Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Units of Length Conversion Charts
Units of length conversion charts are discussed here in metric units of length and customary units of length:
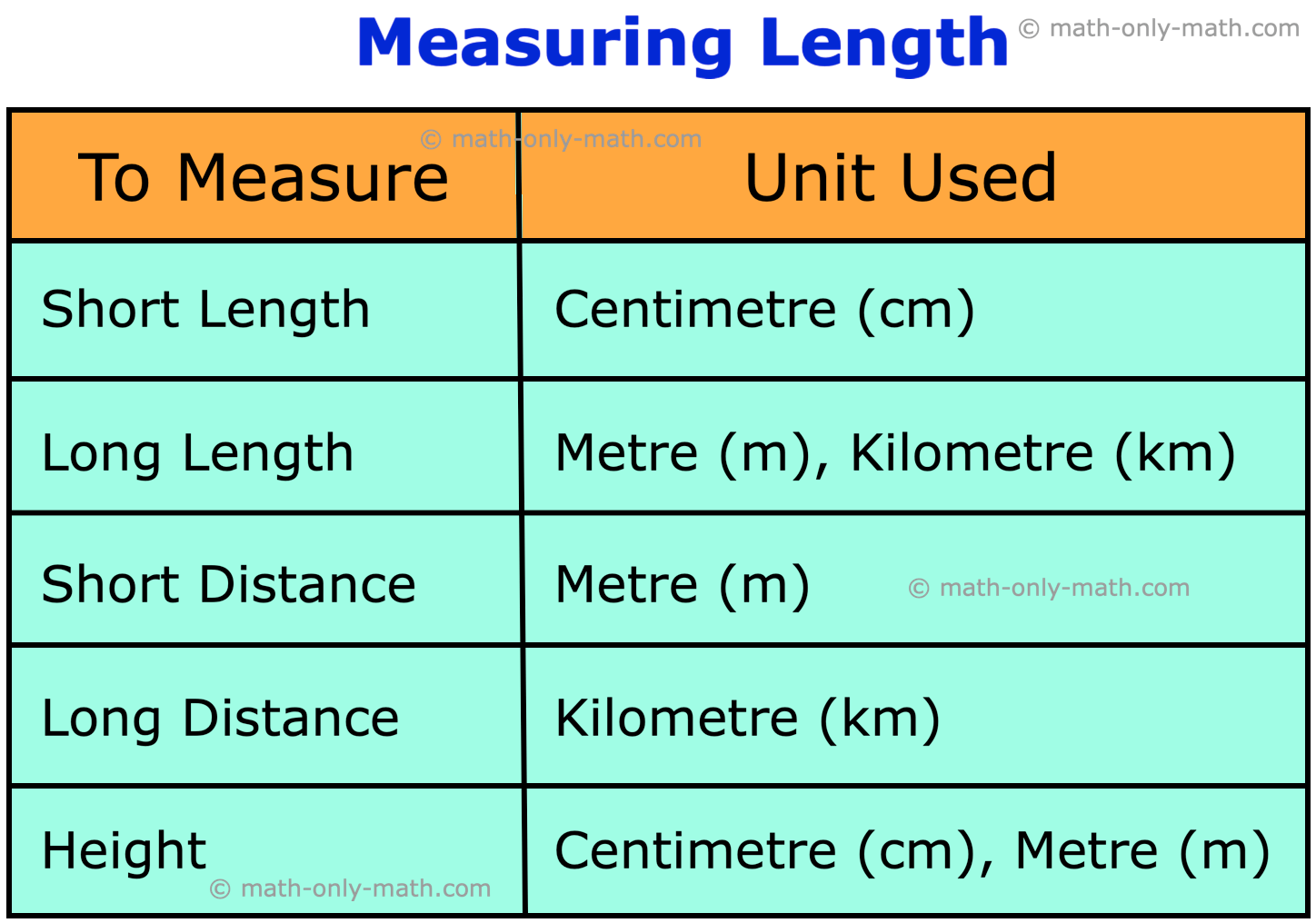
In math when we use length, we know that the standard unit of length is ‘Metre’ which is written in short as ‘m’.
A metre length is divided into 100 equal parts. Each part is named centimetre and written in short as ‘cm’.
Thus, 1 m = 100 cm and 100 cm = 1 m
The long distances are measured in kilometre. This kilometre equals to 1000 metres. The kilometre is written in short as km.
1 kilometre (km) = 1000 metres (m)
Or
1 km = 1000 m
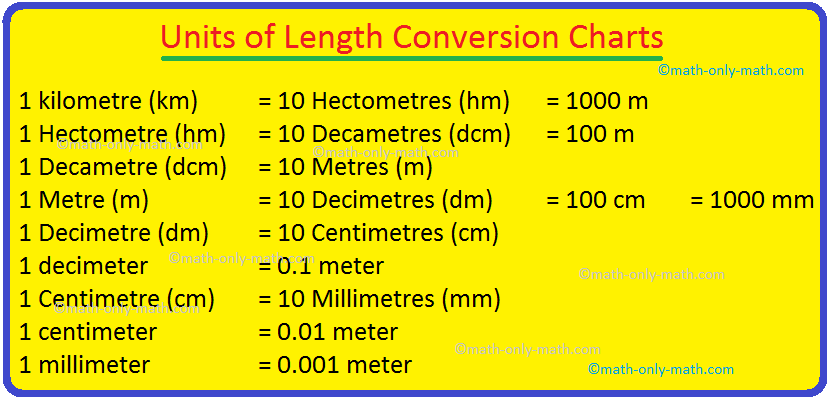
The different units of length conversion charts and their equivalents are given here:
1 kilometre (km) = 10 Hectometres (hm) = 1000 m
1 Hectometre (hm) = 10 Decametres (dcm) = 100 m
1 Decametre (dcm) = 10 Metres (m)
1 Metre (m) = 10 Decimetres (dm) = 100 cm = 1000 mm
1 Decimetre (dm) = 10 Centimetres (cm)
1 decimeter = 0.1 meter
1 Centimetre (cm) = 10 Millimetres (mm)
1 centimeter = 0.01 meter
1 millimeter = 0.001 meter
Mostly we use Kilometre (km), Metre (m) and Centimetre (cm) as the units of length measurement or unit of length conversion chart.
In customary units of length are discussed her in the units of length conversion table:
1 mile = 1760 yards
1 mile = 5280 feet
1 yard = 3 feet
1 foot = 12 inches
Solved Examples on Conversion of Units - Length
Convert Metre to Centimetre
1. Convert 0.56 m in cm.
Solution:
We know that 1 m = 100 cm
0.56 = 0.56 × 100 cm
= 56 cm
2. Convert 9 m 25 cm into cm.
Solution:
Since, 1 m = 100 cm
Therefore, 9 m = 9 × 100 cm
= 900 cm
Now, 9 m 25 cm
= 9 m + 25 cm
= 900 cm + 25 cm
= 925 cm
Therefore, 9 m 25 cm = 925 cm
Note: To convert m into cm simply add two zeroes on the right.
Convert Centimetre to Metre
3. Convert 840 cm into m.
Solution:
840 cm = 800 cm + 40 cm
= 8 m + 40 cm (Since, 100 cm = 1 m)
= 8 m 40 cm
Therefore, 840 cm = 8 m 40 cm
Convert Kilometre to Metre:
To convert km into m, we multiply by 1000.
4. Convert 4 km 300 m into m.
Solution:
Since, 1 km = 1000 m
Therefore, 4 km 300 m
= (4 × 1000) m + 300 m
= 4000 m + 300 m
= 4300 m
Therefore, 4 km 300 m = 4300 m
Note: To convert km into m. Simply add three zeroes on the right.
Convert Metre to Kilometre:
To convert m into km, we divide by 1000.
5. Convert 4245 m into km.
Solution:
4245 m = 4000 m + 245 m
= 4 km + 245 m (Since, 1000 m = 1 km)
= 4 km 245 m
Therefore, 4245 m = 4 km 245 m
Convert Metre Centimetre to Metre
6. Convert 4 m 19 cm into m
Solution:
4 m 19 cm = 4 m + 19 cm
= 4 m + \(\frac{19}{100}\) m
= 4 m + 0.19 m
= 4.19 m
Convert Kilometre metre to Metre:
7. Convert 16 km 750 m into km
Solution:
16 km 750 m = 16 km + 750 m
= 16 km + \(\frac{750}{1000}\) km
= 16 km + 0.75 km
= 16.75 km
8. The length of a square tile is 125 cm. What will be the length of the tile strip in millimeters if 10 tiles are kept in a line?
Solution:
The length of a square tile = 125 cm
125 cm = 125 × 10 mm
= 1250 mm
The length of 10 square tiles = 12500 mm
Units of Length Conversion Charts
Units of Mass and Weight Conversion Chart
Units of Capacity and Volume Conversion Chart
Units of Time Conversion Chart
From Units of Length Conversion Charts to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.