Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Division by Two-Digit Numbers
In division by two-digit numbers we will practice dividing two, three, four and five digits by two-digit numbers.
Consider the following examples on division by two-digit numbers:
Let us use our knowledge of estimation to find the actual quotient.
1. Divide 94 by 12
Round the number
94 ÷ 12 → 90 ÷ 10
Estimated quotient = 9
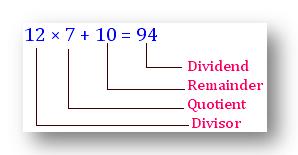
In order to find the actual quotient, multiply the divisor 12 by the estimated quotient.
12 × 9 = 108
12 × 8 = 96
12 × 7 = 84
108 > 94
96 > 94
The actual quotient, we find is 7.
Check:
Quotient - 7
Remainder - 10
12 × 7 + 10 = 94
2. Divide 96 by 16
Solution:
16 x 6 = 96, so, 6 will be the quotient.
We search for the possible quotient. The divisor is a number of two digits.
So, 96 is taken as dividend.
Therefore, Quotient = 6
2-Digit Number by 2-Digit Number Long Division Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
3. Divide 88 by 17
Solution:
17 x 5 = 85 and 17 x 6 = 102,
85 < 88 but 102 > 88
So, 5 will be the quotient
Therefore, Quotient = 5, Remainder = 3
3-Digit Number by 2-Digit Number Long Division Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
4. Divide 192 by 24
Solution:
19 < 24, so, 192 will be taken as dividend.
24 x 8 = 192. So, 8 will be the quotient.
Therefore, Quotient = 8
5. 510 ÷ 32 ⟶ 500 ÷ 30 ⟶ 50 ÷ 3
Estimated quotient = 16
Try:
32 × 16 = 512
32 × 15 = 480
512 > 510
The actual quotient is 15
6. Divide 275 by 24
Solution:
(a) 27 > 24, 24 x 1 = 24, 24 x 2 = 48
So, 1 will be quotient.
Here, 27 is 27T or, 270
So, 1T or 10 is the quotient.
(b) 275 -240 = 35, 24 x 1. = 24,
So, 1 is the quotient.
24 x 11 + 11 = 264 + 11 = 275
Therefore, result is verified
Therefore, Quotient = 11, Remainder =11
7. Divide 803 by 70
Solution:
(a) 80 > 70,
So, 80T will be taken as dividend
70 x 1 = 70, 70 x 2 = 140
So, 1T will be quotient.
(b) 803 - 700 = 103, 70 x 1 = 70, 70 x 2 = 140
So, 1 will be quotient.
70 x 11 + 33 = 770 + 33 = 803
Therefore, result is verified
Therefore, Quotient =11, Remainder = 33
8. Divide 345 by 49
Solution:
34 < 49, So, 345 will be taken as dividend.
By trial 49 x 7 = 343 which is near to 345
So, 7 will be quotient.
Verification: 49 x 7 + 2 = 343 + 2 = 345
Therefore, Quotient = 7, Remainder = 2
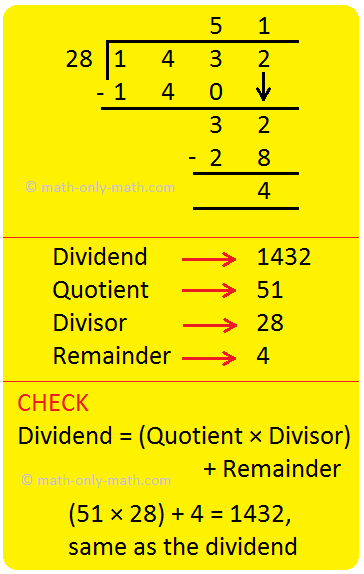
9. Divide 1432 by 28.
Solution:
|
I: 1 < 28 14 < 28 Therefore, take 143 II: We have 28 × 6 = 168; 28 × 5 = 140 Since 140 < 143, write 5 as first digit of the quotient. Write the product 26 × 5 = 140 below 143 and subtract. III: 143 – 140 = 3; Bring down 2 32 > 28 We have 28 × 1 = 28 < 32. 28 × 2 = 56 > 32 Since 28 < 32, write 1 as the second digit of the quotient. Write the product 28 × 1 = 28 below and subtract. IV: 32 – 28 = 4 Since 4 < 28, stop the division. |
10. Divide 4963 by 14
Solution:
(I method)
(a) 14 x 3 = 42 and 14 x 4 = 56, 42 < 49 and 56 > 49
So, 3H will be quotient.
(b) 4963 - 4200 = 763, 14 x 5 = 70 and 14 x 6 = 84
So, 5T will be quotient.
(c) 763 - 700 = 63, 14 x 4 = 56, 14 x 5 = 70
56 < 63, 70 > 63
Therefore, 4 is the quotient.
Verification: 14 x 354 + 7 = 4956 + 7 = 4963
Therefore, Quotient = 354, Remainder = 7
(II method)
(a) 14 x 3 = 42, 14 x 4 = 56,
Therefore, 3H will be quotient.
49 - 42 = 7, 6 is carried down
(b) 14 x 5 = 70, 14 x 6 = 84,
Therefore, 5T will be quotient.
76 - 70 = 6, 3 is carried down.
14 x 4 = 56, 14 x 5 = 70,
Therefore, 4 will be quotient.
63 - 56 = 7 is the remainder
Quotient = 354
Remainder = 7
Verification:
Quotient x divisor + remainder
= 354 x 14 + 7
= 4956 +7
= 4963 (dividend)
So, result is verified
11. Divide 47320 by 35
Solution:
(a) 47 Th is divided by 35, 35 x 1 = 35 < 47,
35 x 2 = 70 > 47, so, 1 Th is quotient.
47 - 35 = 12, 3 is carried down
(b) 123H is divided by 35, 35 x 3 = 105 < 123
35 x 4 = 140 > 123, so, 3 H is quotient
123 - 105 = 18, 2 is carried down.
(c) 182 T is divided by 35, 35 x 5 = 175 < 182
35 x 6 = 210 > 182, therefore, 5T is quotient.
182 - 175 = 7, 0 is carried down.
(d) 70 is divided by 35, 35 x 2 = 70,
2 is the quotient
70 - 70 = 0
Verification: 35 x 1352 + 0 = 47320.
So verified.
Therefore, Quotient = 1352 Remainder = 0
12. Divide 50360 by 43
Solution:
(a) 50Th is divided by 43, 43 x 1 = 43 < 50.
So, 1 Th is quotient, 50 - 43 = 7,3 is taken down.
(b) 73 H is divided by 43, 43 x 1 = 43 < 73
43 x 2 = 86 > 73.
So, 1H is quotient, 73 - 43 = 30, 6 is taken down.
(c) 306 T is divided by 43, 43 x 7 = 301 < 306
7 T is quotient, 306 - 301 = 5, 0 is taken down
(d) 50 is divided by 43, 1 is quotient
50 - 43 = 7 is remainder
Verification: 1171 x 43 + 7 = 50353 + 7 = 50360.
Result is verified.
Quotient =1171 Remainder = 7
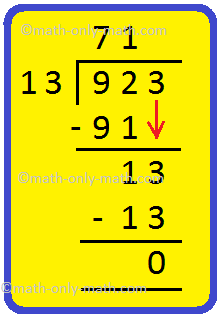
13. Divide 923 by 13
Solution:
|
Let us divide 923 by 13. Step I: Since, the divisor is a 2-digit number, we consider 92 the 2-digit number on the extreme left of the dividend. 92 > 13, we know that 13 x 7 = 91 We write 7 in the quotient. Subtract 91 from 92. Step II: Bring down 3 and write on the right side of the remainder. 13 is the new dividend. Step III: Divide 13 by 13. We know 13 x 1 = 13. Write 1 in the quotient. Subtract 13 from 13. The remainder is 0. |
Hence, quotient = 71 and remainder = 0. |
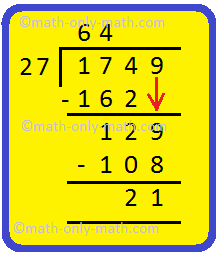
14. Divide 1749 by 27 and check your answer.
|
Solution: Let us divide 1749 by 27. Step I: The divisor 27 is greater than the 2-digit number on the extreme left of the dividend. So, we take the 3-digit number which is 174 and divide by 27. Write 6 in the quotient and subtract 162 from 174. Step II: Bring down 9 and write on the right side of the remainder. 129 is the new dividend. Step III: Divide 129 by 27. Write 4 in the quotient and subtract 108 from 129. Remainder is 21 |
Hence, quotient = 64 and remainder = 21 |
Verification:
We know that
Dividend = Quotient x Divisor + Remainder
= 64 x 27 + 21
= 1728 + 21
= 1749
1749 is the dividend as given in the question.
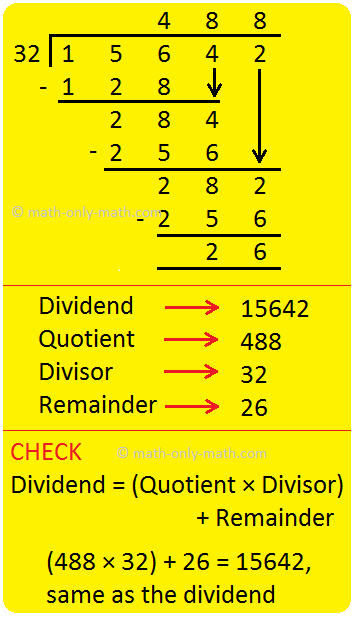
15. Divide 15642 by 32
Solution:
|
I: 1 < 32 15 < 32 Therefore, take 156 II: We have 32 × 5 = 160 > 156 32 × 4 = 128 < 156 Since 128 < 156, write 4 as first digit of the quotient. Write the product 32 × 4 = 128 below 156 and subtract. III: 156 – 128 = 28. Bring down 4. 284 > 32. We have 32 × 9 = 288 > 284. 32 × 8 = 256 < 284. Since 256 < 284, write 8 as the second digit of the quotient. Write the product 32 × 8 = 256 below 284 and subtract. IV: 284 - 256 = 28. Bring down 2. 282 > 32. We have 32 × 9 = 288 > 282 32 × 8 = 256 < 282. V: Write 8 as the third digit of the quotient. Write the product 32 × 8 = 256 below 282 and subtract. 282 – 256 = 26. Since 26 < 32, stop the division. |
Division Activity
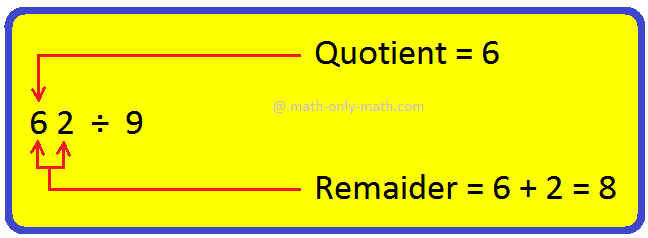
Objective: Dividing a 2-digit number by 9 using short cut method.
Materials Required: Pen and paper only.
Procedure/Demonstration: We can divide any 2-digit number by 9 quickly.
Type 1: When the sum of the digits is less than 9.
In this case, the tens digit of the dividend gives quotient and the sum of the two digits gives remainder.
Type 2: When the sum of the digits is greater than or equal of 9 but less than 18. In this case, 1 more than the tens digit of the dividend gives quotient. To get the remainder, subtract 9 from the sum of the digits of the dividend.
75 ÷ 9 gives quotient = 7 + 1 = 8 and remainder = 12 - 9 = 3
63 ÷ 9 gives quotient = 6 + 1 = 7 and remainder = 9 - 9 = 0
Worksheet on Division by 2-Digit Numbers:
1. Divide the following:
(i) 8629 ÷ 12
(ii) 38245 ÷ 32
(iii) 16928 ÷ 11
(iv) 28724 ÷ 33
(v) 86458 ÷ 15
(v) 7542 ÷ 19
Answer:
1. (i) Quotient: 719; Remainder: 1
(ii) Quotient: 1195; Remainder: 5
(iii) Quotient: 1538; Remainder: 10
(iv) Quotient: 870; Remainder: 14
(v) Quotient: 5763; Remainder: 13
(v) Quotient: 396; Remainder: 18
Related Concept
● Addition
● Check for Subtraction and Addition
● Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction
● Estimating Sums and Differences
● Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number
● Multiplication of a Number by a 3-Digit Number
● Word Problems on Multiplication
● Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division by 10 and 100 and 1000
● Division by Two-Digit Numbers
4th Grade Math Activities
From Division by Two-Digit Numbers to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
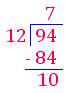
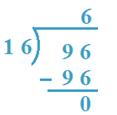
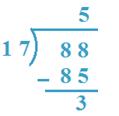
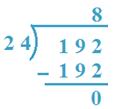
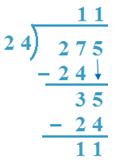
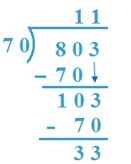
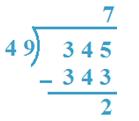
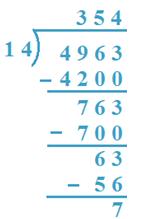
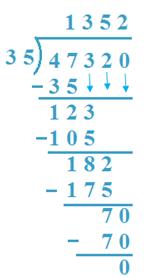
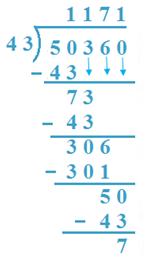


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.