Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Unlike Decimal Fractions
Unlike decimal fractions are discussed here.
We have learnt that the number of digits on the right of the decimal point tells us the number of decimal places in the given number. For example, 5.127 has 3 digits on the right of the decimal point, so it has 3 decimal places.
Decimal numbers having different number of decimal places are called unlike decimals. For example, 15.6, 15.06 and 15.106 are unlike decimals.
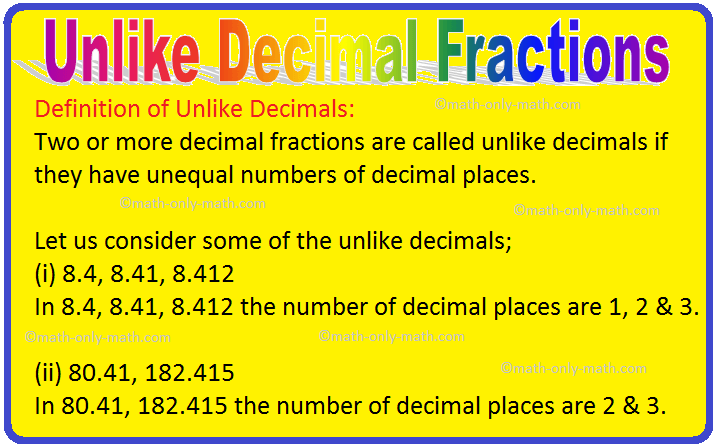
Definition of Unlike Decimals:
Two or more decimal fractions are called unlike decimals if they have unequal numbers of decimal places.
Let us consider some of the unlike decimals;
(i) 8.4, 8.41, 8.412
In 8.4, 8.41, 8.412 the number of decimal places are 1, 2 and 3.
(ii) 80.41, 182.415
In 80.41, 182.415 the number of decimal places are 2 and 3.
(iii) 0.129, 0.12, 0.1
In 0.129, 0.12, 0.1 the number of decimal places are 3, 2 and 1.
(iv) 1.0015, 0.001, 0.1
In 1.0015, 0.001, 0.1 the number of decimal places are 4, 3 and 1.
(v) 1.45, 32.001, 110.1
In 1.45, 32.001, 110.1 the number of decimal places are 2, 3 and 1.
(vi) 111.67, 160.9, 110.101
In 111.67, 160.9, 110.101 the number of decimal places are 2, 1 and 3.
We can convert set of unlike decimals into a set of like decimals or equivalent decimals by placing zeroes on the right of the decimal part. For example, to make 3.01 and 3.4 like decimals we put one zero to the right of the decimal part of 3.4 and write as 3.40. Now, both decimal numbers have two decimal places.
(vii) 0.1, 0.10, 0.100 are equivalent but unlike decimals, therefore unlike decimals may or may not be equivalent decimals.
● Decimal.
Expanded form of Decimal Fractions.
Changing Unlike to Like Decimal Fractions.
Comparison of Decimal Fractions.
Conversion of a Decimal Fraction into a Fractional Number.
Conversion of Fractions to Decimals Numbers.
Addition of Decimal Fractions.
Problems on Addition of Decimal Fractions
Subtraction of Decimal Fractions.
Problems on Subtraction of Decimal Fractions
Multiplication of a Decimal Numbers.
Multiplication of a Decimal by a Decimal.
Properties of Multiplication of Decimal Numbers.
Problems on Multiplication of Decimal Fractions
Division of a Decimal by a Whole Number.
Division of Decimal Fractions by Multiples.
Division of a Decimal by a Decimal.
Division of a whole number by a Decimal.
Properties of Division of Decimal Numbers
Problems on Division of Decimal Fractions
Conversion of fraction to Decimal Fraction.
5th Grade Numbers Page
5th Grade Math Problems
From Unlike Decimal Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.