Division of Two-Digit by a
One-Digit Numbers
In division of two-digit by a one-digit numbers are discussed here step by step.
How to divide 2-digit numbers by single-digit numbers?
Let us follow the examples to learn to divide 2-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
I: Dividing a 2-digit Number by a 1-Digit Number without Remainder:
1. Divide the following and verify the result
(i) 42 ÷ 6
(ii) 85 ÷ 5
Solution:
(i) 42 ÷ 6
Since, 6 sevens are 42, i.e., 6 × 7 = 42
So, 7 will be quotient
6 × 7 + 0 = 42, the dividend
So, quotient 7 is verified
Therefore, 7 is quotient
(ii) 85 ÷ 5
(a) 8 > 5 so first 8 will be divided. 8T ÷ 5 = 1T so quotient will be 1 ten
(b) 8T - 5T = 3T, 3T + 5 = 35 for 35 ÷ 5, 5 × 7 = 35.
So 7 is quotient
(c) 5 × 17 = 85 (dividend)
So, result is verified.
Therefore, Quotient = 17, remainder = 0
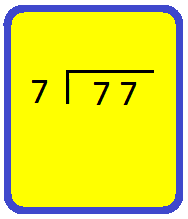
2. Divide 77 by 7
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers as shown.
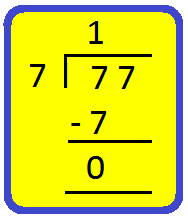
Step II: Divide the tens by 7.
We know 7 × 1 = 7.
Write 1 in tens place of the quotient and 7 below 7.
Subtract 7 from 7 to get 0.
Step III: Bring down 7 ones and divide it by 7.
We know 7 × 1 = 7.
Write 1 in the ones place of the quotient and 7 bellow 7.
Subtract 7 from 7 to get 0.
Thus, 77 ÷ 7 = 11
II: Dividing a 2-digit Number by a 1-Digit Number with Remainder:
1. Divide the following and verify the result
76 ÷ 6
(a) 7 > 6, so 7T will be divided by 6,
6 one is 6, so 1T is quotient
(b) 7 – 6 = 1, 6 is carried down, so 16 will, be divided by 6.
6 twos are 12, 6 threes are 18, so quotient will be 2.
(c) 16 - 12 = 4 is the remainder
(d) 6 × 12 + 4 = 72 + 4 = 76 (dividend)
Therefore, result is verified.
The quotient = 12
Remainder = 4
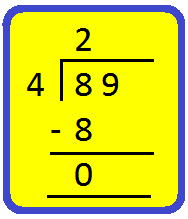
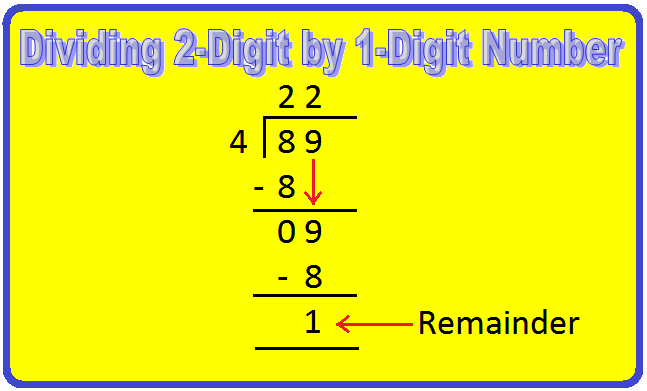
2. Divide 89 by 4.
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers as shown.
Step II: Divide the tens by 4.
Start by looking at the first number (tens place) in the dividend.
Find a number in the table of 4 less than or equal to 8
4 × 1 = 4,
4 × 2 = 8,
So, 2 is the required number.
4 × 2 = 8, write 2 in tens place of the quotient and 8 below 8.
Subtract the number you got by multiplying the divisor. from the number in the dividend.
Subtract 8 from 8 to get 0.
Step III: Divide the ones by 4.
Bring down the next digit (ones place), from the number in the dividend.
i.e., Bring down 9 ones and divide it by 4.
Repeat the same process again.
Find a number in the table of 4 less than or equal to 9
4 × 1 = 4,
4 × 2 = 8,
So, 2 is the required number.
4 × 2 = 8, write 2 in ones place of the quotient and 8 below 9.
Subtract 8 from 9 to get 1.
So, the quotient = 22 and remainder = 1.
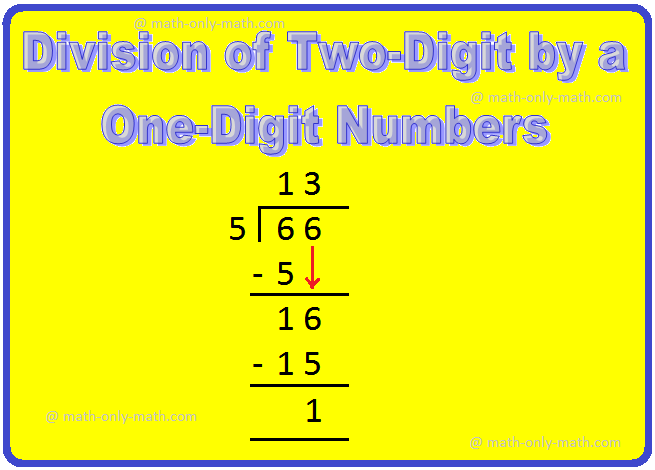
3. Divide 66 by 5 and verify the result.
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers.
Step II: Divide the tens by 5.
Start by looking at the first number (tens place) in the dividend.
Find a number in the table of 5 less than or equal to 6
5 × 1 = 5,
So, 1 is the required number.
5 × 1 = 5, write 1 in tens place of the quotient and 5 below 6.
Subtract the number you got by multiplying the divisor. from the number in the dividend.
Subtract 5 from 6 to get 1.
Step III: Bring down the next digit (ones place), from the number in the dividend.
i.e., Bring down 6 ones
The number is 16
Now and divide 16 by 5.
Repeat the same process again.
Find a number in the table of 5 less than or equal to 16
5 × 1 = 5,
5 × 2 = 10,
5 × 3 = 15,
So, 3 is the required number.
5 × 3 = 15, write 3 in ones place of the quotient and 15 below 16.
Subtract 15 from 16 to get 1.
So, the quotient = 13 and remainder = 1.
So, 66 is dividend,
5 is divisor,
3 is quotient,
1 is remainder.
Check: Dividend = Quotient × Divisor - Remainder
= 13 × 5 + 1
= 65 + 1
= 66 = Dividend
The same method is used when dividing larger numbers.
Worksheet on Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers:
1. Find the quotient and the remainder, using long division method:
(i) 40 ÷ 4
(ii) 36 ÷ 6
(iii) 54 ÷ 6
(iv) 50 ÷ 9
(v) 63 ÷ 8
answer:
1. (i) Quotient: 10; Remainder: 0
(ii) Quotient: 6 ; Remainder: 0
(iii) Quotient: 9 ; Remainder: 0
(iv) Quotient: 5 ; Remainder: 5
(v) Quotient: 7 ; Remainder: 7
2. Divide the following and check your answer using division algorithm:
(i) 46 ÷ 7
(ii) 89 ÷ 9
(iii) 65 ÷ 8
(iv) 35 ÷ 4
(v) 52 ÷ 6
Answer:
2. (i) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(ii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(iii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(iv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(v) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
3. Divide the following:
(i) 89 ÷ 4
(ii) 99 ÷ 9
(iii) 92 ÷ 7
(iv) 82 ÷ 2
(v) 66 ÷ 6
(vi) 46 ÷ 7
(vii) 89 ÷ 9
(viii) 65 ÷ 8
(ix) 35 ÷ 4
(x) 52 ÷ 6
(xi) 46 ÷ 7
(xii) 89 ÷ 9
(xiii) 65 ÷ 8
(xiv) 35 ÷ 4
(xv) 52 ÷ 6
Answer:
3. (i) Quotient: 22; Remainder: 1
(ii) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 0
(iii) Quotient: 13; Remainder: 1
(iv) Quotient: 41; Remainder: 0
(v) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 0
(vi) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(vii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(viii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(ix) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(x) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
(xi) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(xii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(xiii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(xiv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(xv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
4. Divide and check your answer:
(i) 89 ÷ 8
(ii) 45 ÷ 2
(iii) 92 ÷ 3
(iv) 64 ÷ 4
(v) 88 ÷ 5
(vi) 55 ÷ 7
(vii) 65 ÷ 8
(viii) 61 ÷ 6
(ix) 82 ÷ 6
(x) 94 ÷ 6
Answer:
4. (i) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 1
(ii) Quotient: 22; Remainder: 1
(iii) Quotient: 30; Remainder: 2
(iv) Quotient: 16; Remainder: 0
(v) Quotient: 17; Remainder: 3
(vi) Quotient: 7; Remainder: 6
(vii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(viii) Quotient: 10; Remainder: 1
(ix) Quotient: 13; Remainder: 4
(x) Quotient: 15; Remainder: 4
Related Concept
● Addition
● Check for Subtraction and Addition
● Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction
● Estimating Sums and Differences
● Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number
● Multiplication of a Number by a 3-Digit Number
● Word Problems on Multiplication
● Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division by 10 and 100 and 1000
● Division by Two-Digit Numbers
From Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Pictograph to Represent The Collected Data | Forming Pictograph | Math
May 07, 24 05:36 PM
Pictures or symbols are made in a pictograph to represent the collected data. So, we can say that a pictograph represents the data and gives information quickly and clearly. -
Examples of Pictographs |Pictorial Representation|Pictograph Questions
May 07, 24 05:27 PM
Some sample examples of pictographs or pictorial representation are shown, how the objects are used to give information regarding mathematical data. Read the pictograph and gather the information -
Mental Math on Time | 4th Grade Time Worksheet | Tricks | Techniques
May 07, 24 01:36 PM
In mental math on time, we will solve different types of problems on reading time to the nearest minutes, reading time to the exact minutes, use of a.m. and p.m., 24-hours clock, days in a year and ca… -
Telling Time in a.m. and p.m. | Antemeridian and Postmeridian|Examples
May 06, 24 05:54 PM
The clock shows time in 12 hour cycle. The first cycle of the hour hand completes at 12 o’clock midday or noon. The second cycle of the hour hand completes at 12 o’clock midnight. ‘a.m.’ and ‘p.m.’ ar… -
Different Ways of Reading Time | Many Ways to Read Time | Telling Time
May 06, 24 05:23 PM
What are the different ways of reading time? There are many ways to read time: (a) When hour-hand is exactly at any number and minute-hand is at 12, we read the time in full hours. If hour hand is at
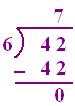
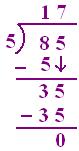

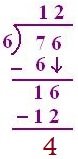






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.