Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Triangle
What is a triangle?
A simple closed curve or a polygon formed by three line-segments (sides) is called a triangle.
The above shown shapes are triangles. The symbol of a triangle is ∆.
Definition of Triangle:
A closed figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
Working Rules to Form a Triangle ABC:
|
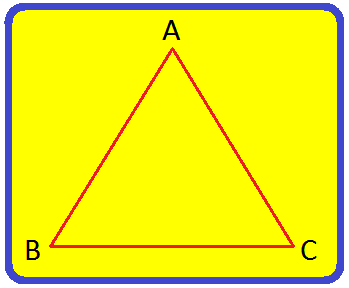
Step I: Draw three points on a piece of paper. Name them A. Band C. Step II: Then, draw the line segment AB. Step III: Next, draw the line segments AC and BC. Step IV: Now, a triangle is drawn as shown in the figure. |
The triangle is named as triangle ABC. It is common to use the symbols '∆' in place of the word 'triangle' i.e., ∆ABC.
NOTE: A triangle is a polygon of three sides.
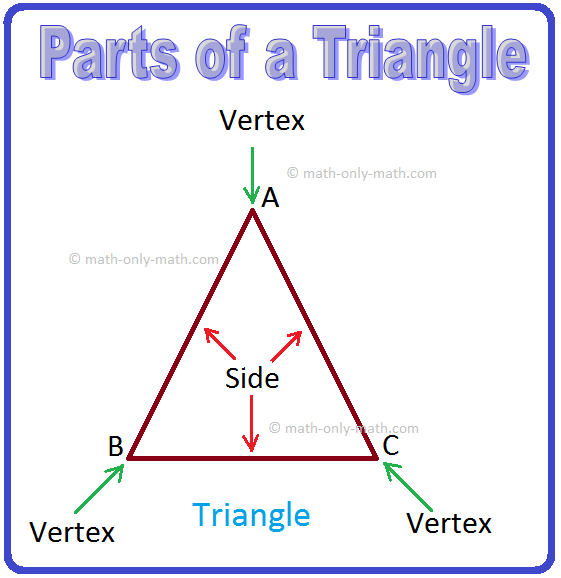
Parts of a Triangle:
|
There are three sides and three angles in a triangle. (i) The three line segments AB, BC and overline CA are the sides of ∆ABC. (ii) The three angles angle ∠ABC angle ∠BAC and angle ∠ACB ; are the angles of ∆ABC. (iii) A, B and C are the vertices of ∆ABC. (iv) Side BC is the side opposite to the vertex A. |
(v) Similarly, sides AB and AC are the sides opposite to the vertices Cand B respectively.
(vi) Vertices A, B and Care the vertices opposite to the sides BC, AC and AB respectively.
(vii) Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180° i.e., ∠A+ ∠B+ ∠C = 180°
NOTE:
1. The three sides and the three angles together are called the six elements or parts of a triangle.
2. In ∆ABC, the three angles can also be denoted as ∠A , ∠B and ∠C, in case only one angle is made at every vertex.
3. The side opposite of ∠A is denoted as a, the side opposite to ∠B is denoted as b and the side opposite to ∠C is denoted as c.
A triangle is a polygon with three sides. In the given figure ABC is a triangle. AB, BC and CA are its sides. The point where two sides meet is called its vertex. A, B, C are its vertices. There are many types of triangles. Triangles can be classified on the basis of sides and angles. Some triangles which are given below have been classified on the basis of their sides.
A triangle has
- three line-segments or sides
- three vertices
- three angles
There are six types of triangles, 3 with respect to sides and 3 with respect to angles.
Three types of triangle with respect to sides
(i) A triangle having all the three line-segments or sides unequal is called a scalene triangle.
Scalene Triangle
A triangle which has no equal sides is called a scalene triangle. ABC in the given figure is a scalene triangle, its sides AB, BC and CA are of different lengths.
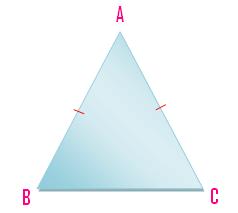
(ii) A triangle having a pair of its sides or two line-segments equal is called an isosceles triangle.
Here AB = AC.
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle which has two equal sides is called an isosceles
triangle. ABC in the given figure is an isosceles triangle, its sides AB and AC are equal.
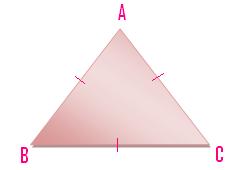
(iii) A triangle having all the three line-segments or sides equal is called an equilateral triangle.
Here AB = BC = CA.
Equilateral Triangle
A triangle which has three equal sides is called an equilateral triangle. ABC in the given figure is an equilateral triangle, its all sides are equal. AB = BC = CA.
Types of triangle with respect to angles
(i) A triangle in which all the three angles are acute is called an acute angled triangle.
∠ABC, ∠ACB and ∠BAC are all acute angles.
Acute Angled Triangle
(ii) A triangle in which one of the three angles is a right angle is called a right angled triangle.
∠ABC = one right angle.
Right Angled Triangle
(iii) A triangle where one of the three angles is more than a right angle (or is an obtuse angle) is called an obtuse angled triangle.
∠ABC is an obtuse angle.
Obtuse Angled Triangle
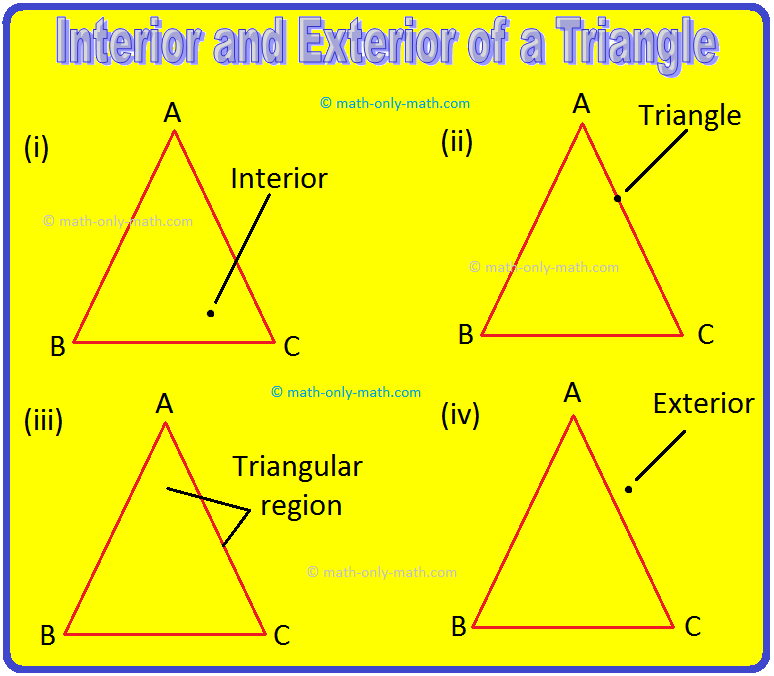
Interior and Exterior of a Triangle:
If you draw a ∆ABC on a sheet of paper, then it will divide all points of the plane into three parts:
(i) The part of the plane which consists of all points such as P is called the interior of the triangle.
(ii) The part of the plane which consists of all points such as R forms the triangle itself.
(iii) The interior of the ∆ABC together with the triangle is called triangular region ABC.
(iv) The part of the plane which consists of all points such as Q is called the exterior of the triangle.
Math Questions and Answers on Triangle:
|
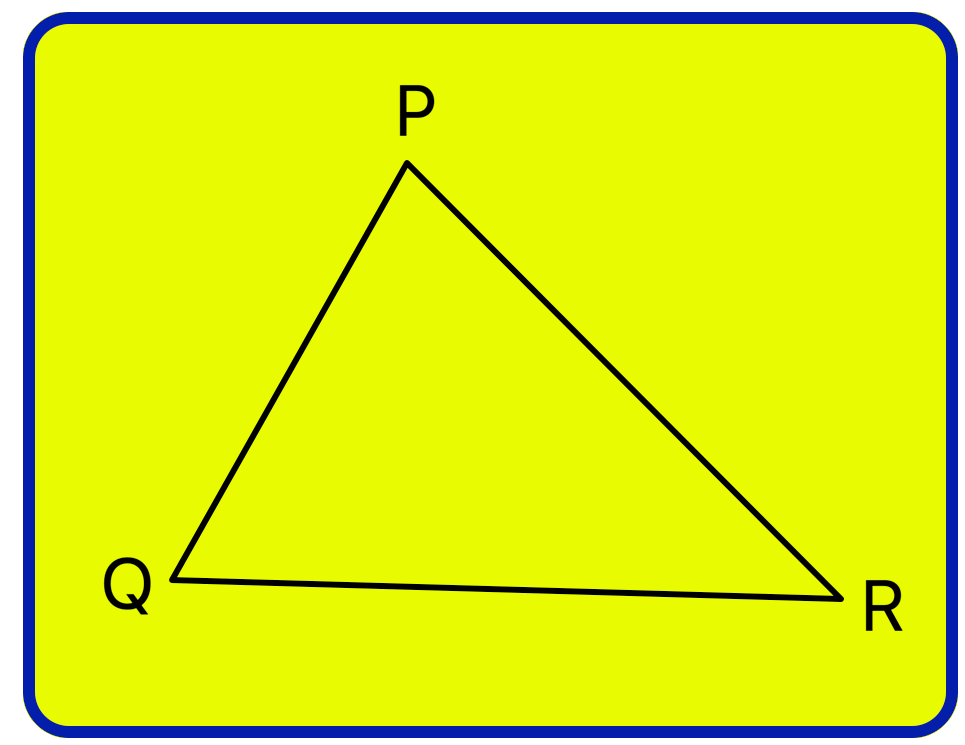
1. In the ∆PQR name: (ii) the angle opposite to QR. (iii) the vertex opposite to PR. (iv) the side opposite to vertex P |
Solution:
(i) The side opposite to ∠R is PQ.
(ii) The angle opposite to QR is ∠P.
(iii) The vertex opposite to PR is Q.
(iv) The side opposite to vertex P is QR.
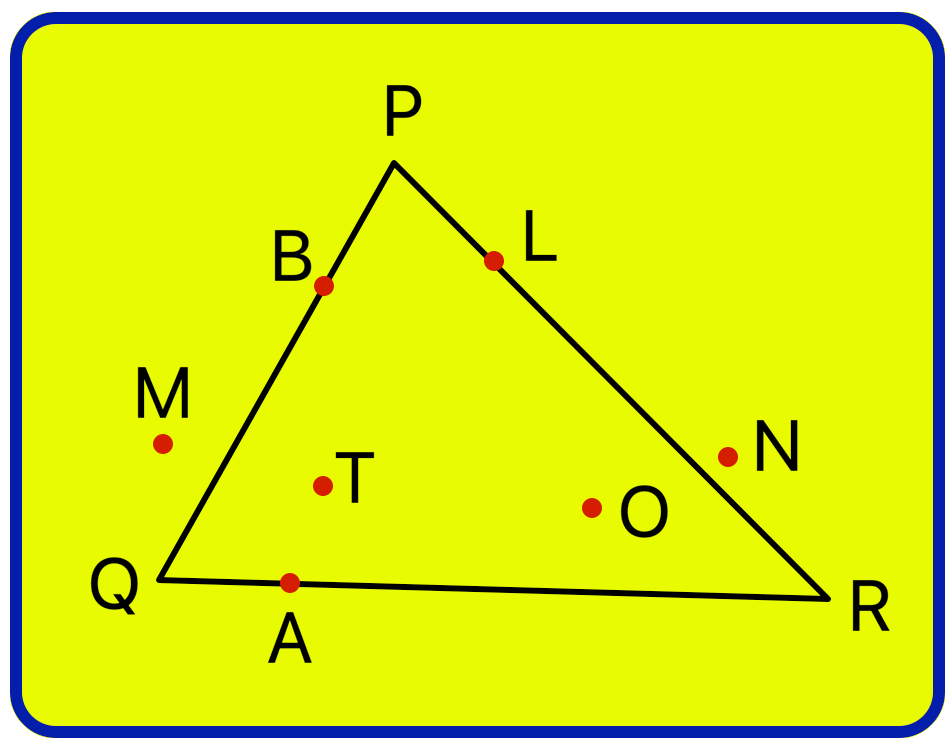
2. Look at the Fig. given below and answer the following:
|
(i) Name the points which are in the triangular region PQR. (ii) Which of these lie on the ∆PQR? (iii) Which points lie in the exterior of ∆PQR? |
Solution:
(i) Points in the triangular region PQR: P, B, Q, A, R, L, O, T
(ii) Points lie on the ∆PQR: P, B, Q, A, R, L
(iii) Points lie in the exterior of ∆PQR: M, N
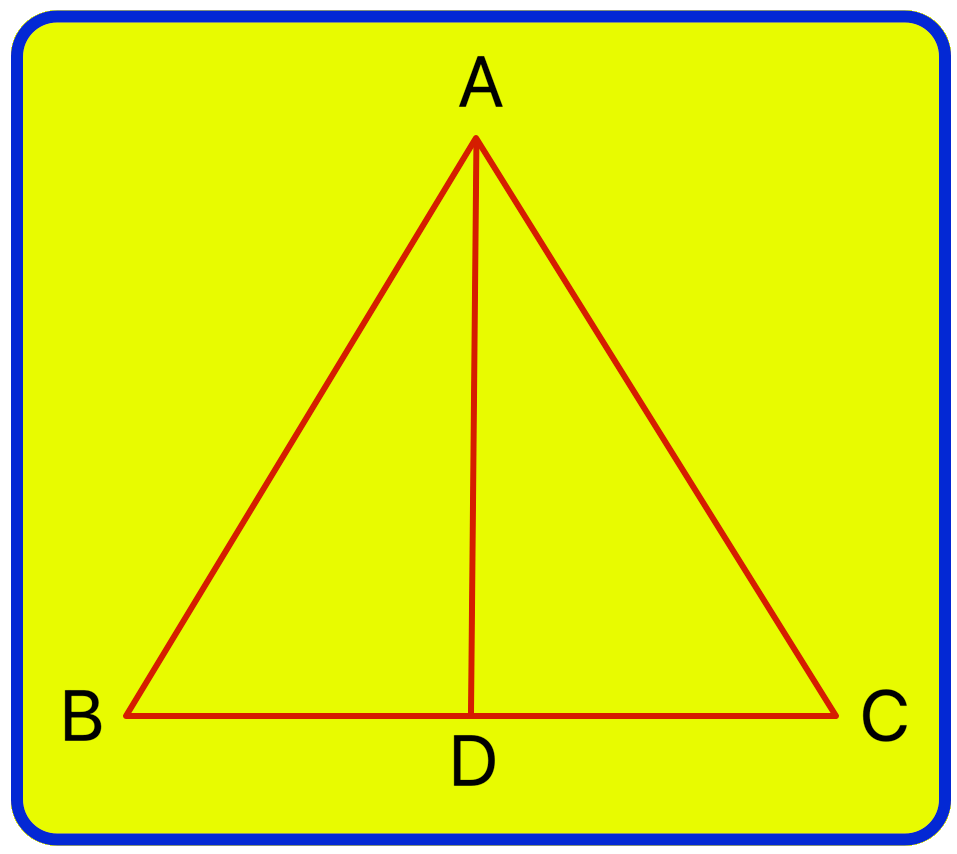
Solution:
(i) Three triangles: ∆ABC, ∆ADC and ∆ADB
(ii) Seven angles: ∠BAC, ∠ABC, ∠ACB, ∠ADB, ∠ADC, ∠DAC, ∠BAD.
Math Only Math is based on the premise that children do not make a distinction between play and work and learn best when learning becomes play and play becomes learning.
However, suggestions for further improvement, from all quarters would be greatly appreciated.
Related Concepts on Geometry - Simple Shapes & Circle
● Polygon
● Angle
● Triangle
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.