Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Apollonius' Theorem
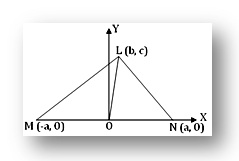
Apollonius' theorem is proved by using co-ordinate geometry. Proof of this geometrical property is discussed with the help of step-by-step explanation along with a clear diagram.
Statement of the Theorem: If O be the mid-point of the side MN of the triangle LMN, then LM² + LN² = 2(LO² + MO²).
Proof: Let us choose origin of rectangular Cartesian co-ordinates at O and x-axis along the side MN and OY as the y – axis . If MN = 2a then the co-ordinates of M and N are (- a, 0) and (a, 0) respectively. Referred to the chosen axes if the co-ordinates of L be (b, c) then
LO² = (b - 0)² + (C - 0)² , [Since, co- ordinates of O are (0, 0)]
= b² + c²;
MO² = (- a - 0)² + (0 – 0)² = a²
LM² = (b + a) ² + (c – 0)² = (a + b)² + c²
And LN² = (b - a) ² + (c - 0) ² = (a - b)² + c²
Therefore, LM² + LN² = (a + b) ² + c² + (b - a)² + c²
= 2(a² + b²) + 2c²
= 2a² + 2(b² + c²)
= 2MO² + 2LO²
= 2(MO² + LO²).
= 2(LO² + MO²). Proved.
● Co-ordinate Geometry
- What is Co-ordinate Geometry?
- Rectangular Cartesian Co-ordinates
- Polar Co-ordinates
- Relation between Cartesian and Polar Co-Ordinates
- Distance between Two given Points
- Distance between Two Points in Polar Co-ordinates
- Division of Line Segment: Internal & External
- Area of the Triangle Formed by Three co-ordinate Points
- Condition of Collinearity of Three Points
- Medians of a Triangle are Concurrent
- Apollonius' Theorem
- Quadrilateral form a Parallelogram
- Problems on Distance Between Two Points
- Area of a Triangle Given 3 Points
- Worksheet on Quadrants
- Worksheet on Rectangular – Polar Conversion
- Worksheet on Line-Segment Joining the Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between Two Points
- Worksheet on Distance Between the Polar Co-ordinates
- Worksheet on Finding Mid-Point
- Worksheet on Division of Line-Segment
- Worksheet on Centroid of a Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Co-ordinate Triangle
- Worksheet on Collinear Triangle
- Worksheet on Area of Polygon
- Worksheet on Cartesian Triangle
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Apollonius' Theorem to HOME PPAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.