Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problems on Trigonometric Ratios
Some trigonometric solutions based problems on trigonometric ratios are shown here with the step-by-step explanation.
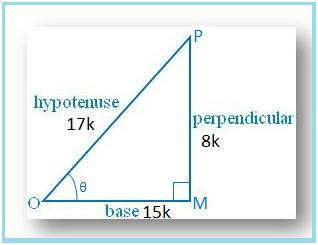
1. If sin θ = 8/17, find other trigonometric ratios of <θ.
Solution:
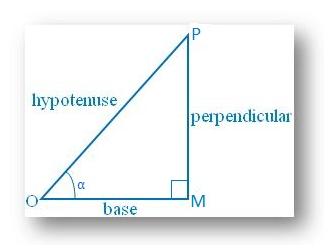
Let us draw a ∆ OMP in which ∠M = 90°.
Then sin θ = MP/OP = 8/17.
Let MP = 8k and OP = 17k, where k is positive.
By Pythagoras’ theorem, we get
OP2 = OM2 + MP2
⇒ OM2 = OP2 – MP2
⇒ OM2 = [(17k)2 – (8k)2]
⇒ OM2 = [289k2 – 64k2]
⇒ OM2 = 225k2
⇒ OM = √(225k2)
⇒ OM = 15k
Therefore, sin θ = MP/OP = 8k/17k = 8/17
cos θ = OM/OP = 15k/17k = 15/17
tan θ = Sin θ/Cos θ = (8/17 × 17/15) = 8/15
csc θ = 1/sin θ = 17/8
sec θ = 1/cos θ = 17/15 and
cot θ = 1/tan θ = 15/8.
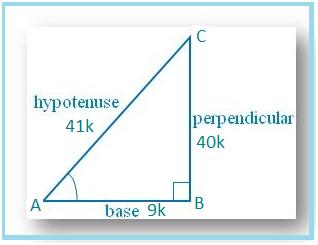
2. If Cos A = 9/41, find other trigonometric ratios of ∠A.
Solution:
Let us draw a ∆ ABC in which ∠B = 90°.
Then cos θ = AB/AC = 9/41.
Let AB = 9k and AC = 41k, where k is positive.
By Pythagoras’ theorem, we get
AC2 = AB2 + BC2⇒ BC2 = AC2 – AB2
⇒ BC2 = [(41k)2 – (9k)2]
⇒ BC2 = [1681k2 – 81k2]
⇒ BC2 = 1600k2
⇒ BC = √(1600k2)
⇒ BC = 40k
Therefore, sin A = BC/AC = 40k/41k = 40/41
cos A = AB/AC = = 9k/41k = 9/41
tan A = Sin A/Cos A = (40/41 × 41/9) = 40/9
csc A = 1/sin A = 41/40
sec A = 1/cos A = 41/9 and
cot A = 1/tan A = 9/40.
3. Show that the value of sin θ and cos θ cannot be more than 1.
Solution:
We know, in a right angle triangle the hypotenuse is the longest side.
sin θ = perpendicular/hypotenuse = MP/OP < 1 since perpendicular cannot be greater than hypotenuse; sin θ cannot be more than 1.
Similarly, cos θ = base/hypotenuse = OM/OP < 1 since base cannot be greater than hypotenuse; cos θ cannot be more than 1.
4. Is that possible when A and B be acute angles, sin A = 0.3 and cos B = 0.7?
Solution:
Since A and B are acute angles, 0 ≤ sin A ≤ 1 and 0 ≤ cos B ≤ 1, that means the value of sin A and cos B lies between 0 to 1. So, it is possible that sin A = 0.3 and cos B = 0.7
5. If 0° ≤ A ≤ 90° can sin A = 0.4 and cos A = 0.5 be possible?
Solution:
We know that sin2A + cos2A = 1Now put the value of sin A and cos A in the above equation we get;
(0.4)2 + (0.5)2 = 0.41 which is ≠ 1, sin A = 0.4 and cos A = 0.5 cannot be possible.
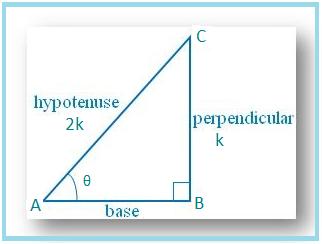
6. If sin θ = 1/2, show that (3cos θ - 4 cos3 θ) =0.
Solution:
Let us draw a ∆ ABC in which ∠B = 90° and ∠BAC = θ.
Then sin θ = BC/AC = 1/2.
Let BC = k and AC = 2k, where k is positive.
By Pythagoras’ theorem, we get
AC2 = AB2 + BC2⇒ AB2 = AC2 – BC2
⇒ AB2 = [(2k)2 – k2]
⇒ AB2 = [4k2 – k2]
⇒ AB2 = 3k2
⇒ AB = √(3k2)
⇒ AB = √3k.
Therefore, cos θ = AB/AC = √3k/2k = √3/2
Now, (3cos θ - 4 cos3 θ)
= 3√3/2 - 4 ×(√3/2)3
= 3√3/2 - 4 × 3√3/8
= 3√3/2 - 3√3/2
= 0
Hence, (3cos θ - 4 cos<sup>3</sup> θ) = 0.
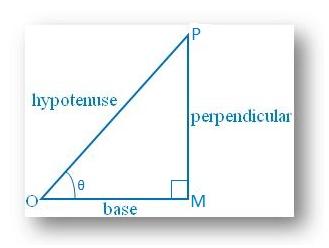
7. Show that sin α + cos α > 1 when 0° ≤ α ≤ 90°
Solution:
From the right triangle MOP,
Sin α = perpendicular/ hypotenuse
Cos α = base/ hypotenuse
Now, Sin α + Cos α
= perpendicular/ hypotenuse + base/ hypotenuse
= (perpendicular + base)/hypotenuse, which is > 1, Since we know that the sum of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
8. If cos θ = 3/5, find the value of (5csc θ - 4 tan θ)/(sec θ + cot θ)
Solution:
Let us draw a ∆ ABC in which ∠B = 90°.
Let ∠A = θ°
Then cos θ = AB/AC = 3/5.
Let AB = 3k and AC = 5k, where k is positive.
By Pythagoras’ theorem, we get
AC2 = AB2 + BC2⇒ BC2 = AC2 – AB2
⇒ BC2 = [(5k)2 – (3k)2]
⇒ BC2 = [25k2 – 9k2]
⇒ BC2 = 16k2
⇒ BC = √(16k2)
⇒ BC = 4k
Therefore, sec θ = 1/cos θ = 5/3
tan θ = BC/AB =4k/3k = 4/3
cot θ = 1/tan θ = 3/4 and
csc θ = AC/BC = 5k/4k = 5/4
Now (5csc θ -4 tan θ)/(sec θ + cot θ)
= (5 × 5/4 - 4 × 4/3)/(5/3 + 3/4)
= (25/4 -16/3)/(5/3 +3/4)
= 11/12 × 12/29
= 11/29
9. Express 1 + 2 sin A cos A as a perfect square.
Solution:
1 + 2 sin A cos A
= sin2 A + cos2 A + 2sin A cos A, [Since we know that sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1]= (sin A + cos A)2
10. If sin A + cos A = 7/5 and sin A cos A =12/25, find the values of sin A and cos A.
Solution:
sin A + cos A = 7/5
⇒ cos A = 7/5 - sin θ
Now from sin θ/cos θ = 12/25
We get, sin θ(7/5 - sin θ) = 12/25
or, 7 sin θ – 5 sin2 θ = 12/5or, 35 sin θ - 35 sin2 θ = 12
or, 25sin2 θ -35 sin θ + 12 = 0
or, 25 sin2 θ -20 sin θ - 15 sin θ + 12 = 0
or, 5 sin θ(5 sin θ - 4) - 3(5 sin θ - 4) = 0
or, (5 sin θ - 3) (5 sin θ - 4) = 0
⇒ (5 sin θ - 3) = 0 or, (5 sin θ - 4) = 0
⇒ sin θ = 3/5 or, sin θ = 4/5
When sin θ = 3/5, cos θ = 12/25 × 5/3 = 4/5
Again, when sin θ = 4/5, cos θ = 12/25 × 5/4 = 3/5
Therefore, sin θ =3/5, cos θ = 4/5
or, sin θ =4/5, cos θ = 3/5.
11. If 3 tan θ = 4, evaluate (3sin θ + 2 cos θ)/(3sin θ - 2cos θ).
Solution: Given,
3 tan θ = 4
⇒ tan θ = 4/3
Now,
(3sin θ + 2 cos θ)/(3sin θ - 2cos θ)
= (3 tan θ + 2)/(3 tan θ - 2), [dividing both numerator and denominator by cos θ]
= (3 × 4/3 + 2)/(3 × 4/3 -2), putting the value of tan θ = 4/3
= 6/2
= 3.
12. If (sec θ + tan θ)/(sec θ - tan θ) = 209/79, find the value of θ.
Solution: (sec θ + tan θ)/(sec θ - tan θ) = 209/79
⇒ [(sec θ + tan θ) - (sec θ - tan θ)]/[(sec θ + tan θ) + (sec θ - tan θ)] = [209 – 79]/[209 + 79], (Applying componendo and dividendo)
⇒ 2 tan θ/2 sec θ =130/288
⇒ sin θ/cos θ × cos θ = 65/144
⇒ sin θ = 65/144.
13. If 5 cot θ = 3, find the value of (5 sin θ - 3 cos θ)/(4 sin θ + 3 cos θ).
Solution:
Given 5 cot θ = 3
⇒ cot θ = 3/5
Now (5 sin θ - 3 cos θ)/(4 sin θ + 3 cos θ)
= (5 - 3 cot θ)/(4 sin θ + 3 cot θ), [dividing both numerator and denominator by sin θ]
= (5 - 3 × 3/5)/(4 + 3 × 3/5)
= (5 - 9/5)/(4 + 9/5)
= (16/5 × 5/29)
= 16/29.
Solution:
⇒ sin2 θ -3 sin θ + 2 = 0
⇒ sin2 θ – 2 sin θ – sin θ + 2 = 0
⇒ sin θ(sin θ - 2) - 1(sin θ - 2) = 0
⇒ (sin θ - 2)(sin θ - 1) = 0
⇒ (sin θ - 2) = 0 or, (sin θ - 1) = 0
⇒ sin θ = 2 or, sin θ = 1
So, value of sin θ can’t be greater than 1,
Therefore sin θ = 1
⇒ θ = 90°
Relations Between the Trigonometric Ratios
Problems on Trigonometric Ratios
Reciprocal Relations of Trigonometric Ratios
Problems on Trigonometric Identities
Elimination of Trigonometric Ratios
Eliminate Theta between the equations
Verify Trigonometric Identities
From Problems on Trigonometric Ratios to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.