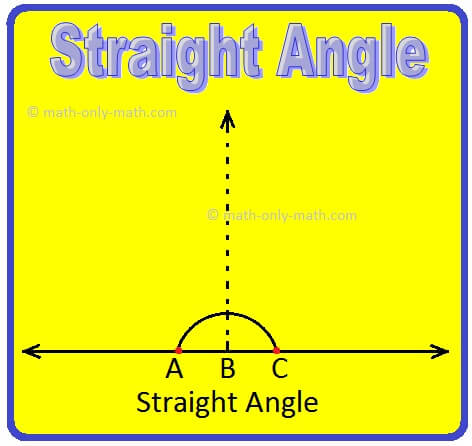
Straight Angle:
An angle whose measure is equal to 180° is called a straight angle.
Definition of Straight Angle:
An angle whose measure is 180° is called a straight angle.
Examples of Straight Angle:
Tubelight, pencil, a line segment form straight angles.
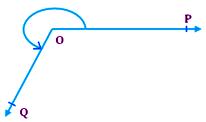
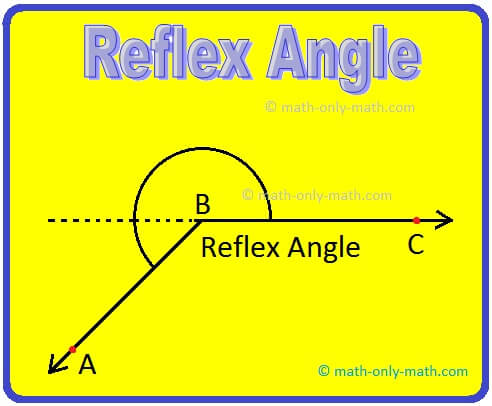
Reflex Angle:
A reflex angle is an angle which is larger than a straight angle. Its measure is more than 180º, but less than 360°.
Definition of Reflex Angle:
An angle whose measure is more than 180° but less than 360° is called a reflex angle.
Angles having magnitudes 220°, 250°, 310° are all reflex angles.
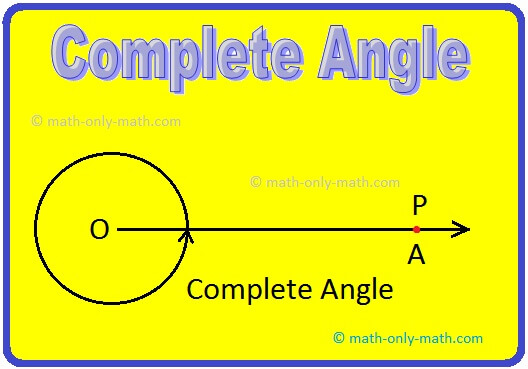
Complete Angle:
A complete angle is formed when the revolving ray OP (say) has made one complete revolution around the fixed point O after starting from the fixed initial position OA. The measure of a complete angle is 360°.
Definition of Complete Angle:
An angle whose measure is equal to 360° is called a complete angle.
Examples of Complete Angle:
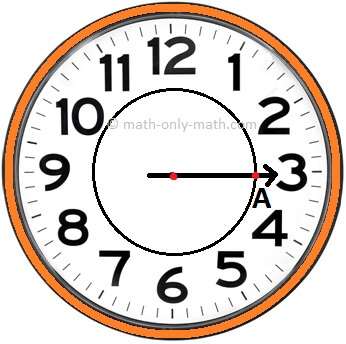
If the minute hand of a clock starts from point A (say) and returns back to this point after one complete revolution, then a complete angle of 360° is formed.
60 minutes = 1 revolution = 1 complete angle.
Zero Angle:
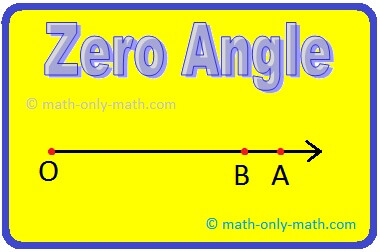
Definition of Zero Angle:
An angle of measure 0° is called a zero angle.
Example of Zero Angle:
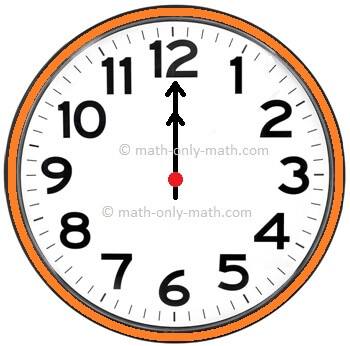
The two hands of a clock in the 12 O' clock position before the start of any movement form zero angle.
The above explanation will help us to understand the classification of angles on the basis of their degree measures.
REMEMBER:
The magnitude of an angle does not depend upon the length of its arms.
Worksheet on Classification of Angles:
1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) on Classification of Angles:
Tick (✔) the correct option.
(i) Which of the following angles is acute?
(a) 45°; (b) 180°; (c) 135°; (d) 90°
(ii) Which of the following is reflex angle?
(a) 195°; (b) 25°; (c) 135°; (d) 180°
Answer:
1. (i) (a) 45°
(ii) (a) 195°
2. What is the magnitude of the complete angle?
Answer:
2. 360°
3. State the angle whose magnitude is 0°.
Answer:
3. Zero angle
● Lines and Angles
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts
Some Geometric Terms and Results
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Parallel and Transversal Lines
8th Grade Math Practice
From Classification of Angles to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.