Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Measuring an Angle
We will discuss here about measuring an angle with the help of a protractor.
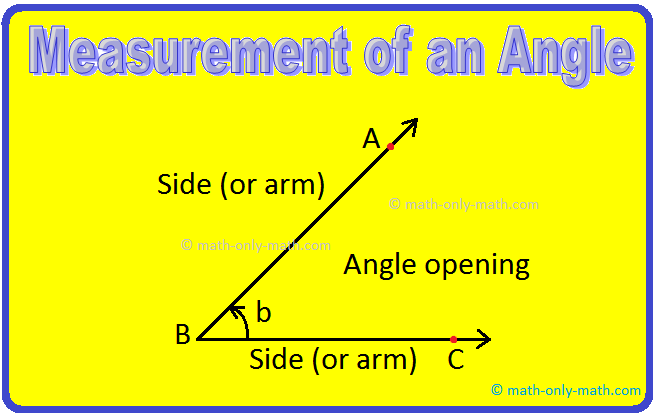
The measurement of an angle or its size depends upon the amount of opening between its sides.
In the above Fig., an ∠ABC has a measurement denoted by b or an arc of a circle drawn in the inside region.
Measuring Angles Using Protractor:
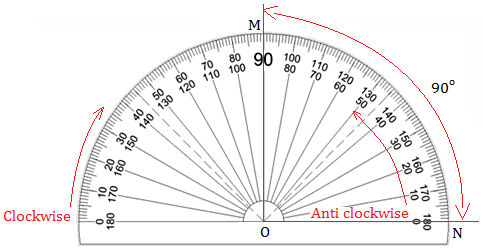
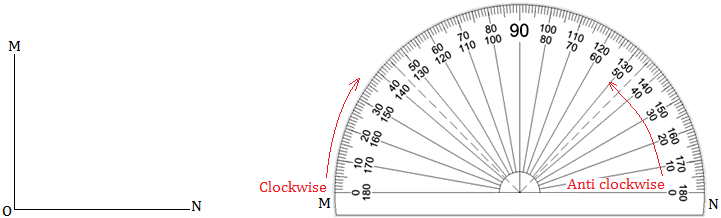
A protractor is a geometrical instrument that looks like the letter D.
You can find it in your Geometry Box. It is used to measure angle and draw angle of required magnitude.
It has the semi-circular shape. The curved edge is divided into 180 equal parts.
i.e., Its semi-circular edge is divided into 180 divisions. Each division represents a degree denoted by °.
Each part is equal to a 'degree'. The markings start from 0° on the right side and end with 180° on the left side and vice- versa.
It is used to measure angle and draw angle of required magnitude.
There are two scales marked on the protractor – outer and inner. The outer scale is marked from 0° to 180° in clockwise direction.
Let us follow the Working Rules given below to measure an angle ABC, using the protractor.
Working Rules for Measurement of an Angle:
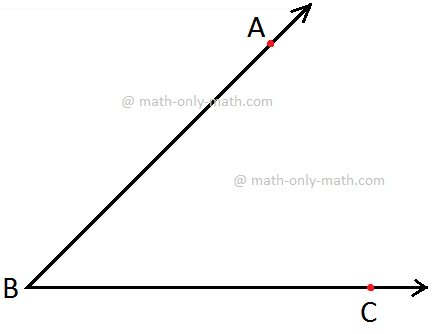
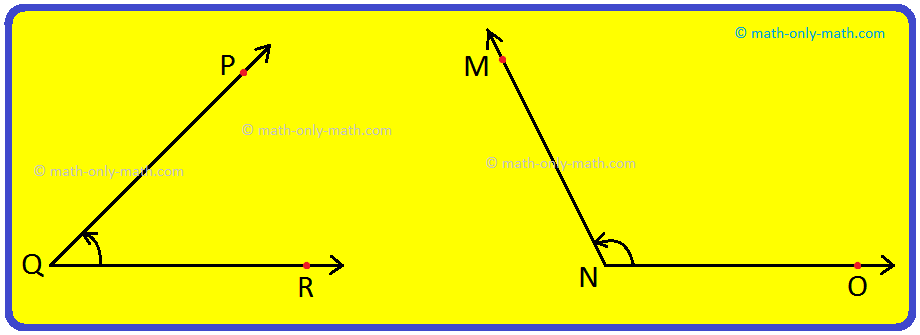
Measuring ∠ABC using the Protractor
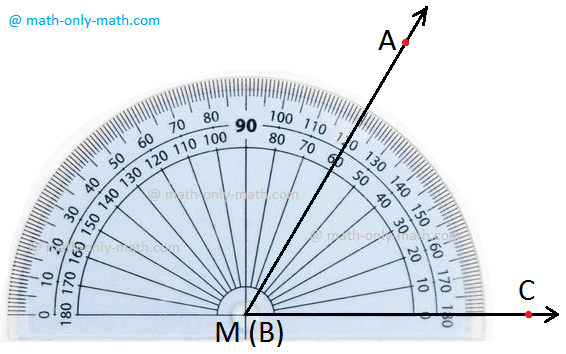
Step I: Place the protractor such that the mid- point (M in the figure) of its straight-edge lies on the vertex B of the angle ABC.
Step II: Adjust the protractor such that BC is along the straight-edge of the protractor.
Step III: There are two 'scales' on the protractor: read that scale which has the 0° make coinciding with the straight-edge (i.e., with ray BC)
Step IV: The mark shown by BA on the curved edge gives the degree measure of the angle.
We write m∠ABC = 60° or ∠ABC = 60°.
Å To measure the given ∠MON, we place the protractor in such way that its centre is on the vertex O of ∠MON and its straight horizontal edge lies on the arm ON of the ∠MON as shown in figure.
Now we see which degree mark on the scale of the protractor, the arm OM coincides with. In the given figure, OM coincides with 90°. So, the ∠MON measures 90°.
Comparison of Angles:
The magnitude of an angle depends upon the opening or inclination between the two ray that form the angle. If two angles have different inclinations, then we say they have different magnitudes.
The magnitudes of two angles can be compared in the following manner.
Comparison by Inspection:
More is the opening between two arms, greater will be the magnitude of the angle.
Observe the opening of the two angles in the following figures
We can say that the angle measure of PQR is less than that of MNO.
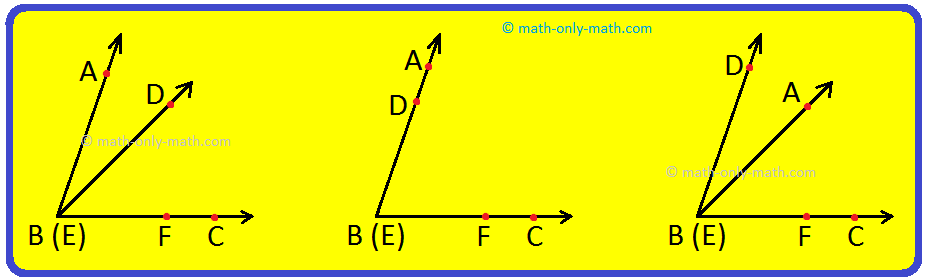
Comparison by Using Trace Paper:
Trace an angle, say ∠ABC on a tracing paper. Place it on another angle, say ∠DEF such that the vertex E falls on the vertex B and arm EF along arm BC. Then, we may have any one of the following three situations for the other arm BA.
(i) Arm BA may fall beyond DE. In this case, ∠ABC > ∠DEF.
(ii) Arm BA may fall exactly along ED. In this case, ∠DEF = ∠ABC.
(iii) Arm BA may fall between DB and BC. In this case, ∠ABC < ∠DEF.
Example:
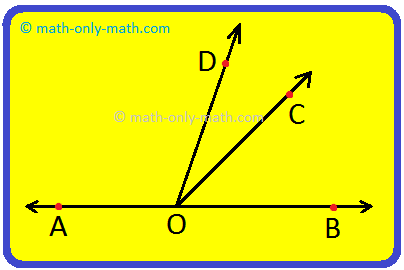
1. In the Figure below, find the largest angle. Also, arrange the angles in the descending order.
Solution:
∠AOB is the largest angle.
Also, the angles in the descending order are:
∠AOB > ∠AOC > ∠AOD > ∠BOD > ∠ COB > ∠DOC
From Measuring an Angle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.