Subscribe to our ▶️YouTube channel🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Home | About Us | Contact Us | Privacy | Math Blog
Exact Value of sin 72°
We will learn to find the exact value of sin 72 degrees using the formula of submultiple angles.
How to find the exact value of sin 72°?
Let, A = 18°
Therefore, 5A = 90°
⇒ 2A + 3A = 90˚
⇒ 2A = 90˚ - 3A
Taking sine on both sides, we get
sin 2A = sin (90˚ - 3A) = cos 3A
⇒ 2 sin A cos A = 4 cos3 A - 3 cos A
⇒ 2 sin A cos A - 4 cos3 A + 3 cos A = 0
⇒ cos A (2 sin A - 4 cos2 A + 3) = 0
Dividing both sides by cos A = cos 18˚ ≠ 0, we get
⇒ 2 sin A - 4 (1 - sin2 A) + 3 = 0
⇒ 4 sin2 A + 2 sin A - 1 = 0, which is a quadratic in sin A
Therefore, sin A = −2±√−4(4)(−1)2(4)
⇒ sin A = −2±√4+168
⇒ sin A = −2±2√58
⇒ sin A = −1±√54
Now sin 18° is positive, as 18° lies in first quadrant.
Therefore, sin 18° = sin A = √5−14
And cos 18° = √(1 - sin2 18°), [Taking positive value, cos 18° > 0]
⇒ cos 18° = √1−(√5−14)2
⇒ cos 18° = √16−(5+1−2√5)16
⇒ cos 18° = √10+2√516
Therefore, cos 18° = √10+2√54
Now sin 72° = sin (90° - 18°) = cos 18° = √10+2√54
- Trigonometric Ratios of Angle A2
- Trigonometric Ratios of Angle A3
- Trigonometric Ratios of Angle A2 in Terms of cos A
- tan A2 in Terms of tan A
- Exact value of sin 7½°
- Exact value of cos 7½°
- Exact value of tan 7½°
- Exact Value of cot 7½°
- Exact Value of tan 11¼°
- Exact Value of sin 15°
- Exact Value of cos 15°
- Exact Value of tan 15°
- Exact Value of sin 18°
- Exact Value of cos 18°
- Exact Value of sin 22½°
- Exact Value of cos 22½°
- Exact Value of tan 22½°
- Exact Value of sin 27°
- Exact Value of cos 27°
- Exact Value of tan 27°
- Exact Value of sin 36°
- Exact Value of cos 36°
- Exact Value of sin 54°
- Exact Value of cos 54°
- Exact Value of tan 54°
- Exact Value of sin 72°
- Exact Value of cos 72°
- Exact Value of tan 72°
- Exact Value of tan 142½°
- Submultiple Angle Formulae
- Problems on Submultiple Angles
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Exact Value of sin 72° to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
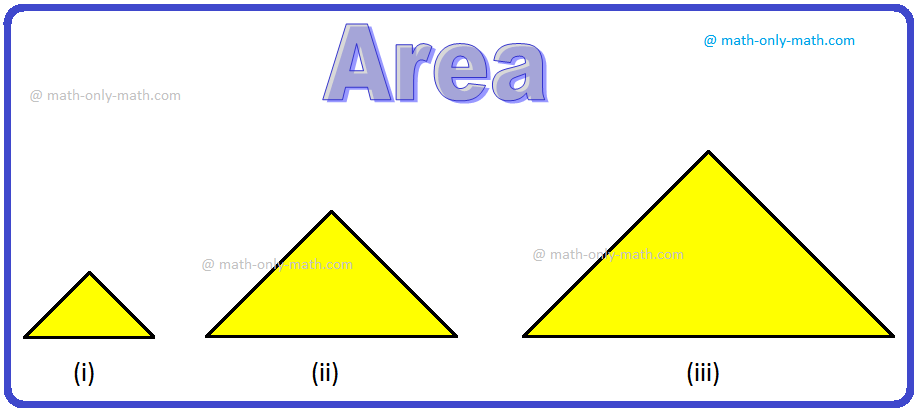
What is Area in Maths? | Units to find Area | Conversion Table of Area
Jul 17, 25 01:06 AM
The amount of surface that a plane figure covers is called its area. It’s unit is square centimeters or square meters etc. A rectangle, a square, a triangle and a circle are all examples of closed pla… -
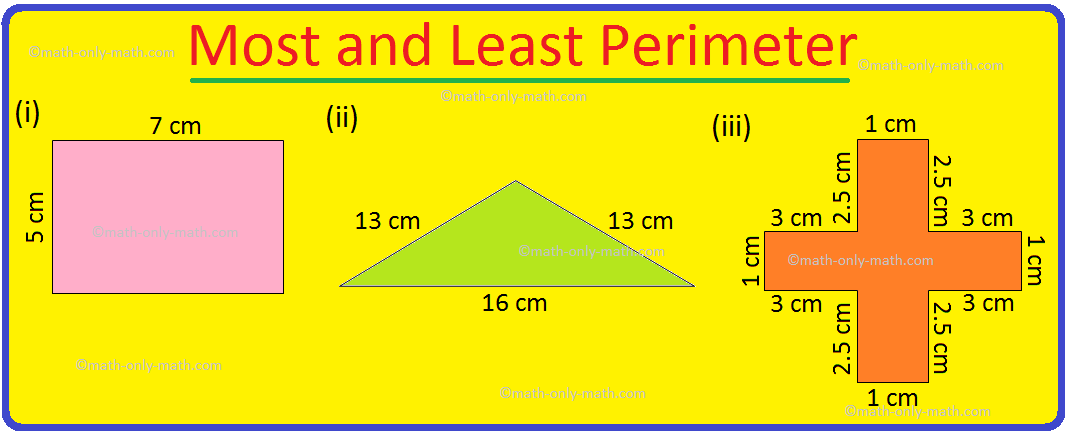
Worksheet on Perimeter | Perimeter of Squares and Rectangle | Answers
Jul 17, 25 12:40 AM
Practice the questions given in the worksheet on perimeter. The questions are based on finding the perimeter of the triangle, perimeter of the square, perimeter of rectangle and word problems. I. Find… -
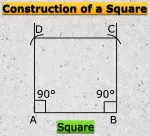
Formation of Square and Rectangle | Construction of Square & Rectangle
Jul 16, 25 11:46 PM
In formation of square and rectangle we will learn how to construct square and rectangle. Construction of a Square: We follow the method given below. Step I: We draw a line segment AB of the required… -
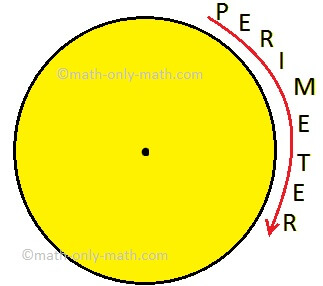
Perimeter of a Figure | Perimeter of a Simple Closed Figure | Examples
Jul 16, 25 02:33 AM
Perimeter of a figure is explained here. Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a closed figure. The perimeter of a simple closed figure is the sum of the measures of line-segments which hav… -
Formation of Numbers | Smallest and Greatest Number| Number Formation
Jul 15, 25 11:46 AM
In formation of numbers we will learn the numbers having different numbers of digits. We know that: (i) Greatest number of one digit = 9,

New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.