Circle Passes through the Origin and Centre Lies on x-axis
We will learn how to find the equation of a circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis.
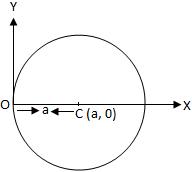
The equation of a circle with centre at (h, k) and radius equal to a, is (x - h)\(^{2}\) + (y - k)\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\).
When the circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis i.e., h = a and k = 0.
Then the equation (x - h)\(^{2}\) + (y - k)\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\) becomes (x - a)\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\)
If a circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis then the abscissa will be equal to the radius of the circle and the y co-ordinate of the centre will be zero. Hence, the equation of the circle will be of the form:
(x - a)\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\)
⇒ x\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) - 2ax = 0
Solved example on
the central form of the equation of a circle passes through the origin and
centre lies on x-axis:
1. Find the equation of a circle passes through the origin and centre lies on y-axis at (0, -2).
Solution:
Centre of the lies on y-axis at (0, -2)
Since, circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis then the abscissa will be equal to the radius of the circle and the y co-ordinate of the centre will be zero.
The required equation of the circle passes through the origin and centre lies on y-axis at (0, 2) is
(x + 7)\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) = (-7)\(^{2}\)
⇒ x\(^{2}\) + 14x + 49 + y\(^{2}\) = 49
⇒ x\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) + 14x = 0
2. Find the equation of a circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis at (12, 0).
Solution:
Centre of the lies on x-axis at (12, 0)
Since, circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis then the abscissa will be equal to the radius of the circle and the y co-ordinate of the centre will be zero.
The required equation of the circle passes through the origin and centre lies on x-axis at (12, 0) is
(x - 12)\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) = 12\(^{2}\)
⇒ x\(^{2}\) - 24x + 144 + y\(^{2}\) = 144
⇒ x\(^{2}\) + y\(^{2}\) - 24x = 0
● The Circle
- Definition of Circle
- Equation of a Circle
- General Form of the Equation of a Circle
- General Equation of Second Degree Represents a Circle
- Centre of the Circle Coincides with the Origin
- Circle Passes through the Origin
- Circle Touches x-axis
- Circle Touches y-axis
- Circle Touches both x-axis and y-axis
- Centre of the Circle on x-axis
- Centre of the Circle on y-axis
- Circle Passes through the Origin and Centre Lies on x-axis
- Circle Passes through the Origin and Centre Lies on y-axis
- Equation of a Circle when Line Segment Joining Two Given Points is a Diameter
- Equations of Concentric Circles
- Circle Passing Through Three Given Points
- Circle Through the Intersection of Two Circles
- Equation of the Common Chord of Two Circles
- Position of a Point with Respect to a Circle
- Intercepts on the Axes made by a Circle
- Circle Formulae
- Problems on Circle
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Circle Passes through the Origin and Centre Lies on x-axis to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Interpreting a Pictograph | Information Regarding the Pictograph |Math
May 08, 24 09:23 AM
In interpreting a pictograph, we get a lot of information regarding the pictograph items. The following examples may illustrate the interpretation of pictographs. -
Pictograph to Represent The Collected Data | Forming Pictograph | Math
May 07, 24 05:36 PM
Pictures or symbols are made in a pictograph to represent the collected data. So, we can say that a pictograph represents the data and gives information quickly and clearly. -
Examples of Pictographs |Pictorial Representation|Pictograph Questions
May 07, 24 05:27 PM
Some sample examples of pictographs or pictorial representation are shown, how the objects are used to give information regarding mathematical data. Read the pictograph and gather the information -
Mental Math on Time | 4th Grade Time Worksheet | Tricks | Techniques
May 07, 24 01:36 PM
In mental math on time, we will solve different types of problems on reading time to the nearest minutes, reading time to the exact minutes, use of a.m. and p.m., 24-hours clock, days in a year and ca… -
Telling Time in a.m. and p.m. | Antemeridian and Postmeridian|Examples
May 06, 24 05:54 PM
The clock shows time in 12 hour cycle. The first cycle of the hour hand completes at 12 o’clock midday or noon. The second cycle of the hour hand completes at 12 o’clock midnight. ‘a.m.’ and ‘p.m.’ ar…




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.