Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Subtraction of Length
The process of subtraction of units of length is exactly similar to that of subtraction of ordinary numbers.
Learn how the values of length are arranged in different columns for the subtraction of length.
1. Subtract 12 m 36 cm from 48 m 57 cm
Solution:
Case 1:
Minuend and subtrahend are both converted into smaller units.
12 m 36 cm = (12 × 100) cm + 36 cm = (1200 + 36) cm = 1236 cm
48 m 57 cm = (48 × 100) cm + 57 cm = (4800 + 57) cm = 4857 cm
Now subtract
48 m 57 cm = 4857 cm
- 12 m 36 cm = - 1236 cm
3621 cm
= 3600 cm + 21 cm
= 36 m 21 cm
Therefore, 48 m 57 cm - 12 m 36 cm = 36 m 21 cm
Case 2:
As minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the subtrahend. Then m and cm are arranged in different columns.
Now subtract
m cm
48 57
- 12 36
36 21
(i) Subtracting cm, 57 cm - 36 cm = 21 cm.
It is placed under cm column.
(ii) Subtracting m, 48 m - 12 m = 36 m.
It is placed under m column.
Hence, difference = 36 m 21 cm
2. Subtract 37 m 50 cm from 53 m 30 cm.
Solution:
Case 1:
Minuend and subtrahend are both converted into smaller units.
53 m 30 cm = (53 × 100) cm + 33 cm = (5300 + 30) cm = 5330 cm
37 m 50 cm = (37 × 100) cm + 50 cm = (3700 + 50) cm = 3750 cm
Now subtract
5330 cm
- 3750 cm
1580 cm
= 1500 cm + 80 cm
= 15 m 80 cm
Therefore, 53 m 30 cm - 37 m 50 cm = 15 m 80 cm.
Case 2:
As minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the subtrahend. Then m and cm are arranged in different columns. Minuend 53 m 30 cm is placed above subtrahend 37 m 50 cm.
m cm
1 100
53 30
- 37 50
15 80
(i) 50 cm > 30 cm. So, 50 cm cannot be subtracted from 30 cm.
1 m or 100 cm is borrowed from 53 m leaving 52 m making 30 cm to 130 cm.
Now 130 - 50 = 80. It is placed under cm column.
(ii) Now in the m column, 53 - 1 = 52 m. 52 m - 37 m = 15 m.
It is placed under m column.
Hence, the difference is 15 m 80 cm.
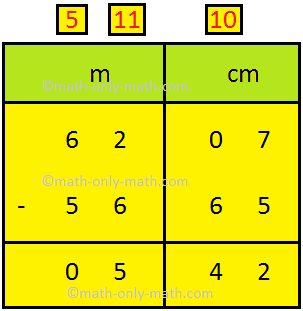
3. Subtract 56 m 65 cm from 62 m 7 cm.
|
Solution: Let us subtract. Step I: Arrange the numbers vertically. Step II: Write the lengths to be subtracted in m and cm as shown. Step III: First, subtract centimetres from right and then subtract the metres. |
Thus, 62 m 7 cm - 56 m 65 cm = 5 m 42 cm
4. Subtract 37 m 6 cm from 70 m.
Solution:
Case 1:
We have, 70 m - 37 m 6 cm
Minuend and subtrahend are both converted into smaller units.
70 m = (70 × 100) cm = 7000 cm
37 m 6 cm = (37 × 100) cm + 6 cm = (3700 + 6) cm = 3706 cm
Now subtract
7000 cm
- 3706 cm
3294 cm
= 3200 cm + 94 cm
= 32 m 94 cm
Therefore, 70 m - 37 m 6 cm = 32 m 94 cm.
Case 2:
As minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the subtrahend. Then m and cm are arranged in different columns. Minuend 70 m 00 cm is placed above subtrahend 37 m 06 cm.
m cm
1 100
70 00
- 37 06
32 94
(i) 06 cm > 0 cm. So, 6 cm cannot be subtracted from 0 cm.
1 m or 100 cm is borrowed from 70 m leaving 69 m in m column.
(ii) Now 100 cm - 06 cm = 94 cm. It is placed under cm column.
(iii) Now in the m column, 69 m - 37 m = 32 m.
It is placed under m column.
Hence, the difference is 32 m 94 cm.
5. Subtract 45 km 282 m from 63 km 70 m.
Solution:
Case 1:
Minuend and subtrahend are both converted into smaller units (conversion method).
63 km 70 m = (63 × 1000) m + 70 m = (63000 + 70) m = 63070 m
45 km 282 m = (45 × 1000) m + 282 m = (45000 + 282) m = 45282 m
Now subtract
63070 m
- 45282 m
17788 m
= 17000 m + 788 m
= 17 km 788 m
Therefore, 63 km 70 m - 45 km 282 m = 17 km 788 m.
Case 2:
As
minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the
subtrahend. Then km and m are arranged in different columns. Minuend 63 km 70 m is placed above subtrahend 45 km 282 m (without conversion).
km m
1 1000
63 070
- 45 282
17 788
(i) 282 m > 70 m. So, 282 m cannot be subtracted from 70 m.
1 km or 1000 m is borrowed from 63 km leaving 62 km making 70 m to 1070 m (Since, 1 km = 1000 m and 70 m = 1070 m).
Now 1070 m - 282 m = 788 m. It is placed under m column.
(ii) Now in the km column, 63 - 1 = 62 km. 62 km - 45 km = 17 km.
It is placed under km column.
Hence, the difference is 17 km 788 m.
6. Subtract 75 km 345 m from 200 km 20 m.
Solution:
As minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the subtrahend. Then km and m are arranged in different columns. Minuend 200 km 20 m is placed above subtrahend 75 km 345 m.
km m
1 1000
200 020
- 275 345
124 675
(i) 345 m > 20 m. So, 345 m cannot be subtracted from 20 m.
1 km or 1000 m is borrowed from 200 km leaving 199 km making 020 m to 1020 m.
Now 1020 m - 345 m = 675 m. It is placed under m column.
(ii) Now in the km column, 200 - 1 = 199 km. 199 km - 75 km = 124 km.
It is placed under km column.
Hence, the difference is 124 km 675 m.
7. Subtract 8 m 7 dm 5 cm from 26 m 4 dm 8 cm.
Solution:
As minuend is greater than subtrahend, the minuend is placed above the subtrahend. Then m, dm and cm are arranged in different columns. Minuend 26 m 4 dm 8 cm is placed above subtrahend 8 m 7 dm 5 cm.
m dm cm
1 10
26 4 8
- 8 7 5
17 7 3
(i) 8 cm - 5 cm = 3 cm. It is placed under cm column.
(ii) 7 dm > 4 dm. So, 7 dm cannot be subtracted from 4 dm.
1 m or 10 dm is borrowed from 26 m leaving 25 m making 4 dm to 14 dm.
Now 14 dm - 7 dm = 7 dm. It is placed under dm column.
(iii) Now in the m column, 26 - 1 = 25 m. 25 m - 8 m = 17 m.
It is placed under m column.
Hence, the difference is 17 m 7 dm 3 cm.
To subtract lengths, write the numbers of km, m and cm in separate columns then subtract like ordinary numbers, starting from right.
8. Subtract 11 m 35 cm from 24 m 45 cm.
Solution:
m cm
24 45
- 11 35
__ 13 10
Answer: 13 m 10 cm
9. Subtract 29 m 84 cm from 69 m 66 m.
Solution:
m cm
18
5 8 16
6 9 6 6
- 2 9 8 4
__ 3 7 8 2
Answer: 37 m 82 cm
10. Subtract following lengths:
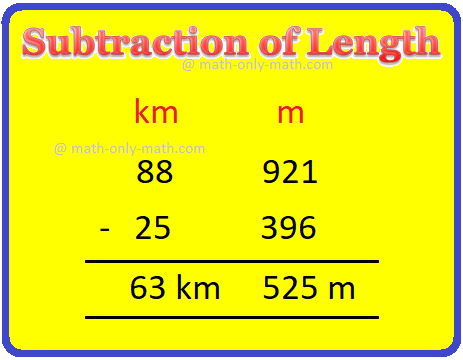
(i) 25 km 396 m from 88 km 921 m
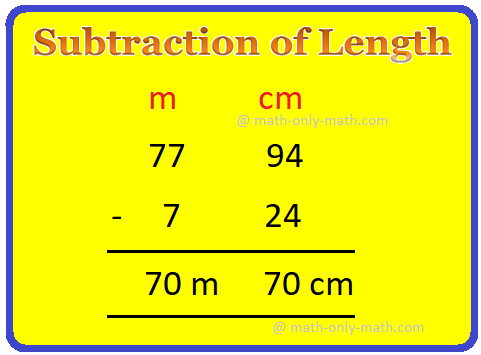
(ii) 7 m 24 cm from 77 m 94 cm
Solution:
|
(i) 25 km 396 m from 88 km 921 m 88 km 921 m - 25 km 396 m First subtract m = (921 - 396) m = 525 m Now subtract km = (88 - 25) km = 63 km |
Therefore, the required difference is 63 km 525 m
|
(ii) 7 m 24 cm from 77 m 94 cm 77 m 94 cm - 7 m 24 cm First subtract cm = 94 cm - 24 cm = 70 cm Now subtract m = 77 m - 7 m = 70 m |
Therefore, the required difference is 70 cm 70 m
Word Problems on Subtraction of Length:
SUBTRACTION OF METRES AND CENTIMETRES
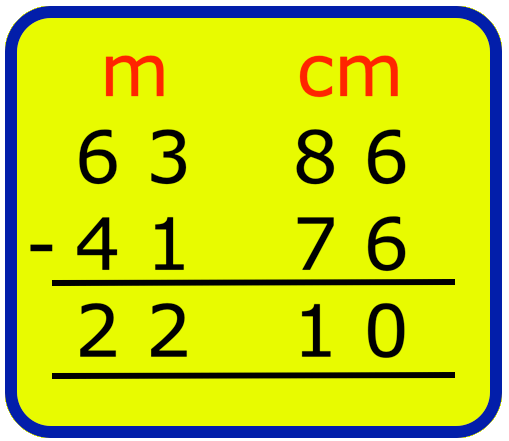
1. Michael, the cloth merchant, had 63 metres 86 centimetres of green cloth. He sold 41 metres 76 centimetres of it. How much cloth is left with him now?
Solution:
Write m and cm in columns as shown.
|
Step I: Subtract cm first. 86 - 76 = 10 Write 10 in the cm column. Step II: Subtract m now. 63 - 41 = 22 Write 22 in the m column. |
Therefore, the length of the green cloth left is 22 m 10 cm.
Worksheet on Subtraction of Length:
1. Subtract the following:
(i) 81 m 9 cm - 52 m 52 cm
(ii) 28 m 98 cm - 16 m 20 cm
(iii) 352 m 917 cm - 148 m 79 cm
(iv) 938 m 33 cm - 619 m 57 cm
(v) 394 m 68 cm - 45 m 79 cm
(vi) 180 m 90 cm - 42 m 33 cm
Answer:
1. (i) 28 m 57 cm
(ii) 12 m 78 cm
(iii) 203 m 38 cm
(iv) 318 m 76 cm
(v) 348 m 89 cm
(vi) 138 m 57 cm
2. Subtract the following:
(i) 81 m 09 cm from 145 m 56 cm
(ii) 14 m 82 cm from 67 m 40 cm
(iii) 174 m 259 cm from 512 m 36 cm
(iv) 79 m 56 cm from 140 m 23 cm
(v) 180 m 90 cm from 287 m 46 cm
Answer:
2. (i) 64 m 47 cm
(ii) 52 m 58 cm
(iii) 338 m 11 cm
(iv) 60 m 67 cm
(v) 106 m 56 cm
3. Subtract the following lengths:
|
(i) |
m cm 63 87 - 32 50 _____________ |
(ii) |
m cm 39 75 - 16 05 _____________ |
|
(iii) |
m cm 28 54 - 12 30 _____________ |
(iv) |
m cm 43 65 - 21 40 _____________ |
|
(v) |
m cm 90 85 - 40 30 _____________ |
(vi) |
m cm 18 72 - 14 20 _____________ |
|
(vii) |
m cm 11 55 - 03 24 _____________ |
(viii) |
m cm 12 75 - 11 35 _____________ |
|
(ix) |
m cm 50 34 - 37 58 _____________ |
(x) |
m cm 64 20 - 35 65 _____________ |
|
(xi) |
m cm 73 38 - 57 19 _____________ |
(xii) |
m cm 81 56 - 43 15 _____________ |
|
(xiii) |
m cm 40 72 - 19 45 _____________ |
(xiv) |
m cm 80 72 - 69 85 _____________ |
|
(xv) |
m cm 40 38 - 16 59 _____________ |
(xvi) |
m cm 33 80 - 09 69 _____________ |
Answer:
3. (i) 31 m 37 cm
(ii) 23 m 70 cm
(iii) 16 m 24 cm
(iv) 22 m 25 cm
(v) 50 m 55 cm
(vi) 4 m 52 cm
(vii) 8 m 31 cm
(viii) 1 m 40 cm
(ix) 12 m 76 cm
(x) 28 m 55 cm
(xi) 16 m 19 cm
(xii) 38 m 41 cm
(xiii) 21 m 27 cm
(xiv) 10 m 87 cm
(xv) 23 m 79 cm
(xvi) 24 m 11 cm
● Related Concepts
● Conversion of Standard Unit of Length
From Subtraction of Length to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.