Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Properties of Division
The properties of division are discussed here:
1. Division by 1 Property:
If we divide a number by 1 the quotient is the number itself.
In other words, when any number is divided by 1, we always get the number itself as the quotient.
When any number is divided by 1, we always get the number itself.
For example:
(i) 7542 ÷ 1 = 7542
(ii) 372 ÷ 1 = 372
(iii) 1522 ÷ 1 = 1522
(iv) 1502 ÷ 1 = 1502
(v) 34 ÷ 1 = 34
(vi) 16 ÷ 1 = 16
(v) 1084 ÷ 1 = 1084
(vi) 1745 ÷ 1 = 1745
(vii) 28456 ÷ 1 = 28456
(viii) 34 ÷ 1 = 34
(ix) 16 ÷ 1 = 16
Dividing a number by 1 gives the number itself as the quotient.
Example:
5 ÷ 1 = 5 as 5 × 1 = 5,
8 ÷ 1 = 8 as 8 × 1 = 8, etc.
When a number is divided by 1, it gives the number itself.
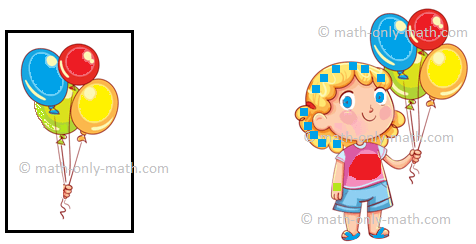
4 balloons are given to 1 child.
|
4 ÷ 1 = 4 |
2. Division by itself Property:
If we divide a number by the number itself, the quotient is 1.
In other words, when any number is divided by the number itself, we always get 1 as the quotient.
When any number is divided by the number itself, we always get 1 as the quotient.
For example:
(i) 275 ÷ 275 = 1
(ii) 105 ÷ 105 = 1
(iii) 572 ÷ 572 = 1
(iv) 1027 ÷ 1027 = 1
(v) 1426 ÷ 1426 = 1
(vi) 1654 ÷ 1654 = 1
(vii) 18520 ÷ 18520 = 1
(viii) 7 ÷ 7 = 1
(ix) 24 ÷ 24 = 1
When a number is divided by itself, the answer is 1.
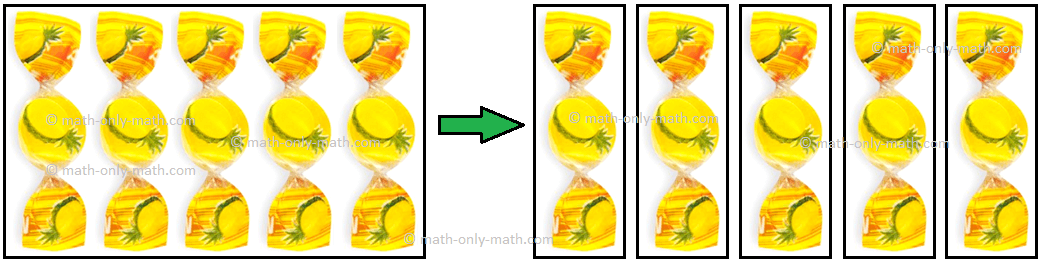
- Divide 5 candies among 5 children.
|
5 ÷ 5 = 1 |
Each child gets 1 candy. |
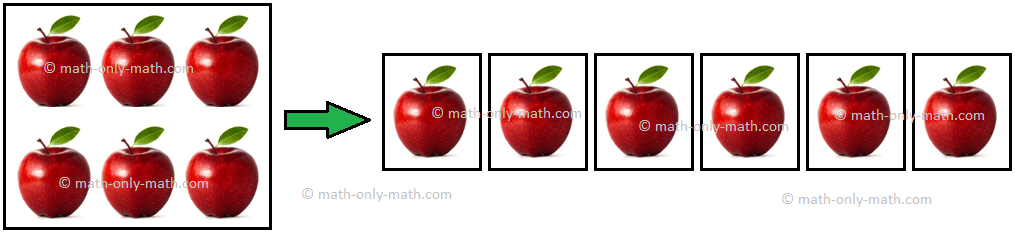
- Divide 6 apples among 6 children.
|
6 ÷ 6 = 1 |
Each child gets 1 apple. |
Dividing a number by itself, gives 1 as the quotient.
Example:
If we divide six flowers among six vases, how many flowers can we put in each vase?
We put 1 flower in each vase. So, 6 ÷ 6 = 1 because 6 × 1 = 6
3. Division any Number by 0 Property:
Division of a number by 0 is meaningless.
In other words,
Division by 0 is meaningless.
For example:
(i) 15 ÷ 0 = meaningless
(ii) 35 ÷ 0 = no meaning
(iii) 65 ÷ 0 = no meaning
(iv) 29 ÷ 0 = no meaning
(v) 47 ÷ 0 = no meaning
(vi) 86 ÷ 0 = no meaning
Note: The divisor can never be zero. Division by zero is not possible.
4. Division of 0 by any Number Property:
0 divided by a number gives 0 as the quotient.
In other words, when 0 is divided by any number, we always get 0 as the quotient.
Dividing zero by a number gives zero as the quotient.
0 ÷ 5 = 0 because 5 × 0 = 0
For example:
(i) 0 ÷ 25 = 0
(ii) 0 ÷ 100 = 0
(iii) 0 ÷ 4255 = 0
(iv) 0 ÷ 15246 = 0
(v) 0 ÷ 2 = 0
(vi) 0 ÷ 75 = 75
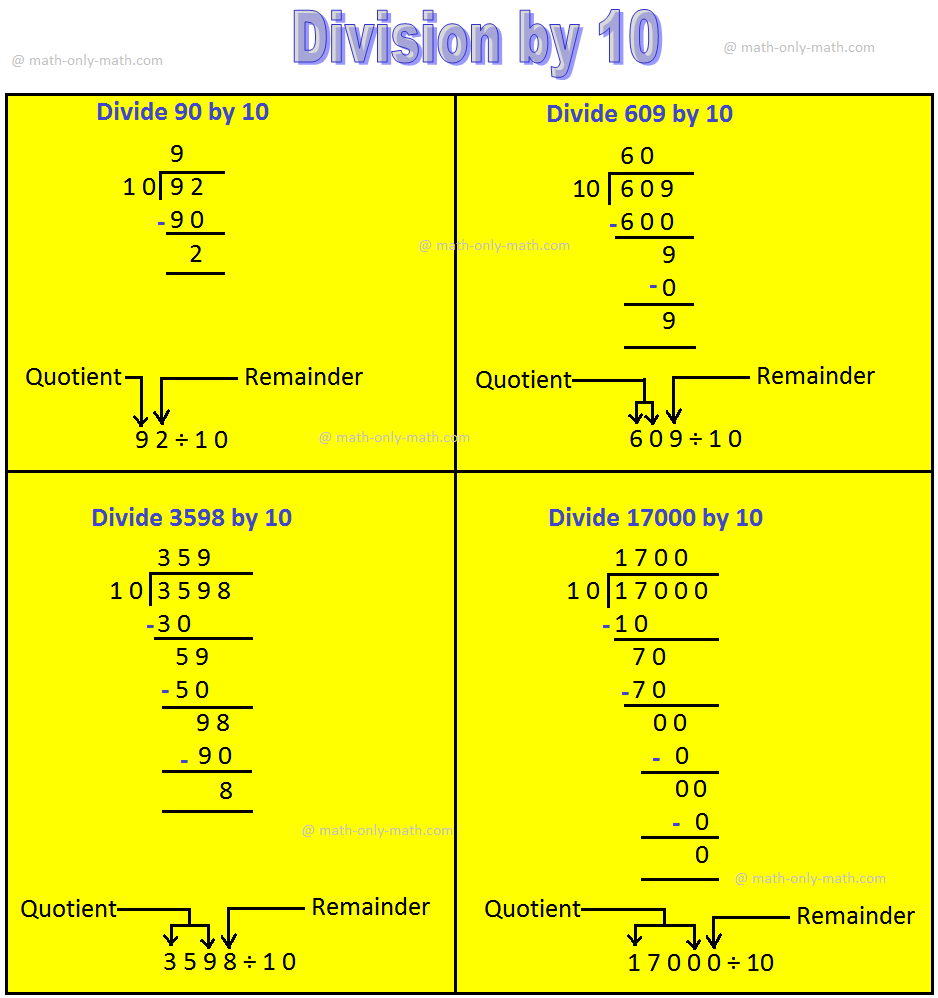
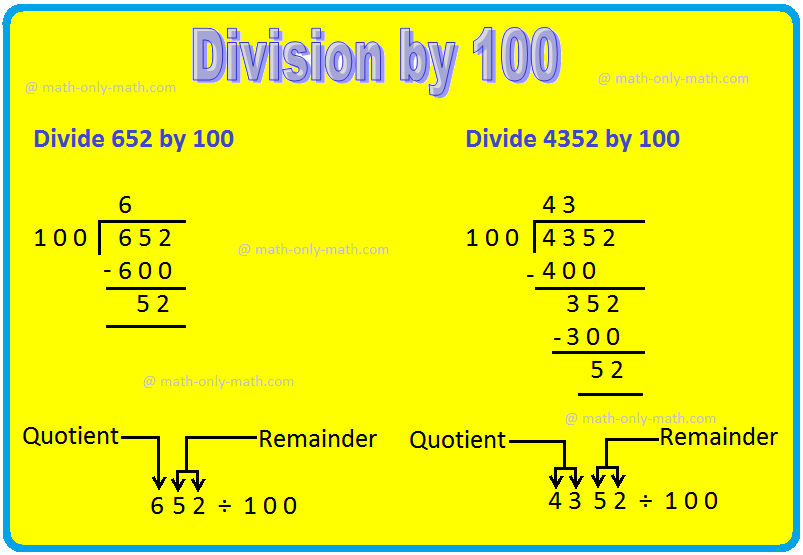
5. Division by 10, 100 and 1000 Property:
For example:
(i) When a number is divide by 10, the digit in the once place is the remainder.
867 ÷ 10;
Quotient = 86 and Remainder =7.
What do we observe?
We see that when a number (dividend) is divided by 10 the quotient is obtained by removing the ones digit from the number (dividend) and the digit at ones place is the remainder.
(ii) When a number is divided by 100, the number formed by the tens and once place is the remainder.
2764 ÷ 100;
Quotient = 27 and Remainder = 64.
What do we observe?
We sew that when a number (dividend) is divided by 100 the quotient is obtained by removing the last two digits on the extreme right of the number (dividend). The number formed by these last to digits is the remainder.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Division by 1 Property?
Ans: When divisor is 1, the quotient is the same as the dividend.
For Example:
5 ÷ 1 = 5; 15 ÷ 1 = 15; 50 ÷ 1 = 50.
2. What is Division by itself Property?
Ans: When the divisor and the dividend are the same non-zero numbers, the quotient is 1.
For Example:
7 ÷ 7 = 1; 13 ÷ 13 = 1; 70 ÷ 70 = 1.
3. What is Division of 0?
Ans: When the dividend is 0, the quotient is 0.
For Example:
0 ÷ 6 = 0; 0 ÷ 19 = 0; 0 ÷ 81 = 0
4. What is Division By Zero?
Ans: The divisor can never be 0. Or, division by 0 is meaningless.
For Example:
20 ÷ 0 = no meaning / not defined
52 ÷ 0 = no meaning / not defined
75 ÷ 0 = no meaning / not defined
Worksheet on Properties of Division:
1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) 6 ÷ 6 = ……….
(ii) 5 ÷ 1 = ……….
(iii) 3 ÷ 3 = ……….
(iv) 9 ÷ 1 = ……….
(v) 8 ÷ 8 = ……….
(vi) 10 ÷ 1 = ……….
Answer:
1. (i) 1
(ii) 5
(iii) 1
(iv) 9
(v) 1
(vi) 10
2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) 23 ÷ 23 = ………
(ii) 21 ÷ ……… = 21
(iii) 15 ÷ 1 = ………
(iv) ……… ÷ 15 = 0
(v) 0 ÷ 12 = ………
(vi) 8 ÷ ……… = 1
(vii) 65 ÷ 65 = ………
(viii) ……… ÷ 12 = 1
(ix) 8 ÷ 1 = _____
(x) 6 ÷ 6 = _____
(xi) 0 ÷ 10 = _____
(xii) 21 ÷ 21 = _____
(xiii) 12 ÷ _____ = 1
(xiv) 21 ÷ 1 = _____
(xv) _____ ÷ 12 = 0
(xvi) 12 ÷ 0 = _____
Answer:
2. (i) 1
(ii) 1
(iii) 15
(iv) 0
(v) 0
(vi) 8
(vii) 1
(viii) 12
(ix) 8
(x) 1
(xi) 0
(xii) 1
(xiii) 12
(xiv) 21
(xv) 0
(xvi) undefined / meaningless
● Subtraction Of Whole Numbers.
● Multiplication Of Whole Numbers.
● Properties Of Multiplication.
From Properties of Division to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.