Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Related Angles
Related angles are the pairs of angles and specific names are given to the pairs of angles which we come across. These are called related angles as they are related with some condition.
Complementary angles:
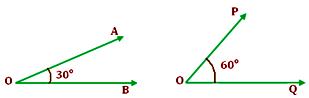
When the sum of the measures of two angles is 90°, such angles are called complementary angles.
For example:
An angle of 30° and another angle of 60° are complementary angles of each other.
Also, complement of 30° is 90° - 30° = 60°.
And complement of 60° is 90° - 60° = 30°
∠AOB + ∠POQ = 90°
Supplementary angles:
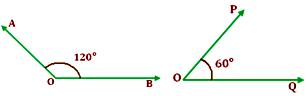
When the sum of the measures of two angles is 180°, such angles are called supplementary angles.
For example:
An angle of 120° and another angle of 60° are supplementary angles of each other. Also, supplement of 120° is 180° - 120° = 60°.
And supplement of 60° is 180° - 60° = 120°
∠AOB + ∠POQ = 180°
Adjacent angles:
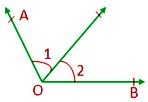
Two angles in a plane are said to be adjacent if they have a common arm, a common vertex and the non-common arms lie on the opposite side of the common arm.
In the given figure, ∠AOC and ∠BOC are adjacent angles as OC is the common arm, O is the common vertex, and OA, OB are on the opposite side of OC.
Linear pair:
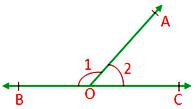
Two adjacent angles form a linear pair of angles if their non-common arms are two opposite rays, i.e., the sum of two adjacent angles is 180°.
Here, ∠AOB + ∠AOC
= 180°
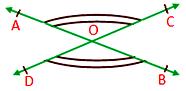
Vertically opposite angles:
When two lines intersect, then the angles having their arms in the opposite direction are called vertically opposite angles. The pair of vertically opposite angles is equal.
Here the pairs of vertically opposite angles are ∠AOD and ∠BOC, ∠AOC and ∠BOD.
Theorems on related angles:
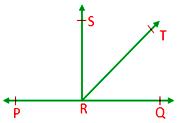
1. If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of adjacent angles formed is 180°.
Given: A ray RT standing on (PQ) ⃡ such that ∠PRT and ∠QRT are formed.
Construction: Draw RS ⊥ PQ.
Proof: Now ∠PRT = ∠PRS + ∠SRT ……………. (1)
Also ∠QRT = ∠QRS - ∠SRT ……………. (2)
Adding (1) and (2),
∠PRT + ∠QRT = ∠PRS + ∠SRT + ∠QRS - ∠SRT
= ∠PRS + ∠QRS
= 90° + 90°
= 180°
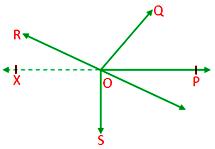
2. The sum of all the angles around a point is equal to 360°.
Given: A point O and rays OP, OQ, OR, OS, OT which make angles around O.
Construction: Draw OX opposite to ray OP
Proof: Since, OQ stands on XP therefore
∠POQ + ∠QOX = 180°
∠POQ + (∠QOR + ∠ROX) = 180°
∠POQ + ∠QOR + ∠ROX = 180° ……………. (i)
Again OS stands on XP, therefore
∠XOS + ∠SOP = 180°
∠XOS + (∠SOT + ∠TOP) = 180°
∠XOS + ∠SOT + ∠TOP = 180° ……………. (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),
∠POQ + ∠QOR + ∠ROX + ∠XOS + ∠SOT + ∠TOP
= 180° + 180°
= 360°
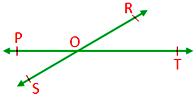
3. If two lines intersect, then vertically opposite angles are equal.
Given: PQ and RS intersect at point O.
Proof: OR stands on PQ.
Therefore, ∠POR + ∠ROQ = 180° ……………. (i)
PO stands on RS
∠POR + ∠POS = 180° ……………. (ii)
From (i) and (ii),
∠POR + ∠ROQ = ∠POR + ∠POS
∠ROQ + ∠POS
Similarly, ∠POR = ∠QOS can be proved.
● Lines and Angles
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts
Some Geometric Terms and Results
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Parallel and Transversal Lines
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Related Angles to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.