Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Angle
We will discuss here about an Angle.
Let us recall about the ray. It has only one end point. The arrow shows that it is extended indefinitely in one direction.
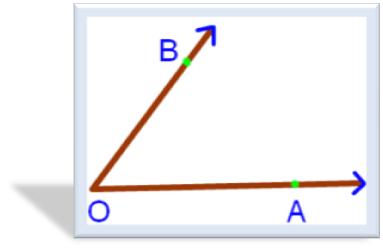
When two rays meet at a point, they form an angle. In the given figure, OA and OB are rays. They meet at a common point O and form an angle named AOB. An angle is represented by the symbol (∠AOB).
The inside space between the arms in known as the interior of the angle. The outside space is called the exterior of the angle.
We name the angles by using any point on one ray, the vertex and ray point on the other ray. We name an angle with the vertex in the middle. For example, the above mentioned angle is represented by ∠AOB.
An angle is formed when two rays meet at a point.
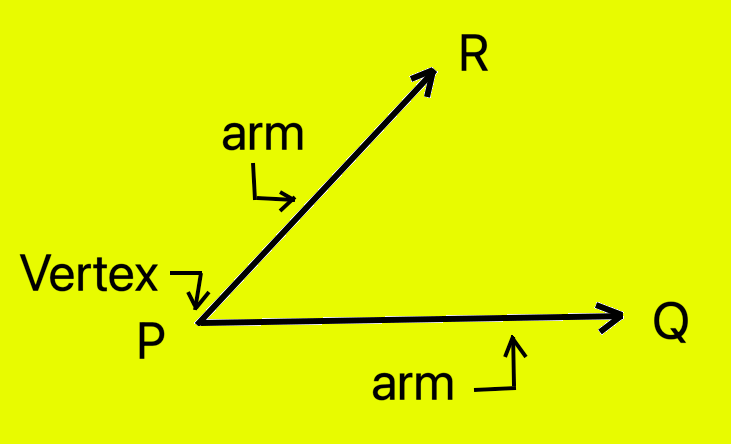
PQ and PR are two rays forming an angle.
These two rays are called the sides or arms of the angle.
The common end point of the two rays are called the vertex of the angle.
How to Name an Angle?
An angle can be named using the letter of the vertex point where the angle is formed or with three letters (using the rays) central letter pointing out the angle.
Thus the above angle is named as angle P or QPR or angles RPQ.
The symbol used to denote an angle is ∠ or ∧
angle P = ∠P or \(\hat{P}\)
angle QPR = ∠QPR
angle RPQ = ∠RPQ
Observe the angles given below and answer the following questions.
1. Name the three angles:
(i) ∠T or ∠STU or ∠UTS
(ii) ∠B or ∠ABC or ∠CBA
(iii) ∠Y or ∠XYZ or ∠ZYX
2. Name the vertices:
(i) T
(ii) B
(iii) Y
3. Name the arms (sides):
(i) The arms of ∠STU are \(\overrightarrow{ST}\) and \(\overrightarrow{TU}\)
(ii) The arms of ∠ABC are \(\overrightarrow{BA}\) and \(\overrightarrow{BC}\)
(iii) The arms of ∠XYZ are \(\overrightarrow{YX}\) and \(\overrightarrow{YZ}\)
What is an angle?
When two sides or line-segments are inclined and meet at a point, then this inclination is called an angle.
A polygon has as many angles as number of sides or number of vertices.
The triangle has 3 angles, quadrilateral has 4 angles, pentagon has 5
angle, etc.
The angles have different measures.
Types of Angles:
Angles can be classified into different types according to their measures.
Look at the angles given below.
1. Right Angle:
When a side or line-segment meets another side or line-segment in such a way that one stands upright on the other, then the inclination between the two is called a right angle.
Right Angle
Right angle: An angle which is equal to 90° is called a right angle.
2. Acute Angle:
If the inclination is less than the right angle, then it is called an acute angle.
Acute Angle
Acute Angles: All the angles which are less than 90° are called acute angles.
3. Obtuse Angle:
If the inclination is more than the right angle, then it is called an obtuse angle.
Obtuse Angle
Obtuse Angles: All the angles which are more than 9090° and less than 180° are called obtuse angle.
4. Straight angle: The angle which is equal to 180° is called a straight angle.
5. Reflex angle: An angle which is more than 180° and less than 360° is called a reflex angle.
In the figure, STU is a reflex angle.
Look at the figure.
∠BOA = 180° ∠AOB = 180°
Complete angle = ∠BOA + ∠AOB
= 180° + 180°
= 360°
How to Measure an Angle?
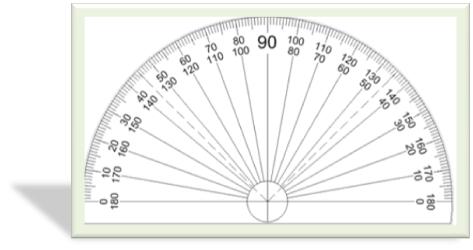
An angle is measured using a protractor.
A protractor is semicircular in shape.
It has one straight edge and a curved edge.
The curved edge is
divided into 180 equal sub divisions starting from 0 to 180. Each sub division
measures one degree (1°). ‘o’ is the symbol for degree.
It has two scales, outer and inner. The outer scale is marked from 0° to 180° in clockwise direction.
The inner scale is marked from 0° to 180° in anticlockwise direction. The line segment joining 0° and 180° marks is called the base line of the protractor.
The midpoint of the base line is called the centre of the protractor.
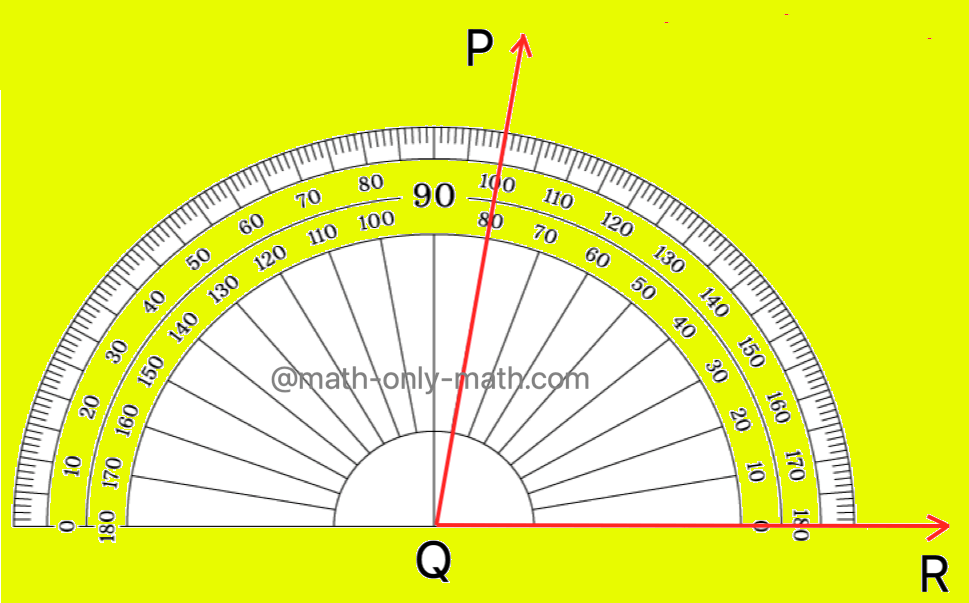
Measure the given Angle PQR
Place the protractor with the base line along one ray of the angle and the centre of the protractor at the vertex.
Select the readings of the scale which shows 0° along the base ray. Note the reading on the protractor along the other ray. The measure of ∠PQR is 80°.
How to measure a reflex angle?
A reflex angle can be measured by first measuring the acute angle formed and then by subtracting it from 360°.
What is the measurement of the reflex angle DOC?
Reflex angle COD = 360° - acute angle 45°
= 360° - 45°
= 315°
How to construct an angle?
For example:
1. Draw an angle ABC = 60°
Steps:
Draw a ray BC as shown in the figure.
Place the centre of the protractor at the vertex B.
Adjust the base line of the protractor along \(\overrightarrow{BC}\).
Find the ‘0’ on the scale where the ray crosses the protractor.
Follow along that scale and mark a point ‘A’ against the mark 60°.
Remove the protractor and draw a ray from the vertex B to the point A.
∠ABC = 60° is the required angle.
2. Draw an angle DEF = 120°
Steps:
Draw a ray EF as shown in the figure.
Keep the centre of the protractor at the vertex E.
Adjust the base line of the protractor along \(\overrightarrow{EF}\).
Find the ‘0’ on the scale where the ray crosses the protractor.
Follow along that scale and mark a point ‘D’ against the 120° mark.
Remove the protractor and draw a ray from the vertex E to the point D.
∠DEF = 120° is the required angle.
Related Concepts on Geometry - Simple Shapes & Circle
● Polygon
● Angle
● Triangle
4th Grade Math Activities
From Angle to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.