Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Straight Line in Normal Form
We will learn how to find the equation of a straight line in normal form.
The equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is p and this perpendicular makes an angle α with x-axis is x cos α + y sin α = p
If the line length of the perpendicular draw from the origin upon a line and the angle that the perpendicular makes with the positive direction of x-axis be given then to find the equation of the line.
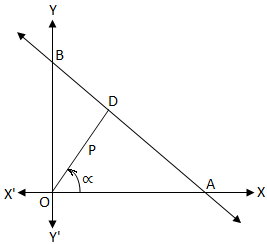
Suppose the line AB intersects the x-axis at A and the y-axis at B. Now from the origin O draw OD perpendicular to AB.
The length of the perpendicular OD from the origin = p and ∠XOD = α, (0 ≤ α ≤ 2π).
Now we have to find the equation of the
straight line AB.
Now, from the right-angled ∆ODA we get,
\(\frac{OD}{OA}\) = cos α
⇒ \(\frac{p}{OA}\) = cos α
⇒ OA = \(\frac{p}{cos α}\)
Again, from the right-angled ∆ODB we get,
∠OBD = \(\frac{π}{2}\) - ∠BOD = ∠DOX = α
Therefore, \(\frac{OD}{OB}\) = sin α
or, \(\frac{p}{OB}\) = sin α
or, OB = \(\frac{p}{sin α}\)
Since the intercepts of the line AB on x-axis and y-axis are OA and OB respectively, hence the required
\(\frac{x}{OA}\) + \(\frac{y}{OB}\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{x}{\frac{p}{cos α}}\) + \(\frac{y}{\frac{p}{sin α}}\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{x cos α}{p}\) + \(\frac{y sin α}{p}\) = 1
⇒ x cos α + y sin α = p, which is the required form.
Solved examples to find the equation of a straight line in normal form:
Find the equation of the straight line which is at a of distance 7 units from the origin and the perpendicular from the origin to the line makes an angle 45° with the positive direction of x-axis.
Solution:
We know that the equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is p and this perpendicular makes an angle α with x-axis is x cos α + y sin α = p.
Here p = 7 and α = 45°
Therefore, the equation of the straight line in normal form is
x cos 45° + y sin 45° = 7
⇒ x ∙ \(\frac{1}{√2}\) + y ∙ \(\frac{1}{√2}\) = 7
⇒ \(\frac{x}{√2}\) + \(\frac{y}{√2}\) = 7
⇒ x + y = 7√2, which is the required equation.
Note:
(i) The equation of a, straight line in the form of x cos α + y sin α = p is called its normal form.
(ii) In equation x cos α + y sin α = p, the value of p is always positive and 0 ≤ α≤ 360°.
● The Straight Line
- Straight Line
- Slope of a Straight Line
- Slope of a Line through Two Given Points
- Collinearity of Three Points
- Equation of a Line Parallel to x-axis
- Equation of a Line Parallel to y-axis
- Slope-intercept Form
- Point-slope Form
- Straight line in Two-point Form
- Straight Line in Intercept Form
- Straight Line in Normal Form
- General Form into Slope-intercept Form
- General Form into Intercept Form
- General Form into Normal Form
- Point of Intersection of Two Lines
- Concurrency of Three Lines
- Angle between Two Straight Lines
- Condition of Parallelism of Lines
- Equation of a Line Parallel to a Line
- Condition of Perpendicularity of Two Lines
- Equation of a Line Perpendicular to a Line
- Identical Straight Lines
- Position of a Point Relative to a Line
- Distance of a Point from a Straight Line
- Equations of the Bisectors of the Angles between Two Straight Lines
- Bisector of the Angle which Contains the Origin
- Straight Line Formulae
- Problems on Straight Lines
- Word Problems on Straight Lines
- Problems on Slope and Intercept
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Equation of a Straight Line in Normal Form to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.