Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Polar Co-ordinates
What is Polar Co-ordinates?
Besides Cartesian co-ordinate system we have several other methods for locating position of a point on a plane. Of all these system we shall make here a brief discussion on Polar Co-ordinates only. Polar Co-ordinates are widely used in higher mathematics as well as in other branches of science.
In polar co-ordinate system the position of a point on the reference plane is uniquely determined referred to a fixed point on the plane and a half line drawn through the fixed point. The fixed point is called the Pole or Origin and the half line drawn through the pole is called the Initial Line.
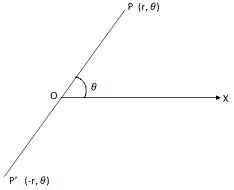
Let OX be the initial line drawn through the pole O on the plane of reference. Take any point P on the plane and join OP .
If OP = r and ∠XOP = θ then the real numbers r and θ are together called the Polar Co-ordinates of P and denoted by (r, θ); here OP. If OP = r and Polar Co-ordinates of P and denoted by (r, θ); here OP = r is called the Radius Vector and ∠XOP = θ, the Vectorial Angle of P. the angle θ is measured by the method of measurement of trigonometrical angle i.e., θ is taken to be positive when it is measured in the anti-clockwise sense from the initial line and negative when it is measured in the clockwise sense from the initial line.
By convection, to represent the polar co-ordinate of a point we first write the radius vector (r) and then the vectorial angle (θ) and they are put together in braces putting a comma between them.
Note:
(i) for given values of r and θ we shall get one and only one point on the reference plane; conversely, for a given point on the plane r possesses a definite finite value but θ can have infinite number of value (viz ., θ, 2π + θ, 4π + θ,…….etc.).
(ii) The polar Co-ordinates of the pole are assumed to be (0, 0).
(iii) If the sense of radius vector is taken into account then the value of r may be negative. Thus, if the direction from O to P is taken as positive then the direction from P to O will be negative. Hence, if the points P, O, P’ are collinear such that OP = OP’ = r and ∠XOP = θ then the polar co-ordinates of P and P' are (r, θ) and (-r, θ) respectively.
However, in practice, it is convenient to take both the radius vector (r) and the vectorial angle (θ) as positive.
(iv) Remembering the rules regarding the signs of r and θ we can represent the polar co-ordinate of P in following different ways:
(r, θ); (-r, π + θ); [r, -(2π - θ)]; [-r, -(π - θ)].
● Co-ordinate Geometry
- What is Co-ordinate Geometry?
- Rectangular Cartesian Co-ordinates
- Polar Co-ordinates
- Relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates
- Distance between Two given Points
- Distance between Two Points in Polar Co-ordinates
- Division of Line Segment: Internal & External
- Area of the Triangle Formed by Three co-ordinate Points
- Condition of Collinearity of Three Points
- Medians of a Triangle are Concurrent
- Apollonius' Theorem
- Quadrilateral form a Parallelogram
- Problems on Distance Between Two Points
- Area of a Triangle Given 3 Points
- Worksheet on Quadrants
- Worksheet on Rectangular – Polar Conversion
- Worksheet on Line-Segment Joining the Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between Two Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between the Polar Co-ordinates
- Worksheet on Finding Mid-Point
- Worksheet on Division of Line-Segment
- Worksheet on Centroid of a Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Co-ordinate Triangle
- Worksheet on Collinear Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Polygon
- Worksheet on Cartesian Triangle
From Polar Co-ordinates to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.