Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates
Here we will learn to find the relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates.
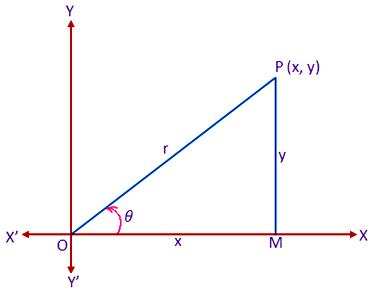
Let XOX’ and YOY’ be a set of rectangular Cartesian axes of polar Co-ordinates through the origin O. now, consider a polar Co-ordinates system whose pole and initial line coincide respectively with the origin O and the positive x-axis of the Cartesian system. Let P be any point on the plane whose Cartesian and polar Co-ordinates are (x, y) and (r, θ) respectively. Draw PM perpendicular to OX. Then we have,
OM = x, PM = y, OP = r and < MOP = θ
Now, from the right-angled triangle MOP we get,
x/r = cos θ or, x = r cos θ …… (1)
and
y/r = sin θ or, y = r sin …… (2)
Using (1) and (2) we can find Cartesian Co-ordinates (x, y) of the point whose polar Co-ordinates (r, θ) are given.
Again, from the right angled triangle OPM we get,
r² = x² + y²
or, r = √(x² + y²) …… (3)
and tan θ = y/x or, θ = tan\(^{-1}\) y/x ……… (4)
Using (3) and (4) we can find the polar Co-ordinates (r, θ) of the points whose Cartesian Co-ordinates (x, y) are given.
Note:
If the Cartesian Co-ordinates (x, y) of a point are given then to find the value of the vectorial angle θ by the transformation equation θ = tan\(^{-1}\) y/x we should note the quadrant in which the point (x, y) lies.
Examples on the relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates.
1. The cartesian co-ordinates of a point are (- 1, -√3); find its polar co-ordinates.
Solution:
If the pole and initial line of the polar system coincide with the origin and positive x-axis respectively of the cartesian system and the cartesian and polar co-ordinates of a point are ( x, y ) and ( r, θ ) respectively, then
x = r cos θ and y= r sin θ.
In the given problem, x = -1 and y = -√3
Therefore, r cos θ = -1 and r sin θ = -√3
Therefore, r² Cos² θ + r² sin² = (- 1)² + (-√3)²
And tan θ = (r sin θ)/(r cos θ) = (-√3)/(-1) = √3 = tan π/3
Or, tan θ =tan(π+ π/3) [Since, the point (- 1, - √3) lise in the third quadrant]
Or, tan θ = tan 4π/3
Therefore, θ = 4π/3
Therefore, the polar co-ordinates of the point (- 1, - √3) are (2, 4π/3).
2. Find the cartesian co-ordinates of the point whose polar co-ordinates are (3, - π/3).
Solution:
Let (x, y) be the cartesian co-ordinates of the point whose polar co-ordinates are (3, - π/3). Then,
x= r cos θ = 3 cos (- π/3) = 3 cos π/3 = 3 ∙ 1/2 = 3/2
and y = r sin θ = 3 sin (- π/3) = 3 sin π/3 = -(3√3)/2.
Therefore, the required cartesian co-ordinates of the point (3, -π/3) are (3/2, -(3√3)/2)
3. Transfer, the cartesian form of equation of the curve x² - y² = 2ax to its polar form.
Solution:
Let OX and OY be the rectangular cartesian axes and the pole and the initial line of the polar system coincide with O and OX respectively. If (x, y) be the cartesian co-ordinates of the point whose polar co-ordinates are (r, θ), then we have,
x = r cos θ and y = r sin θ.
Now, x² - y² = 2ax
or, r² cos² θ - r² sin² θ = 2a.r cos θ
or, r² (cos² θ - sin² θ) = 2ar cos θ
or, r cos 2 θ = 2a cos θ (Since, r ≠0)
which is the required polar form of the given cartesian equation.
4. Transform the polar form of equation \(r^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = \(a^{\frac{1}{2}}\)
cos θ/2 to its cartesian form.
Solution:
Let OX and OY be the rectangular cartesian axes and the pole and the initial line of the polar system coincide with O and OX respectively. If (x, y) be the cartesian co-ordinates of the point whose polar co-ordinates are (r, θ), then we have,
x = r cos θ and y = r sin θ.
Clearly, x² + y²
= r² cos² θ + r² sin² θ
= r²
Now, \(r^{\frac{1}{2}}\) = \(a^{\frac{1}{2}}\) cos θ/2
or, r = a cos² θ/2 (squaring both sides)
or, 2r = a ∙ 2 cos² θ/2
or, 2r = = a(1 + cosθ); [Since, cos² θ/2 = 1 + cosθ]
or, 2r² = a(r + r cosθ) [multiplying by r (since, r ≠0)]
or, 2(x² + y ²) = ar + ax [r² = x² + y² and r cos θ = x]
or, 2x² + 2y² - ax = ar
or, (2x² + 2y² - ax)² = a²r² [Squaring both sides]
or, (2x² + 2y² - ax)² = a² (x² + y²),
which is the required cartesian form of the given polar form of equation.
● Co-ordinate Geometry
- What is Co-ordinate Geometry?
- Rectangular Cartesian Co-ordinates
- Polar Co-ordinates
- Relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates
- Distance between Two given Points
- Distance between Two Points in Polar Co-ordinates
- Division of Line Segment: Internal & External
- Area of the Triangle Formed by Three co-ordinate Points
- Condition of Collinearity of Three Points
- Medians of a Triangle are Concurrent
- Apollonius' Theorem
- Quadrilateral form a Parallelogram
- Problems on Distance Between Two Points
- Area of a Triangle Given 3 Points
- Worksheet on Quadrants
- Worksheet on Rectangular – Polar Conversion
- Worksheet on Line-Segment Joining the Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between Two Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between the Polar Co-ordinates
- Worksheet on Finding Mid-Point
- Worksheet on Division of Line-Segment
- Worksheet on Centroid of a Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Co-ordinate Triangle
- Worksheet on Collinear Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Polygon
- Worksheet on Cartesian Triangle
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.