Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Parallel and Transversal Lines
Here we discuss how the angles formed between parallel and transversal lines.
When the transversal intersects two parallel lines:
• Pairs of corresponding angles are equal.
• Pairs of alternate angles are equal
• Interior angles on the same side of transversal are supplementary.
Worked-out problems for solving parallel and transversal lines:
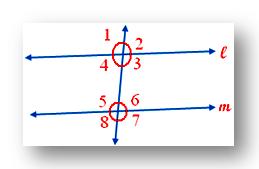
1. In adjoining figure l ∥ m is cut by the transversal t. If ∠1 = 70, find the measure of ∠3, ∠5, ∠6.
Solution:
We have ∠1 = 70°
∠1 = ∠3 (Vertically opposite angles)
Therefore, ∠3 = 70°
Now, ∠1 = ∠5 (Corresponding angles)
Therefore, ∠5 = 70°
Also, ∠3 + ∠6 = 180° (Co-interior angles)
70° + ∠6 = 180°
Therefore, ∠6 = 180° - 70° = 110°
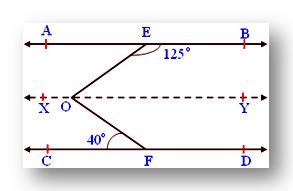
2. In the given figure AB ∥ CD, ∠BEO = 125°, ∠CFO = 40°. Find the measure of ∠EOF.
Solution:
Draw a line XY parallel to AB and CD passing through O such that AB ∥ XY and CD ∥ XY
∠BEO + ∠YOE = 180° (Co-interior angles)
Therefore, 125° + ∠YOE = 180°
Therefore, ∠YOE = 180° - 125° = 55°
Also, ∠CFO = ∠YOF (Alternate angles)
Given ∠CFO = 40°
Therefore, ∠YOF = 40°
Then ∠EOF = ∠EOY + ∠FOY
= 55° + 40° = 95°
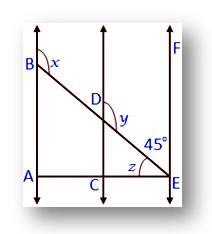
3. In the given figure AB ∥ CD ∥ EF and AE ⊥ AB.
Also, ∠BAE = 90°. Find the values of ∠x, ∠y and ∠z.
Solution:
y + 45° = 1800
Therefore, ∠y = 180° - 45° (Co-interior angles)
= 135°
∠y =∠x (Corresponding angles)
Therefore, ∠x = 135°
Also, 90° + ∠z + 45° = 180°
Therefore, 135° + ∠z = 180°
Therefore, ∠z = 180° - 135° = 45°
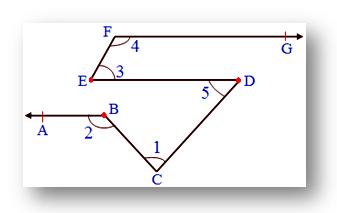
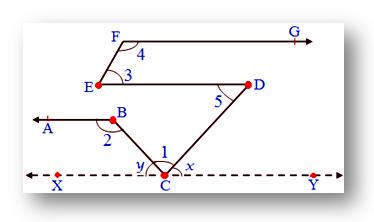
4. In the given figure, AB ∥ ED, ED ∥ FG, EF ∥ CD
Also, ∠1 = 60°, ∠3 = 55°, then find ∠2, ∠4, ∠5.
Solution:
Since, EF ∥ CD cut by transversal ED
Therefore, ∠3 = ∠5 we know, ∠3 = 55°
Therefore, ∠5 = 55°
Also, ED ∥ XY cut by transversal CD
Therefore, ∠5 = ∠x we know ∠5 = 55°
Therefore,∠x = 55°
Also, ∠x + ∠1 + ∠y = 180°
55° + 60° + ∠y = 180°
115° + ∠y = 180°
∠y = 180° - 115°
Therefore, ∠y = 65°
Now, ∠y + ∠2 = 1800 (Co-interior angles)
65° + ∠2 = 180°
∠2 = 180° - 65°
∠2 = 115°
Since, ED ∥ FG cut by transversal EF
Therefore, ∠3 + ∠4 = 180°
55° + ∠4 = 180°
Therefore, ∠4 = 180° - 55° = 125°
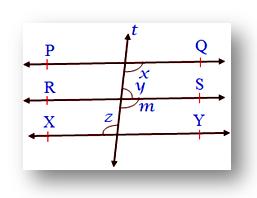
5. In the given figure PQ ∥ XY. Also, y : z = 4 : 5 find.
Solution:
Let the common ratio be a
Then y = 4a and z = 5a
Also, ∠z = ∠m (Alternate interior angles)
Since, z = 5a
Therefore, ∠m = 5a [RS ∥ XY cut by transversal t]
Now, ∠m = ∠x (Corresponding angles)
Since, ∠m = 5a
Therefore, ∠x = 5a [PQ ∥ RS cut by transversal t]
∠x + ∠y = 180° (Co-interior angles)
5a + 4a = 1800
9a = 180°
a = 180/9
a = 20
Since, y = 4a
Therefore, y = 4 × 20
y = 80°
z = 5a
Therefore, z = 5 × 20
z = 100°
x = 5a
Therefore, x = 5 × 20
x = 100°
Therefore, ∠x = 100°, ∠y = 80°, ∠z = 100°
● Lines and Angles
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts
Some Geometric Terms and Results
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Parallel and Transversal Lines
8th Grade Math Practice
From Parallel and Transversal Lines to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.