Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Telling Time in 5-minute Intervals
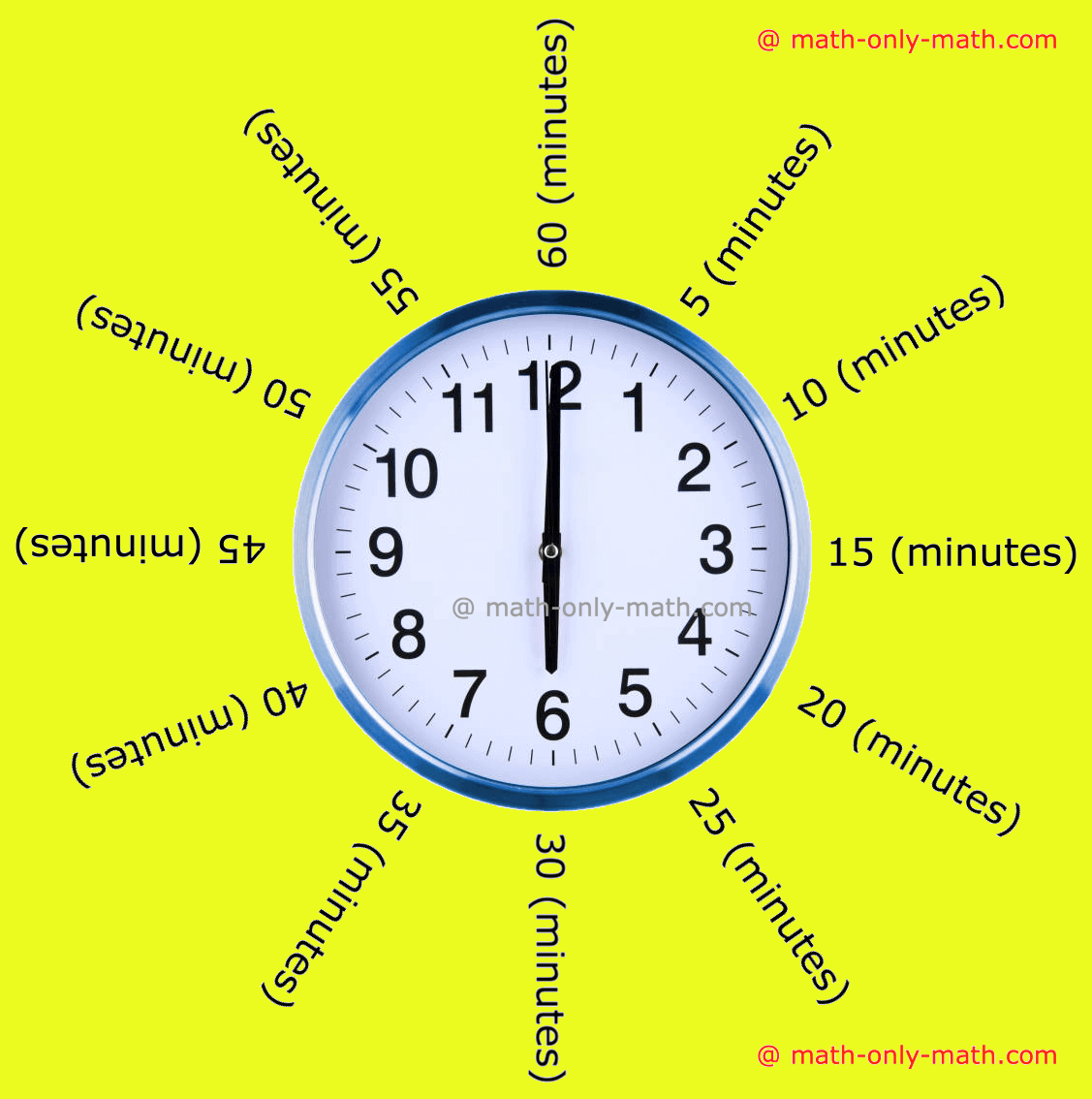
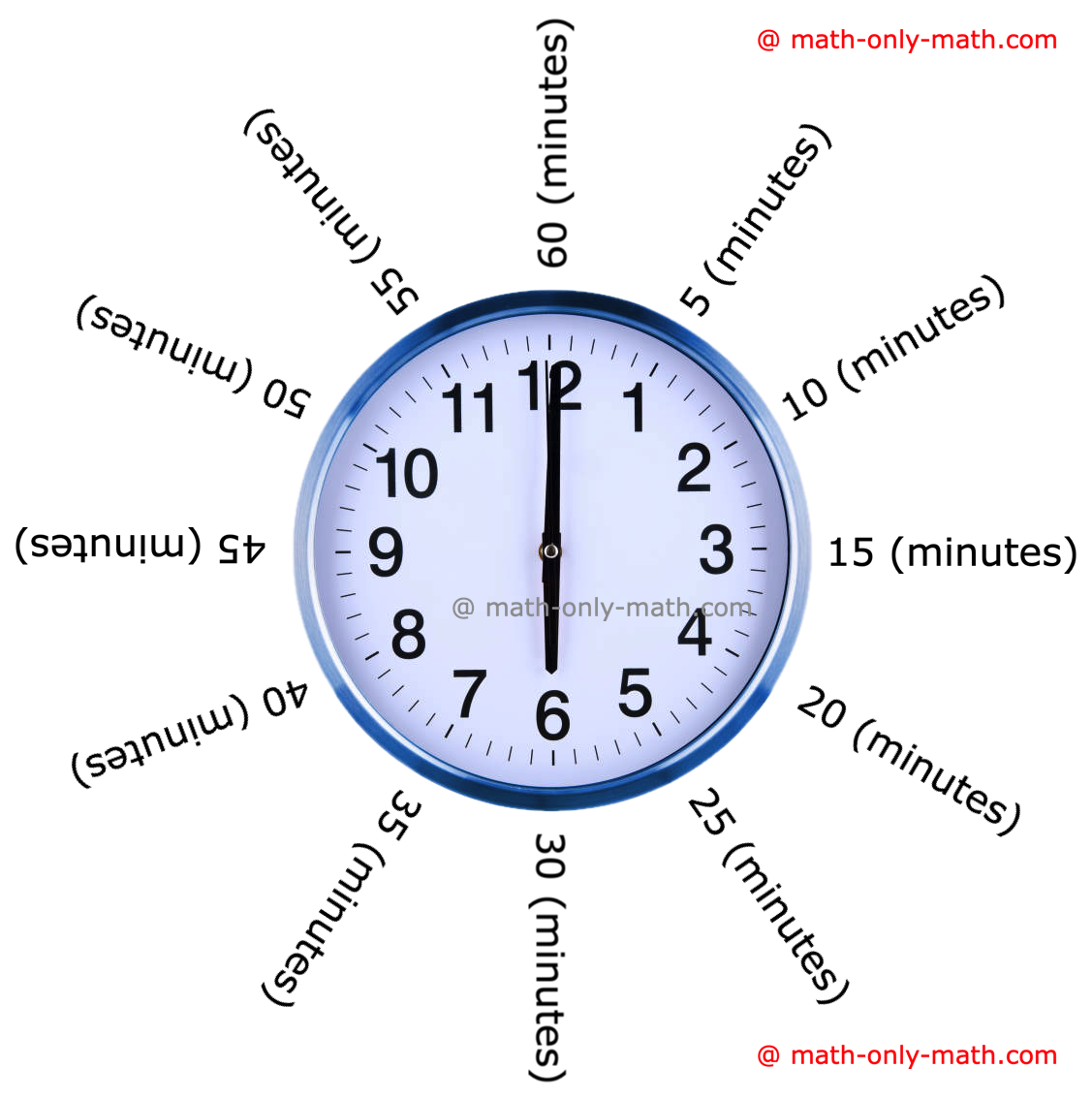
The clock has numbers from 1 to 12 marked on its dial. These numbers divide the clock face into 12 equal parts. Between any two numbers there are 5 small divisions. Each small division represents a minute. So, the minute hand takes 5 minutes more from one number to the next number. When the minute hand is at 1 it is read as 1 × 5 = 5 minutes. Thus, the minute hand takes 60 minutes to complete one round.
12 × 5 = 60 minutes = 1 hour
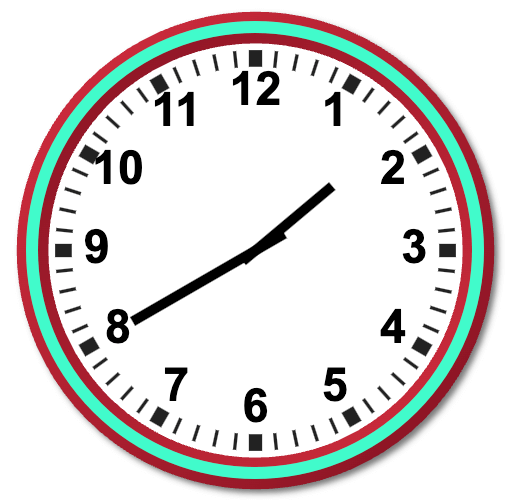
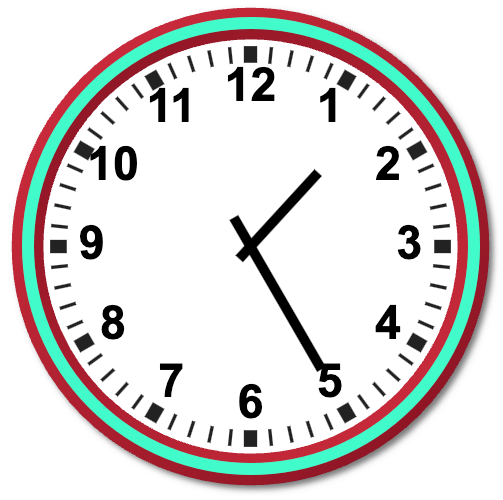
Look at the clock in the picture. The hour hand is between 1 and 2. The minute hand is at 5. The time is 25 minutes past 1. It is written as 1:25. We read as ‘one twenty-five’.
The minute hand moves from one digit to the next in 5 minutes.
When the minute hand is at 1, it shows 5 minutes past the hour.
When the minute hand is at 2, it shows 10 minutes past the hour. And so on.
We can read the time in two ways.
From the above explanation we can easily read the time in 5-minutes interval.
Worksheet on Telling Time in 5-minute Intervals:
Questions and Answers on Telling Time in 5-minute Intervals:
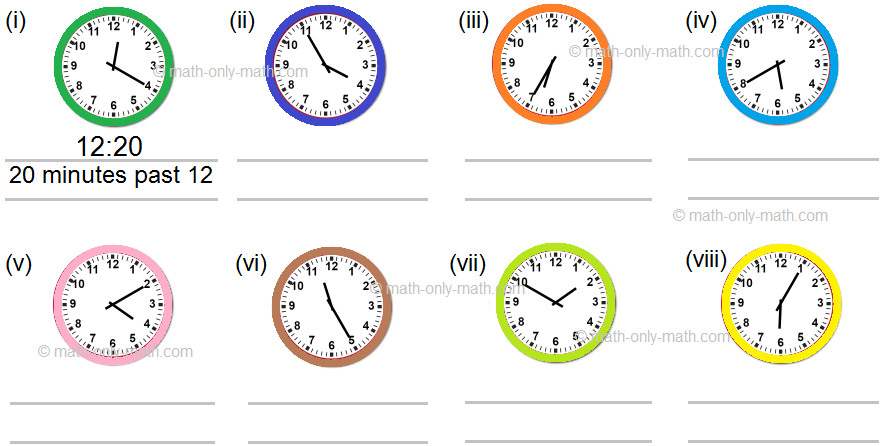
I. Read and write the time shown on the given clocks in two ways:
Answer:
(ii) 3:55; 5 minutes to 4
(iii) 6:35, 25 minutes to 7
(iv) 5:40; 20 minutes to 6
(v) 4:10; 10 minutes past 4
(vi) 11:25; 25 minutes past 11
(vii) 1:50 10 minutes to 2
(viii) 6:05; 5 minutes past 6
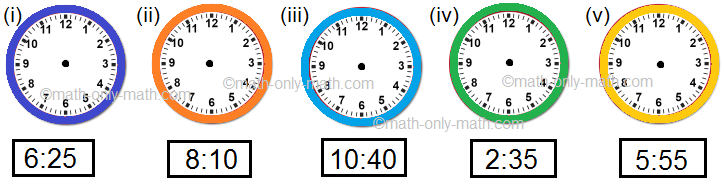
II. Read the time given below each clock. Draw the hour hand and minute hand in each clock.
Answer:
III. Match the columns:
|
(i) |
5:15 |
(a) |
20 minutes past 7 |
|
(ii) |
8:40 |
(b) |
half past 9 |
|
(iii) |
9:30 |
(c) |
quarter past 5 |
|
(iv) |
7:20 |
(d) |
quarter to 11 |
|
(v) |
10:45 |
(e) |
20 minutes to 9 |
Answer:
III. (i) → (c)
(ii) → (e)
(iii) → (b)
(iv) → (a)
(v) → (d)
From Telling Time in 5-minute Intervals to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.