Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Math Blog
Newly added pages can be seen from this page. Keep visiting to this page so that you will remain updated.
Jul 10, 2025
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
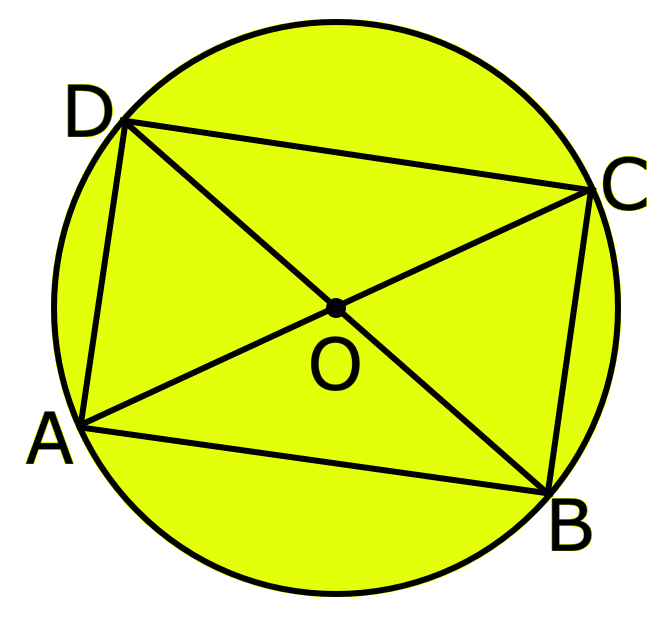
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circle.
Continue reading "5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math"
Jul 09, 2025
Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Construction of a Circle when the length of its Radius is given. Working Rules | Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be put on a mark say 4 cm (Let the radius of the circle be 4 cm).
Continue reading "Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |"
Jul 08, 2025
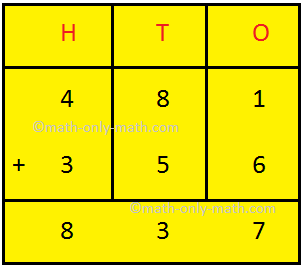
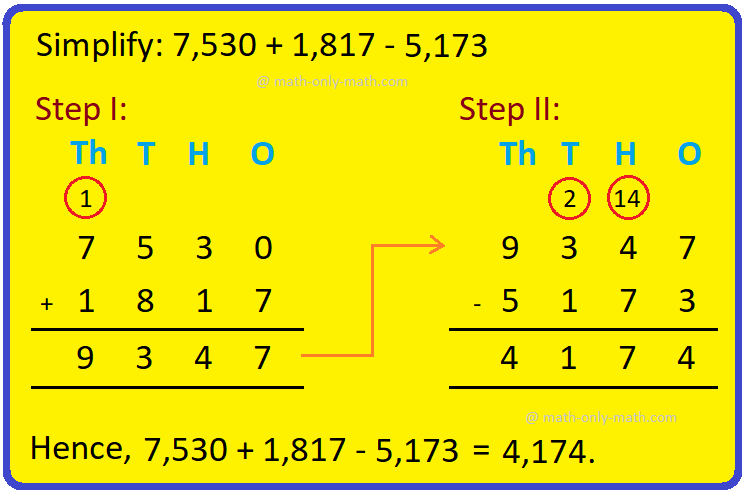
Combination of Addition and Subtraction | Mixed Addition & Subtraction
We will discuss here about the combination of addition and subtraction. The rules which can be used to solve the sums involving addition (+) and subtraction (-) together are: I: First add
Continue reading "Combination of Addition and Subtraction | Mixed Addition & Subtraction"
Jul 08, 2025
Addition & Subtraction Together |Combination of addition & subtraction
We will solve the different types of problems involving addition and subtraction together. To show the problem involving both addition and subtraction, we first group all the numbers with ‘+’ and ‘-‘ signs. We find the sum of the numbers with ‘+’ sign and similarly the sum
Continue reading "Addition & Subtraction Together |Combination of addition & subtraction"
Jul 08, 2025
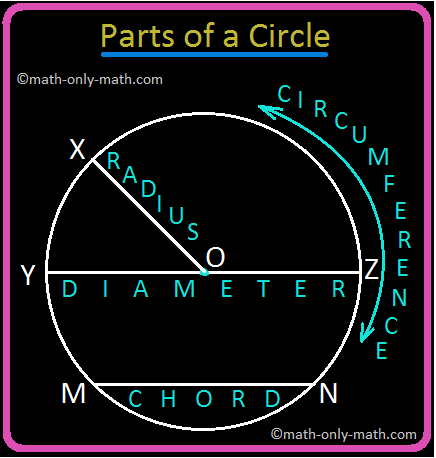
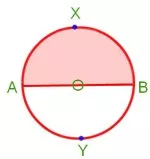
5th Grade Circle | Radius, Interior and Exterior of a Circle|Worksheet
A circle is the set of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is known
Continue reading "5th Grade Circle | Radius, Interior and Exterior of a Circle|Worksheet"
Jul 06, 2025
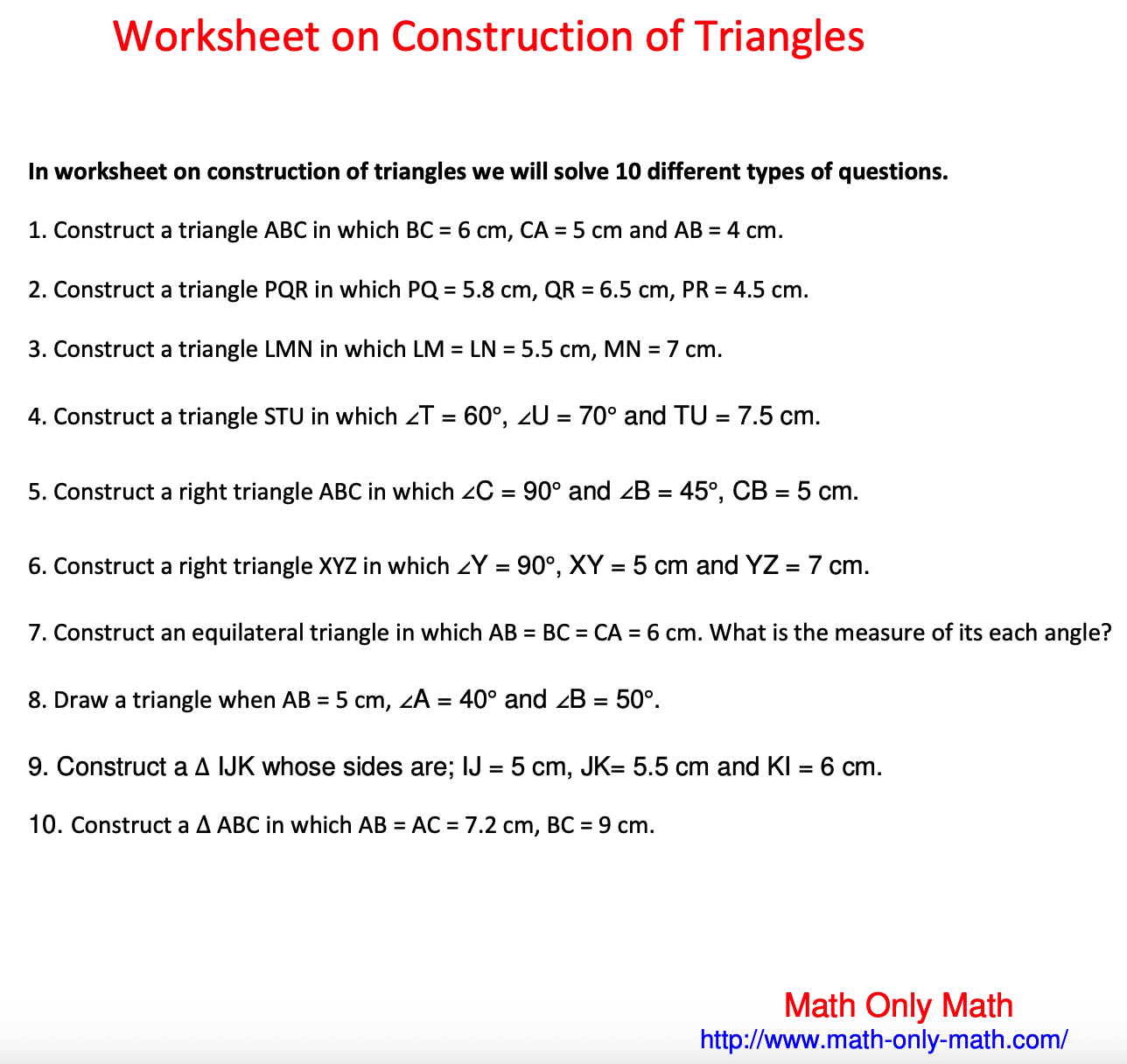
Worksheet on Construction of Triangles | Constructing Triangles | Math
In worksheet on construction of triangles we will solve different types of questions. 1. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, CA = 5 cm and AB = 4 cm.
Continue reading "Worksheet on Construction of Triangles | Constructing Triangles | Math"
Jul 04, 2025
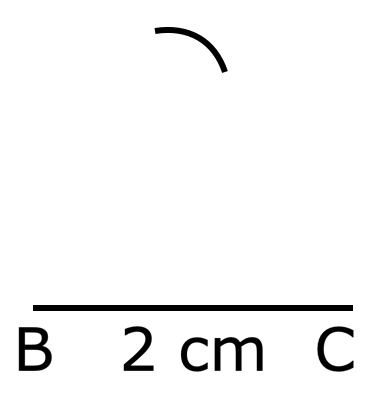
Construction of Triangles | Equilateral Triangle | Isosceles Triangle
Here we will learn to construct different types of triangles. We can draw an equilateral triangle of the given length as given below. Step I: First, we draw a base line segment BC of the given length.
Continue reading "Construction of Triangles | Equilateral Triangle | Isosceles Triangle"
Jul 03, 2025
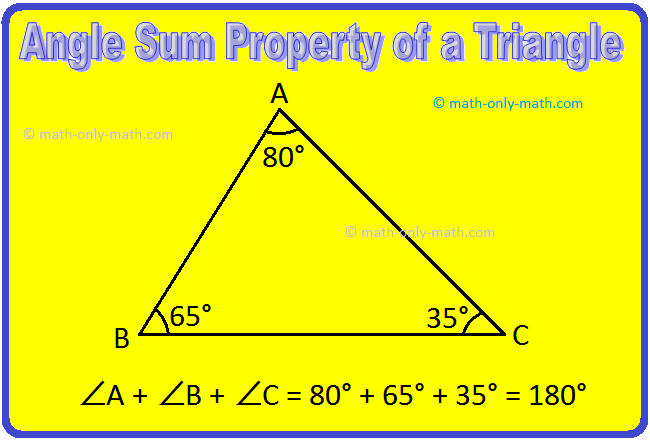
Properties of Triangle | Angle Sum Property | Triangle Inequality Prop
We will discuss here about the properties of triangle. Property 1: Relation between the measures of three angles of triangle: Draw three triangles on your not book. Name them as ∆PQR, ∆ABC and ∆LMN.
Continue reading "Properties of Triangle | Angle Sum Property | Triangle Inequality Prop"
Jul 02, 2025
5th Grade Triangle | Definition | Elements of the Triangle | Geometry
A triangle is a simple closed figure made up of three line segments. It has three sides and three vertices. It is represented by the symbol ∆. Triangle is one of the basic shape in geometry. We know that we can mark many points on any given line. Three or more points which
Continue reading "5th Grade Triangle | Definition | Elements of the Triangle | Geometry"
Jul 01, 2025
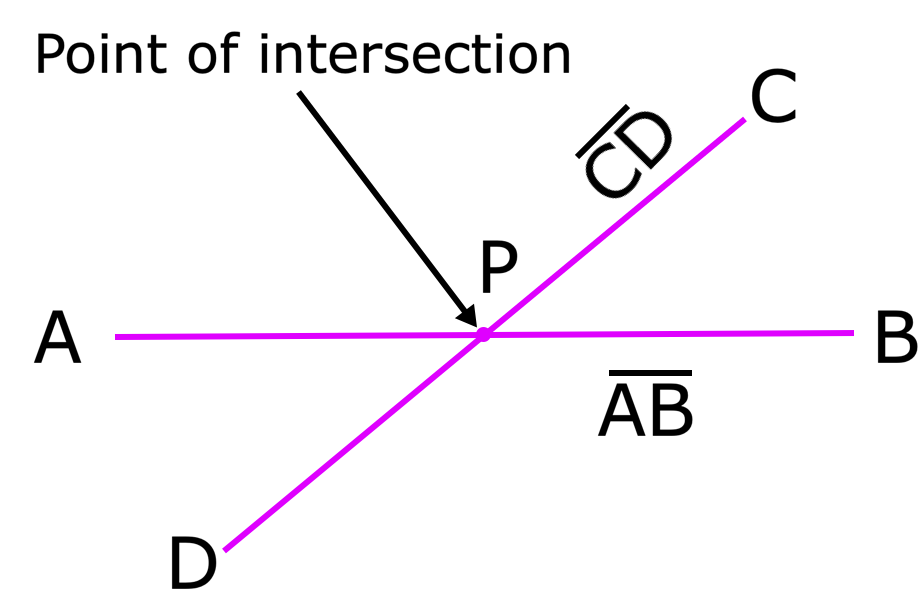
Lines and Angles |Intersecting & Parallel Lines|Angles|Types of Angle
In this lines and angles
Continue reading "Lines and Angles |Intersecting & Parallel Lines|Angles|Types of Angle "
Jun 30, 2025
Geometry | 5th Grade Geometry | Geometrical Figures | Solid and Plane
Geometry is one of the oldest and main branches of mathematics. Measurement of the earth is the exact meaning of the word ‘Geometry’. The geometry began when men felt the need to measure their lands
Continue reading "Geometry | 5th Grade Geometry | Geometrical Figures | Solid and Plane"
Jun 30, 2025
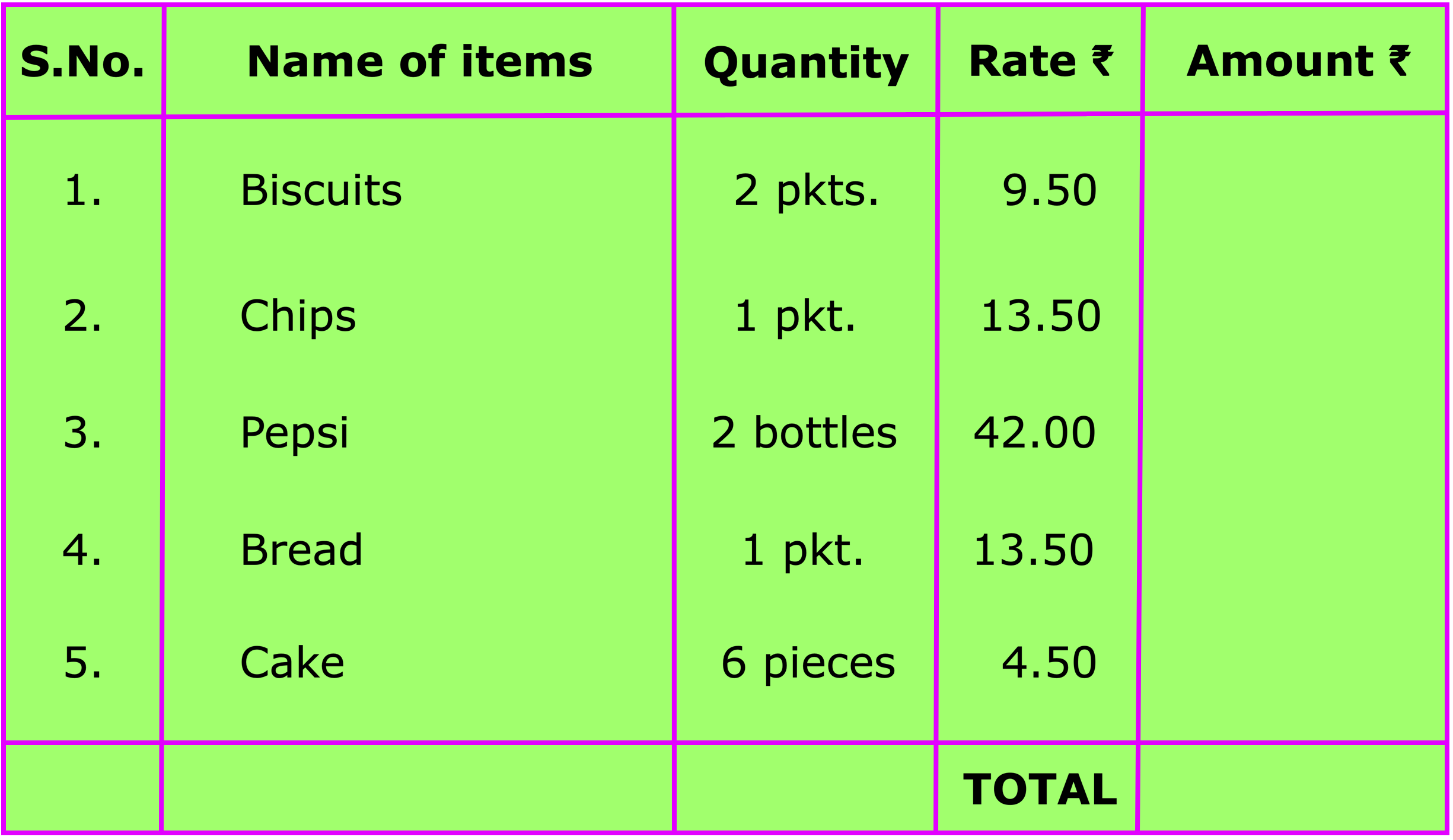
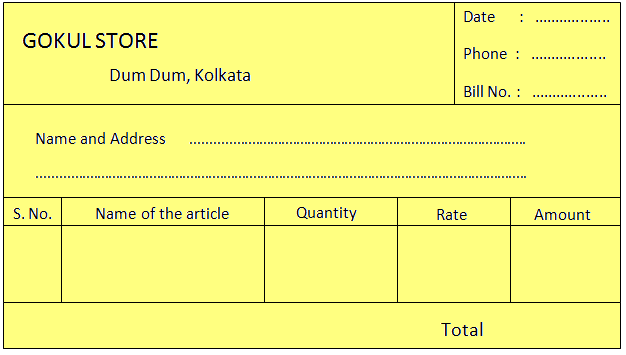
Worksheet on Preparing a Bill | Calculation of Total Amount of a Bill
In this worksheet on Preparing a Bill you will get the different types of questions on money bill, bill and find the total amount of a bill, check the bill for its correctness, present a correct bill and find the errors and correct them.
Continue reading "Worksheet on Preparing a Bill | Calculation of Total Amount of a Bill"
Jun 26, 2025
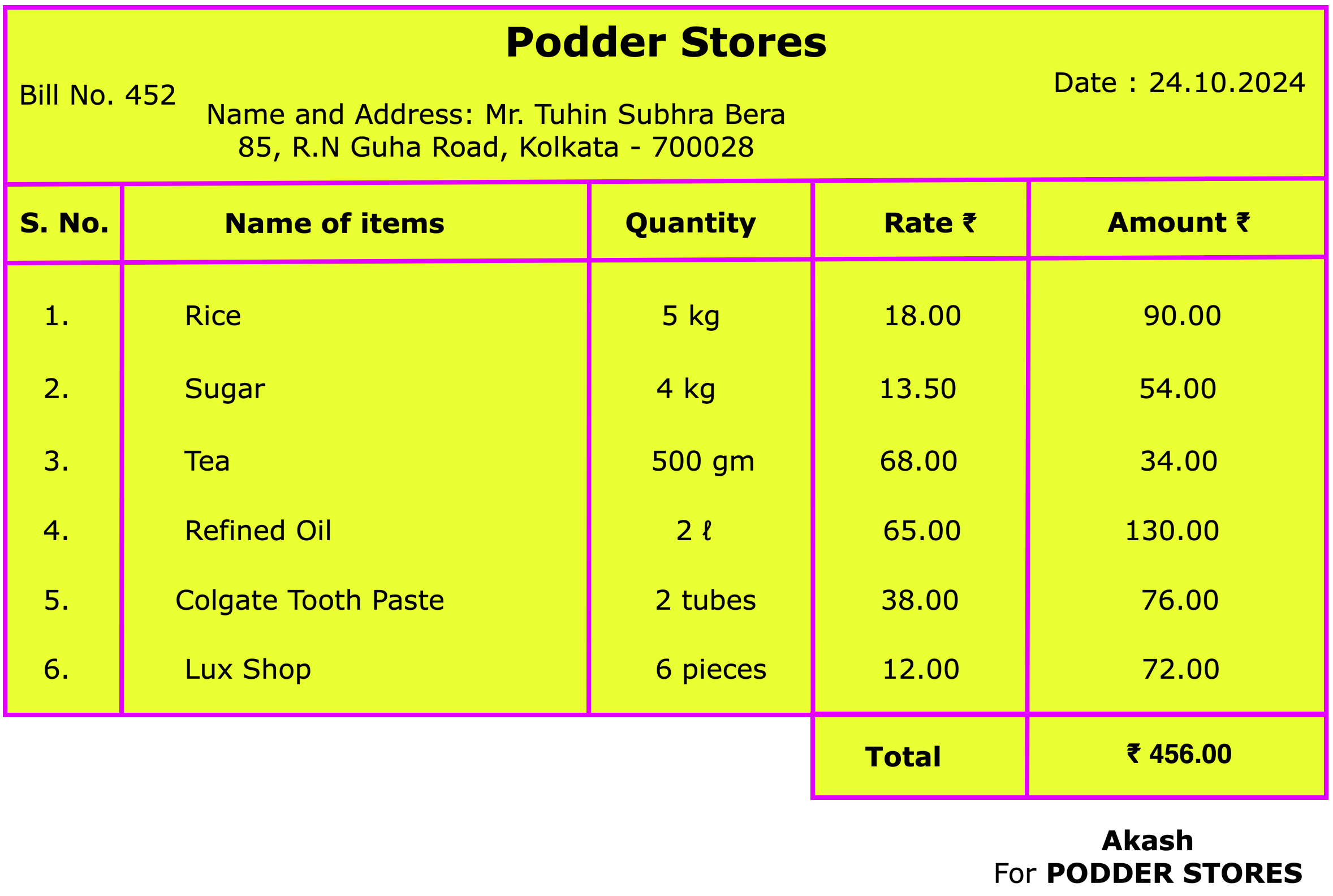
5th Grade Money Bills | Concept of the Bill | Preparation of a Bill
In 5th Grade Money Bills we will learn the concept of the bill, preparation of a bill and calculation of the total amount of a bill. In our daily life, we receive many types of bills like Electricity Bill, Telephone Bill, Water Bill, etc. The shopkeeper also gives us a bill
Continue reading "5th Grade Money Bills | Concept of the Bill | Preparation of a Bill"
Jun 26, 2025
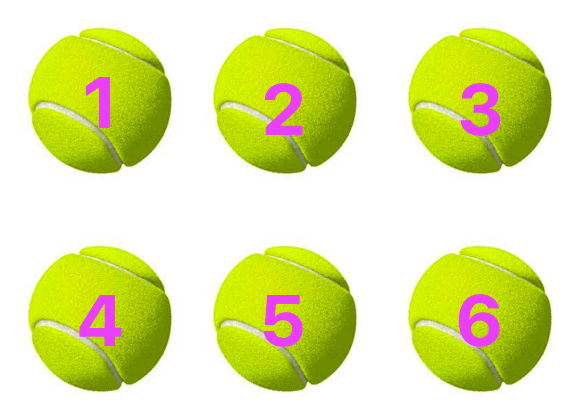
Cardinal Numbers and Ordinal Numbers | Cardinal Numbers | Ordinal Num
Cardinal numbers and ordinal numbers are explained here with the help of colorful pictures. There are many steps in a staircase as shown in the above figure. The given staircase has nine steps,
Continue reading "Cardinal Numbers and Ordinal Numbers | Cardinal Numbers | Ordinal Num"
Jun 25, 2025
What is Bills in Maths? |Use of Bill | Format of a Blank Bill |Billing
We will learn about bills and billing of different items. Sometime we go to market to buy various items like potatoes, fruits, vegetables, clothes etc. in different quantity. The shopkeeper
Continue reading "What is Bills in Maths? |Use of Bill | Format of a Blank Bill |Billing"
Jun 25, 2025
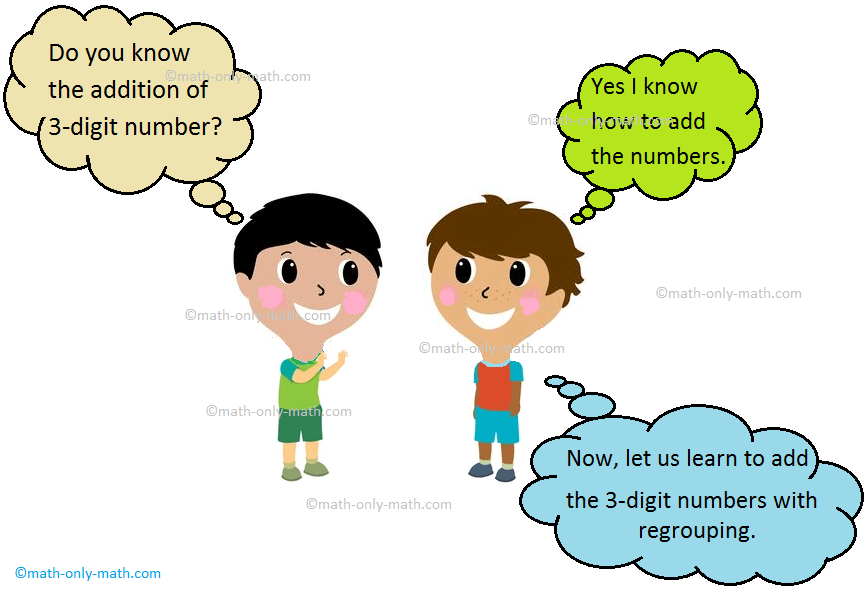
Addition of 3-Digit Numbers with Regrouping | Step-by-Step Method
We will learn addition of 3-digit numbers with regrouping. Do you know the addition of 3-digit number? Yes I know how to add the numbers. Now, let us learn to add the 3-digit numbers with regrouping.
Continue reading "Addition of 3-Digit Numbers with Regrouping | Step-by-Step Method"
Jun 25, 2025
Ordinal Numbers | Cardinal Numbers | First Ten Ordinal Numbers
Ordinal numbers indicate the position of the objects or the order of the objects. When some objects are placed in an order then to tell their position we use ordinal numbers. Ordinal numbers
Continue reading "Ordinal Numbers | Cardinal Numbers | First Ten Ordinal Numbers"
Jun 25, 2025
Circle the Greatest Number | Encircle the Greatest Number | Identify
In math worksheet on circle the greatest number that comes accordingly so that kids can practice this sheet at home. In this sheet children need to analyze the greater number and then identify
Continue reading "Circle the Greatest Number | Encircle the Greatest Number | Identify"
Jun 25, 2025
Circle the Smallest Number | Encircle the Smallest Number | Small Numb
In math worksheet on circle the smallest number that comes accordingly so that kids can practice this sheet at home. In this sheet children need to analyze the smaller number and then identify
Continue reading "Circle the Smallest Number | Encircle the Smallest Number | Small Numb"
Jun 25, 2025
Examples on the Formation of Greatest and the Smallest Number |Example
In examples on the formation of greatest and the smallest number we know that the procedure of arranging the numbers in ascending and descending order.
Continue reading "Examples on the Formation of Greatest and the Smallest Number |Example"
Jun 25, 2025
Formation of Greatest and Smallest Numbers | Arranging the Numbers
the greatest number is formed by arranging the given digits in descending order and the smallest number by arranging them in ascending order. The position of the digit at the extreme left of a number increases its place value. So the greatest digit should be placed at the
Continue reading "Formation of Greatest and Smallest Numbers | Arranging the Numbers"
Jun 24, 2025
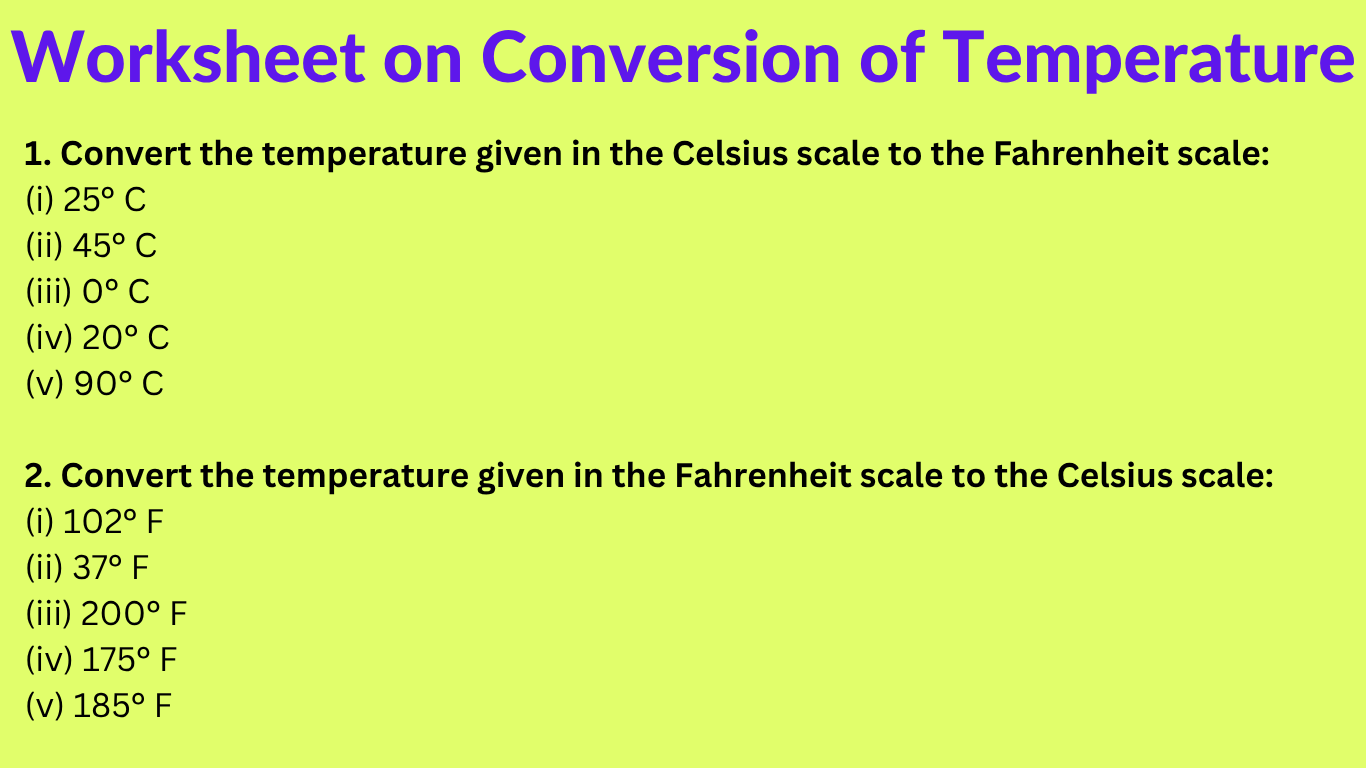
Worksheet on Conversion of Temperature | Temperature Worksheets | Ans
We will practice the questions given in the worksheet on conversion of temperature from one scale into another. We know the two different temperature scales are the Fahrenheit scale and the
Continue reading "Worksheet on Conversion of Temperature | Temperature Worksheets | Ans"
Jun 24, 2025
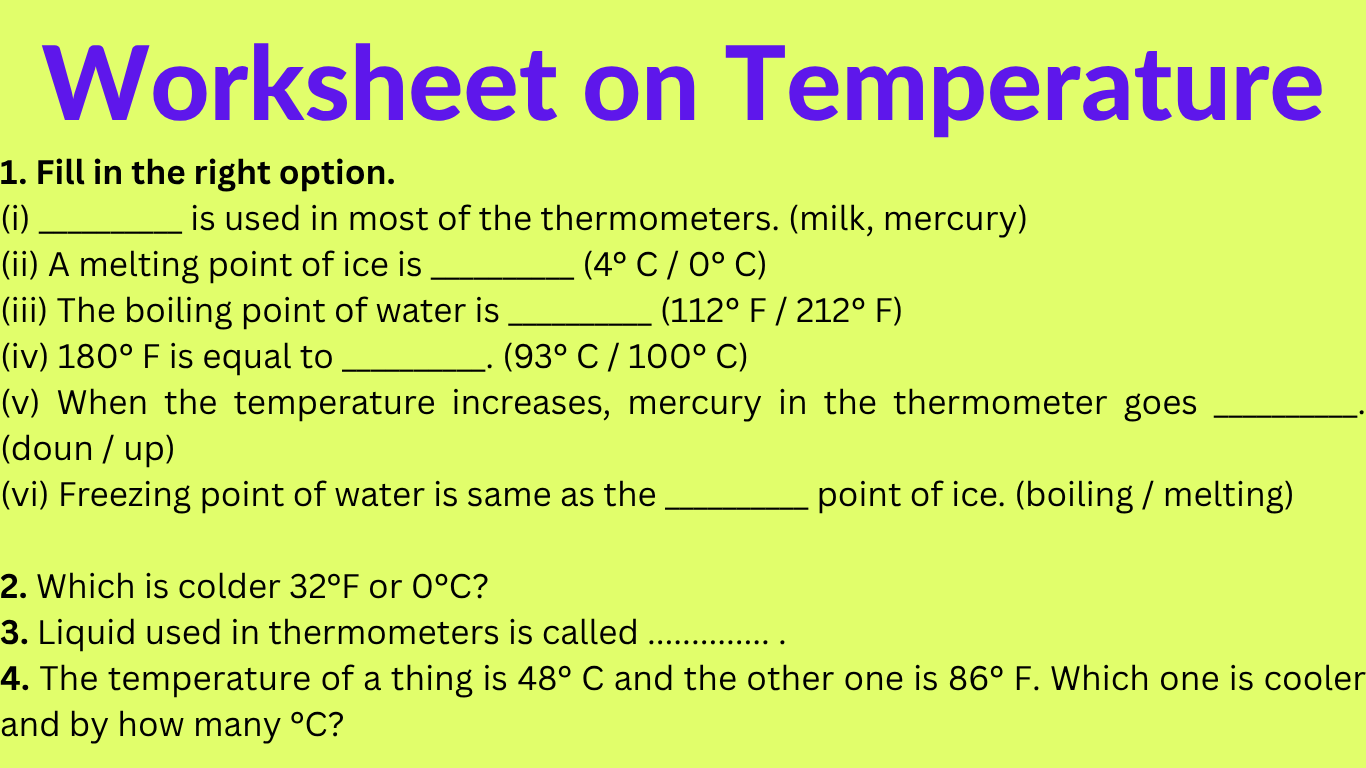
Worksheet on Temperature |Celsius to Fahrenheit, Fahrenheit to Celsius
In the worksheet on temperature we will solve 10 different types of questions.1. Which is colder 32°F or 0°C? 2. Water boils at ...°C and freezes at ....°F.
Continue reading "Worksheet on Temperature |Celsius to Fahrenheit, Fahrenheit to Celsius"
Jun 24, 2025
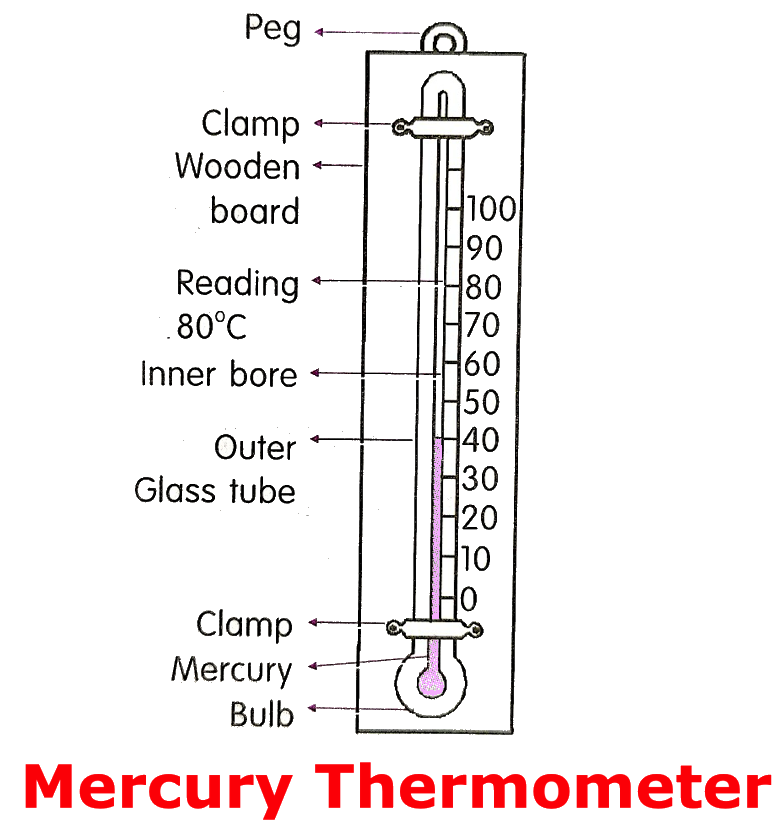
5th Grade Temperature | Fahrenheit Scale | Celsius Scale | Thermometer
We will discuss here about the concept of temperature. We have already learned about various types of measurements like length, mass capacity and time. But if we have fever, non of these measurements
Continue reading "5th Grade Temperature | Fahrenheit Scale | Celsius Scale | Thermometer"
Jun 20, 2025
Converting the Temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius | Examples
In converting the temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius the formula is, C = (5/9)(F - 32); The steps of converting from Fahrenheit to Celsius are reversed here.
Continue reading "Converting the Temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius | Examples"
Jun 20, 2025
Converting the Temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit | Examples
In converting the temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit the formula is F = (9/5)C + 32. Steps of converting from Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F)
Continue reading "Converting the Temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit | Examples"
Jun 20, 2025
Word Problems on Simple Interest | Simple Interest Formula | Worksheet
Word Problems on Simple Interest are solved here: 1. Robert deposits $ 3000 in State Bank of India for 3 year which earn him an interest of 8%.What is the amount
Continue reading "Word Problems on Simple Interest | Simple Interest Formula | Worksheet"
Jun 19, 2025
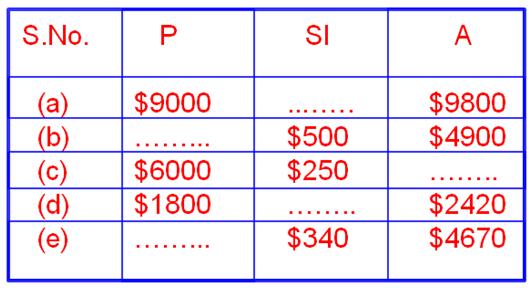
Worksheet on Simple Interest | Word problem on Simple Interest | Free
In worksheet on simple interest we will get different types of question on calculating the simple interest, the principal amount, the rate of interest and the word problems on simple interest.
Continue reading "Worksheet on Simple Interest | Word problem on Simple Interest | Free"
Jun 19, 2025
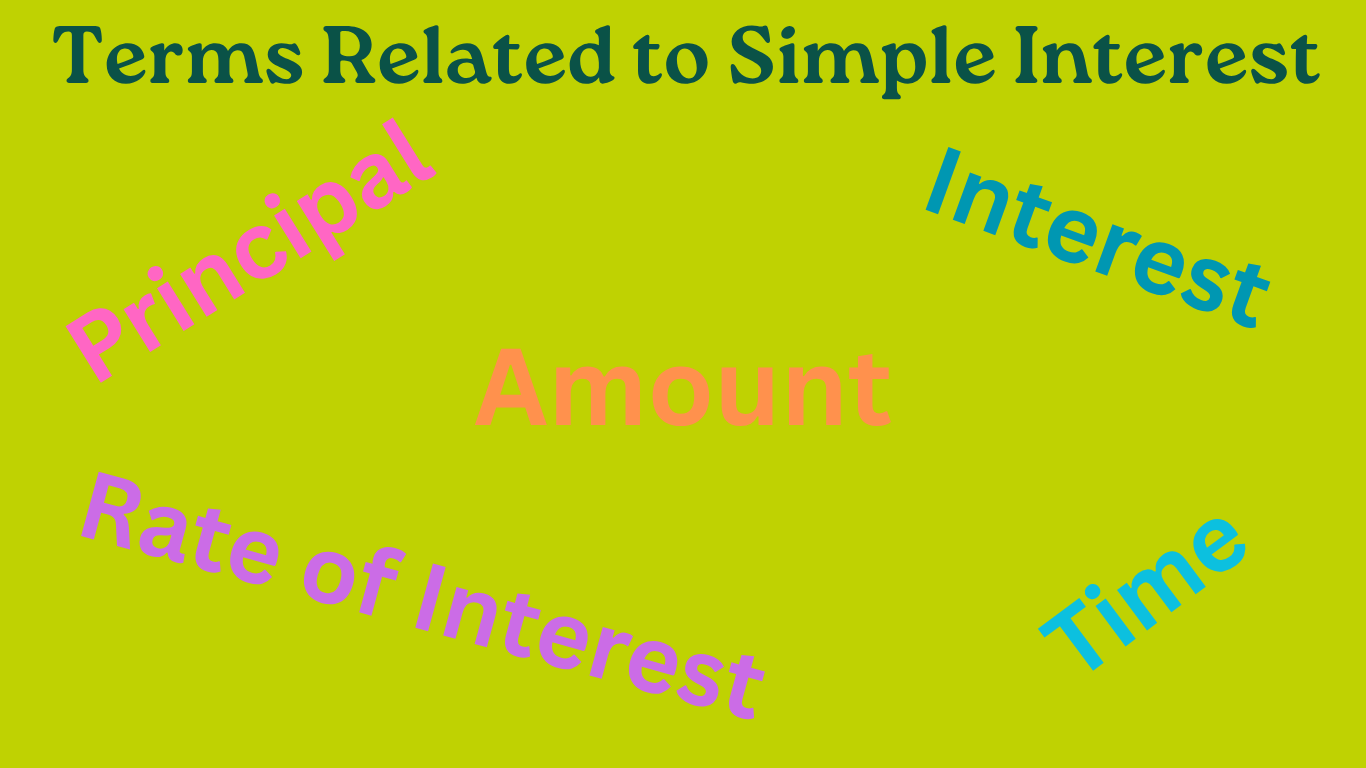
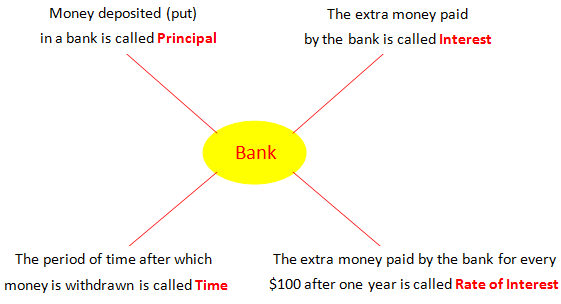
Terms Related to Simple Interest | Simple Interest Formula | Principal
In terms related to simple interest we will learn all the terms related to simple interest. The terms related to simple interest are Interest, Principal, Amount, Simple Interest, Time or period of time, Rate or rate of interest and Simple interest formula.
Continue reading "Terms Related to Simple Interest | Simple Interest Formula | Principal"
Jun 18, 2025
Introduction to Simple Interest | Definition | Formula | Examples
In simple interest we will learn and identify about the terms like Principal, Time, Rate, Amount, etc. PRINCIPAL (P): The money you deposit or put in the bank is called the PRINCIPAL.
Continue reading "Introduction to Simple Interest | Definition | Formula | Examples "
Jun 18, 2025
5th Grade Profit and Loss Percentage Worksheet | Profit and Loss | Ans
In 5th grade profit and loss percentage worksheet you will get different types of problems on finding the profit or loss percentage when cost price and selling price are given, finding the selling price when cost price and profit or loss percentage are given & word problems
Continue reading "5th Grade Profit and Loss Percentage Worksheet | Profit and Loss | Ans"
Jun 18, 2025
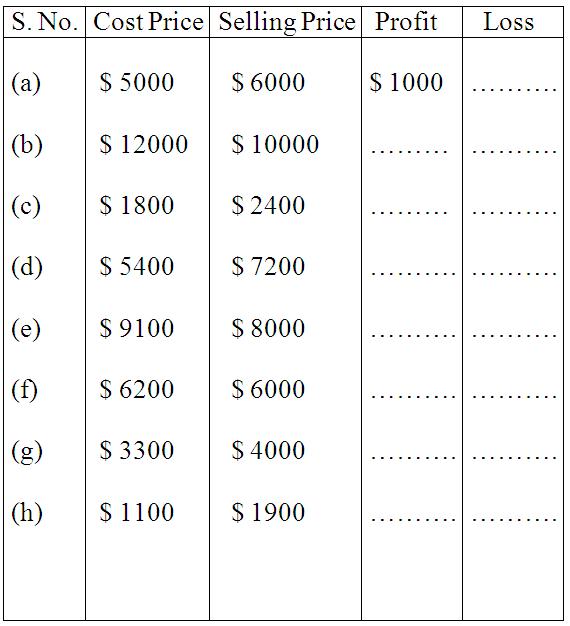
Worksheet on Profit and Loss | Word Problem on Profit and Loss | Math
In worksheet on profit and loss, we can see below there are some different types of questions which we can practice in our homework.
Continue reading "Worksheet on Profit and Loss | Word Problem on Profit and Loss | Math"
Jun 15, 2025
Calculating Profit Percent and Loss Percent | Profit and Loss Formulas
In calculating profit percent and loss percent we will learn about the basic concepts of profit and loss. We will recall facts and formula while calculating profit percent and loss percent. Now we wil
Continue reading "Calculating Profit Percent and Loss Percent | Profit and Loss Formulas"
Jun 14, 2025
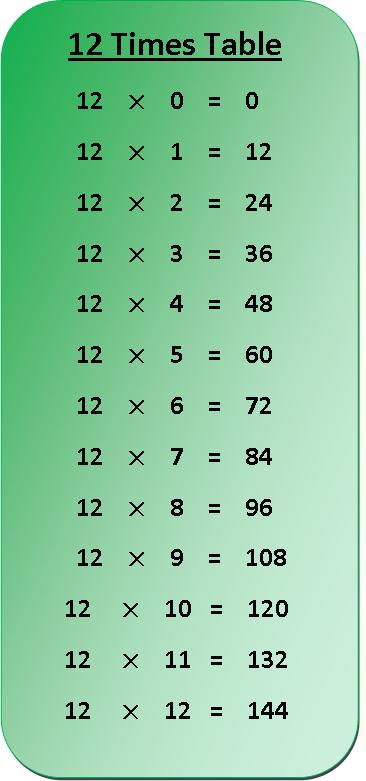
12 Times Table Multiplication Chart | Exercise on 12 Times Table | 12
In 12 times table multiplication chart we will learn about the tables and then we will practice the exercise. Print out the multiplication table of 12 and hang it on your wall which will help you to
Continue reading "12 Times Table Multiplication Chart | Exercise on 12 Times Table | 12"
Jun 14, 2025
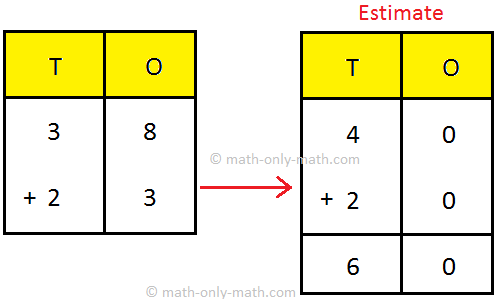
Estimating a Sum | Round the Number | Numbers by Rounding | Estimating
We will learn the basic knowledge for estimating a sum. Here we will learn an easy way to estimate a sum of two numbers by rounding. In case of two digit numbers we can only round the number
Continue reading "Estimating a Sum | Round the Number | Numbers by Rounding | Estimating"
Jun 13, 2025
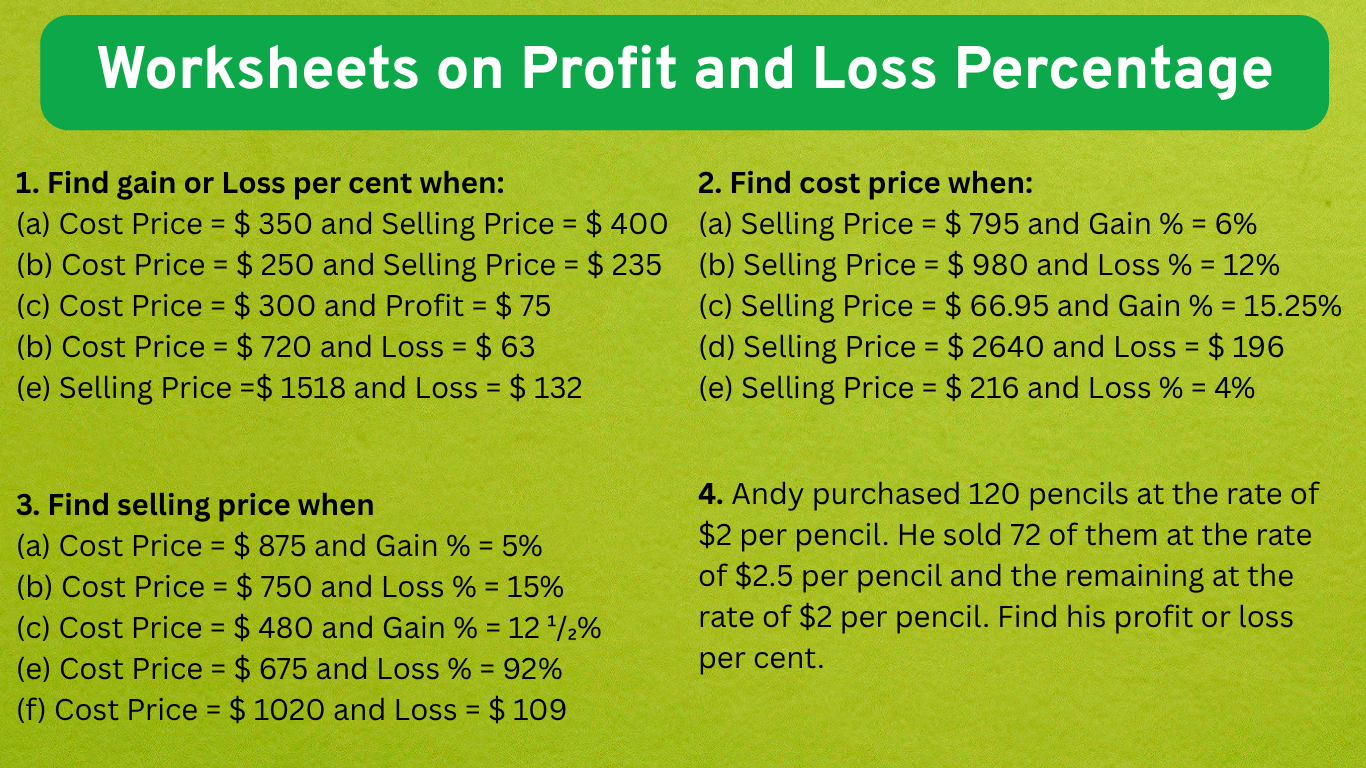
Worksheets on Profit and Loss Percentage | Profit & Loss Word Problems
Math worksheets on profit and loss percentage will help us to practice different types of questions on finding gain or loss per cent, cost price, selling price and also word problems on profit and los
Continue reading "Worksheets on Profit and Loss Percentage | Profit & Loss Word Problems"
Jun 11, 2025
Word Problems on Profit and Loss Worksheet |Cost Price |Selling Price
In word problems on profit and loss worksheet you will get different types of problems on cost price and selling price, profit and loss, calculating profit o loss, calculating selling price and cost price, calculating profit or loss percent
Continue reading "Word Problems on Profit and Loss Worksheet |Cost Price |Selling Price "
Jun 11, 2025
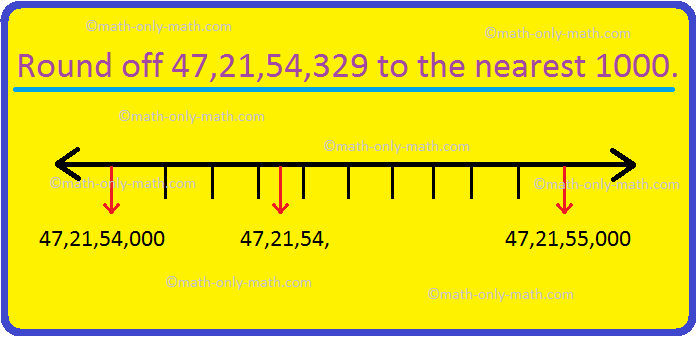
Round off to Nearest 1000 |Rounding Numbers to Nearest Thousand| Rules
Round off to nearest 1000 is discussed here. While rounding off to the nearest 1000, if the digit in the hundreds place is between 0 – 4 i.e., < 5, then the hundreds place is replaced by ‘0’. If the digit in the hundreds place is = to or > 5, then the hundreds place is
Continue reading "Round off to Nearest 1000 |Rounding Numbers to Nearest Thousand| Rules"
Jun 11, 2025
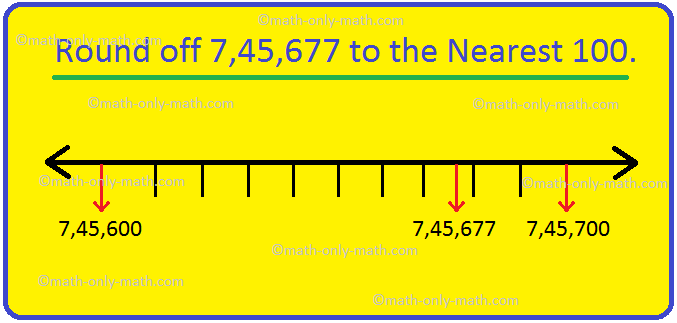
Round off to Nearest 100 | Rounding Numbers To Nearest Hundred | Rules
While rounding off to the nearest hundred, if the digit in the tens place is between 0 – 4 i.e. < 5, then the tens place is replaced by ‘0’. If the digit in the units place is equal to or >5, then the tens place is replaced by ‘0’ and the hundreds place is increased by 1.
Continue reading "Round off to Nearest 100 | Rounding Numbers To Nearest Hundred | Rules"
Jun 10, 2025
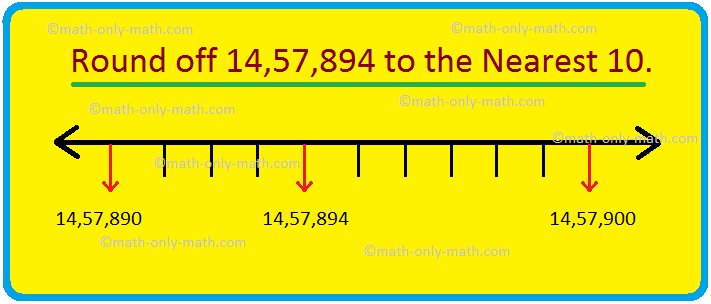
Round off to Nearest 10 |How To Round off to Nearest 10?|Rounding Rule
Round off to nearest 10 is discussed here. Rounding can be done for every place-value of number. To round off a number to the nearest tens, we round off to the nearest multiple of ten. A large number may be rounded off to the nearest 10. Rules for Rounding off to Nearest 10
Continue reading "Round off to Nearest 10 |How To Round off to Nearest 10?|Rounding Rule"
Jun 09, 2025
Calculating Selling Price | Formulas to Calculate Selling Price | Math
We will learn how to solve different types of problems on calculating selling price. Formulas to calculate selling price: (i) If Cost Price of an article and gain on its selling are given
Continue reading "Calculating Selling Price | Formulas to Calculate Selling Price | Math"
Jun 09, 2025
Calculating Cost Price | Formulas to Calculate Cost Price | Cost Price
We will learn how to solve different types of problems on calculating cost price. Formulas to calculate cost price: (i) If Selling Price of an article and gain on its selling are given, the Cost Price
Continue reading "Calculating Cost Price | Formulas to Calculate Cost Price | Cost Price"
Jun 09, 2025
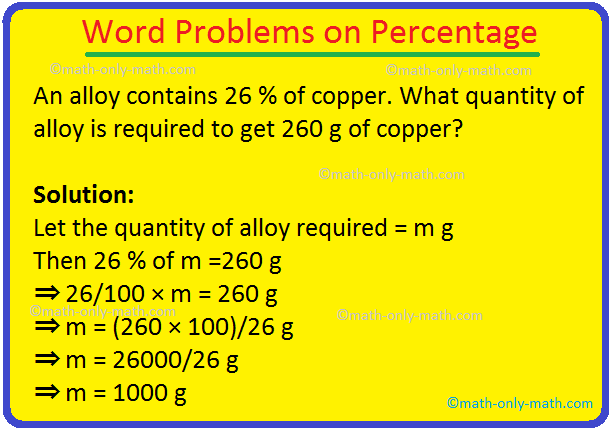
Word Problems on Percentage | Percent Problems | Real Life Problems
Word problems on percentage will help us to solve various types of problems related to percentage. Follow the procedure to solve similar type of percent problems. 1. In an exam Ashley secured 332 marks. If she secured 83 % makes, find the maximum marks.
Continue reading "Word Problems on Percentage | Percent Problems | Real Life Problems"
Jun 06, 2025
Finding Profit or Loss | Solved Examples on Finding Profit or Loss
We will solve different types of problems on finding profit or loss. We know, when Selling Price (S.P.) is greater than the Cost Price (C.P.) we have a gain (Profit) and when Cost Price (C.P.)
Continue reading "Finding Profit or Loss | Solved Examples on Finding Profit or Loss"
Jun 06, 2025
5th Grade Profit and Loss | Profit and Loss Formulas | Problems | Math
5th grade profit and loss are discussed here. Ron is a shopkeeper. He buys his goods either from the factory directly or from the whole seller. He then tries to sell each of goods or item at a higher
Continue reading "5th Grade Profit and Loss | Profit and Loss Formulas | Problems | Math"
Jun 05, 2025
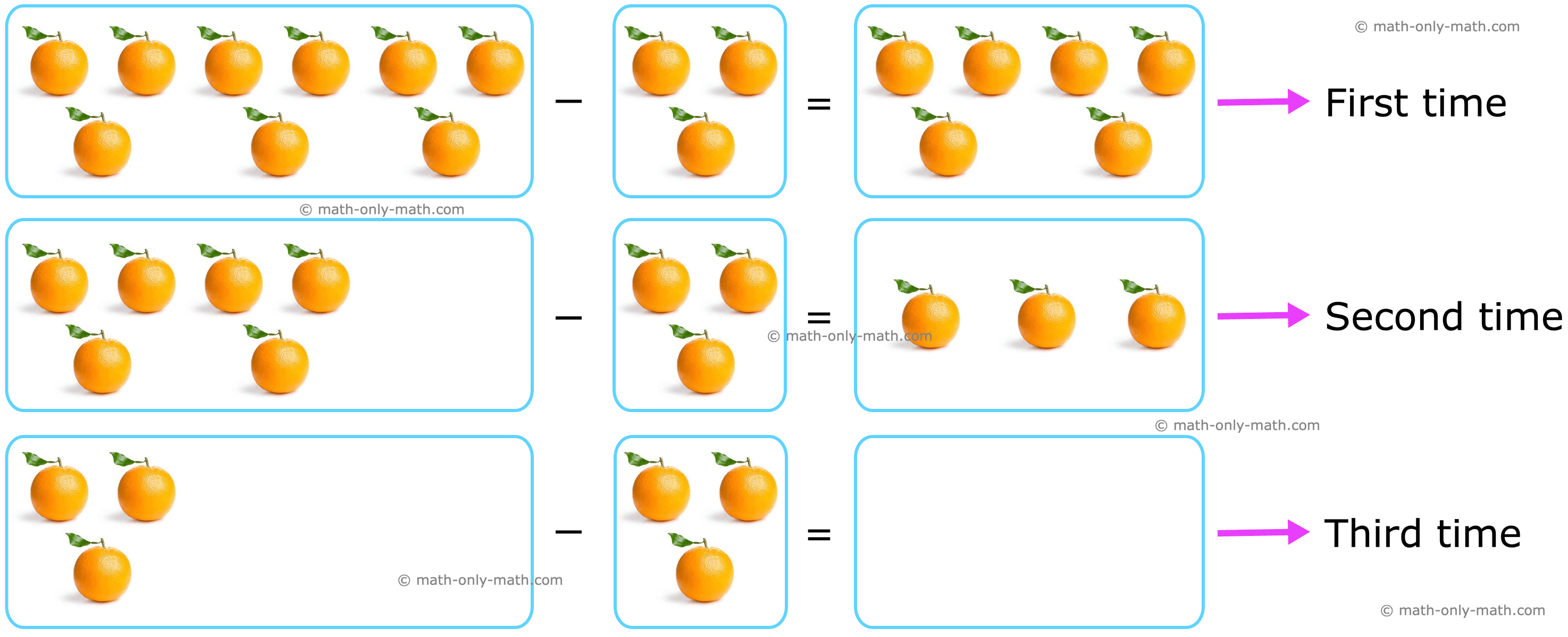
Divide by Repeated Subtraction | Division as Repeated Subtraction
How to divide by repeated subtraction? We will learn how to find the quotient and remainder by the method of repeated subtraction a division problem may be solved.
Continue reading "Divide by Repeated Subtraction | Division as Repeated Subtraction"
Jun 05, 2025
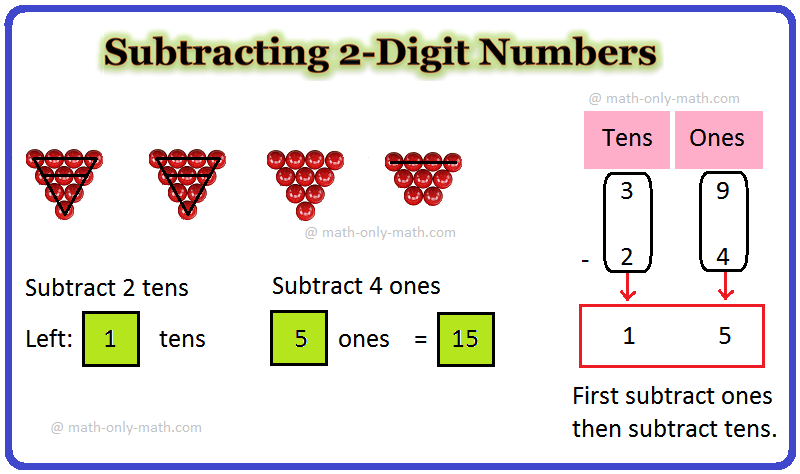
Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers | Video |How to Subtract Two Digit Numbers
In subtracting 2-digit numbers we will subtract or minus a two-digit number from another two-digit number. To find the difference between the two numbers we need to ‘ones from ones’ and ‘tens from
Continue reading "Subtracting 2-Digit Numbers | Video |How to Subtract Two Digit Numbers"
Jun 05, 2025
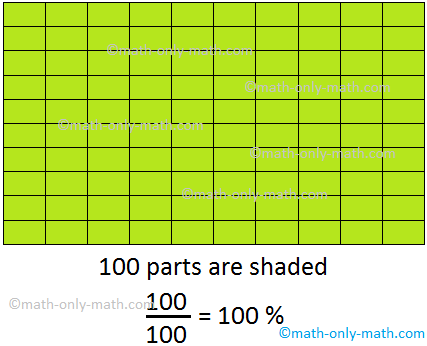
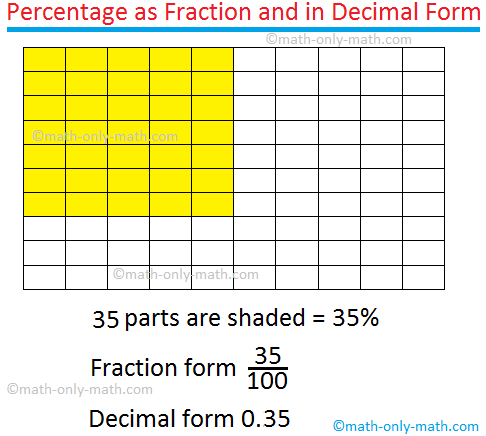
What is a Percentage in Math? | Symbol | Fraction with Denominator 100
A fraction with denominator 100 is called percentage and is denoted by the symbol %. In our daily life, we see a lot of statements with numbers followed by a symbol %. A number followed by % is called a percentage or percent. The term percent comes from the Latin phrase per
Continue reading "What is a Percentage in Math? | Symbol | Fraction with Denominator 100"
Jun 05, 2025
Convert Percentage into Decimal | Percentage as Decimals Conversion
How to convert a given percentage into decimal? We will follow the following steps for converting a percentage into a decimal: Step I: Obtain the percentage which is to be converted into decimal Step II: Remove the percentage sign (%) and divide it by 100.
Continue reading "Convert Percentage into Decimal | Percentage as Decimals Conversion"
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
5th Grade Circle Worksheet | Free Worksheet with Answer |Practice Math
Jul 10, 25 11:41 AM
In 5th Grade Circle Worksheet you will get different types of questions on parts of a circle, relation between radius and diameter, interior of a circle, exterior of a circle and construction of circl… -
Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Jul 09, 25 01:29 AM
Construction of a Circle when the length of its Radius is given. Working Rules | Step I: Open the compass such that its pointer be put on initial point (i.e. O) of ruler / scale and the pencil-end be… -
Combination of Addition and Subtraction | Mixed Addition & Subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:32 PM
We will discuss here about the combination of addition and subtraction. The rules which can be used to solve the sums involving addition (+) and subtraction (-) together are: I: First add -
Addition & Subtraction Together |Combination of addition & subtraction
Jul 08, 25 02:23 PM
We will solve the different types of problems involving addition and subtraction together. To show the problem involving both addition and subtraction, we first group all the numbers with ‘+’ and… -
5th Grade Circle | Radius, Interior and Exterior of a Circle|Worksheet
Jul 08, 25 09:55 AM
A circle is the set of all those point in a plane whose distance from a fixed point remains constant. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is known






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.