Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Estimating the Quotient
We will learn estimating the quotient.
To estimate the quotient, we first round off the divisor and the dividend to the nearest tens, hundreds, or thousands and then divide the rounded numbers.
In a division sum, when the divisor is made up of 2 digits or more than 2 digits, it helps if we first estimate the quotient and then try to find the actual number.
(i) Divide 84 by 21
Round the number to the nearest ten
84 ÷ 21 → 80 ÷ 20
Calculate mentally.
8 ÷ 2 = 4
Estimated quotient = 4
(ii) 242 ÷ 22
Round to the nearest ten
240 ÷ 20
Calculate mentally
24 ÷ 2 = 12
Estimated quotient = 12
In the process of division, the estimation of quotient plays a great role in its solution.
Let us see this in the following questions on division.
1. 74 ÷ 35
2. 627 ÷ 23
3. 694 ÷ 56
4. 975 ÷ 48
1. 74 ÷ 35 is approximately the same as 70 ÷ 40, i.e., 7 ÷ 4 (74 → 70 & 35 → 40)
7 ÷ 4 is approximately 2.
So, estimated quotient is 2.
2. 627 ÷ 23 is approximately the same as 600 ÷ 20 = 60 ÷ 2 = 30
(627 → 600 & 23 → 20)
So, the estimated quotient is 30.
3. 694 ÷ 56 is approximately the same as 700 ÷ 60 or 70 ÷ 6
70 ÷ 6 is approximately = 12.
So, the estimated quotient =12
4. 975 ÷ 48 is approximately 1000 ÷ 50 = 100 ÷ 5 = 20
So, estimated quotient = 20
Note: To estimate the quotient, round off the dividend to the nearest multiple of the divisor.
5. Estimate the quotient:
(i) 682 ÷ 7
(ii) 253 ÷ 15
Solution:
(i) Given: 682 ÷ 7
We have to round off 682 to the multiple of 7.
We find 679 and 686 as two multiples of 7. Of these, 679 is closer to 682.
So, we round off 682 to 679.
Now, 679 ÷ 7 = 97.
Hence, the estimated value of quotient is 97.
(ii) Given: 253 ÷ 15
We have to round off 253 to the multiple of 15.
We find 240 and 255 as two multiples of 15. Of these, 255 is closer to 253.
So, we round off 253 to 255.
Now, 255 ÷ 15 = 17
Hence, the estimated value of quotient is 17.
Worksheet on Estimating the Quotient:
Question and Answers on Estimation in Division:
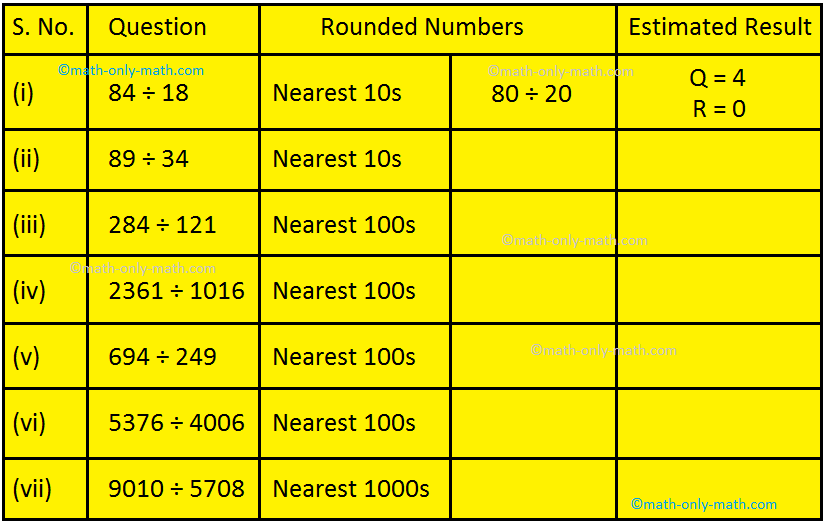
1. Estimate by rounding each number and then divide. One is done for you.
Answers:
(ii) 90 ÷ 30; Q = 3, R = 0
(iii) 300 ÷ 100; Q = 3, R = 0
(iv) 2400 ÷ 1000; Q = 2, R = 400
(v) 700 ÷ 200; Q = 3, R = 100
(vi) 5400 ÷ 4000; Q = 1, R = 1400
(vii) 9000 ÷ 6000; Q = 1, R = 3000
Related Concept
● Addition
● Check for Subtraction and Addition
● Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction
● Estimating Sums and Differences
● Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number
● Multiplication of a Number by a 3-Digit Number
● Word Problems on Multiplication
● Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division by 10 and 100 and 1000
● Division by Two-Digit Numbers
From Estimating the Quotient to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.