Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Prime Factorisation
Prime factorisation or complete factorisation of the given number is to express a given number as a product of prime factor.
When a number is expressed as the product of its prime factors, it is called prime factorization.
For example, 15 = 3 × 5. So, 3 and 5 are prime factors of 15.
Prime factors of a number are always the prime numbers, when a number is expressed as product of prime numbers, it is called prime factorization. Prime factorization can be done, using two methods: division method and factor tree method.
HCF of two or more numbers can be obtained by prime factorization. To find the HCF by prime factorization, we first find all the prime factors of the given numbers and then find the product of all the common prime factors. The product is the HCF of the given numbers.
Factor Tree Method:
We write pairs of factors for the given number in circles which make branches of a factor tree.
Division Method:
Divide the given numbers by the smallest prime number. Continue the division until it is not further divisible. Factorization stops when we reach a prime number.
Prime Factorisation of 1440 Using Division Method Video

Observe the following examples of Prime factorization in two methods i.e., Factor Tree Method and Division Method.
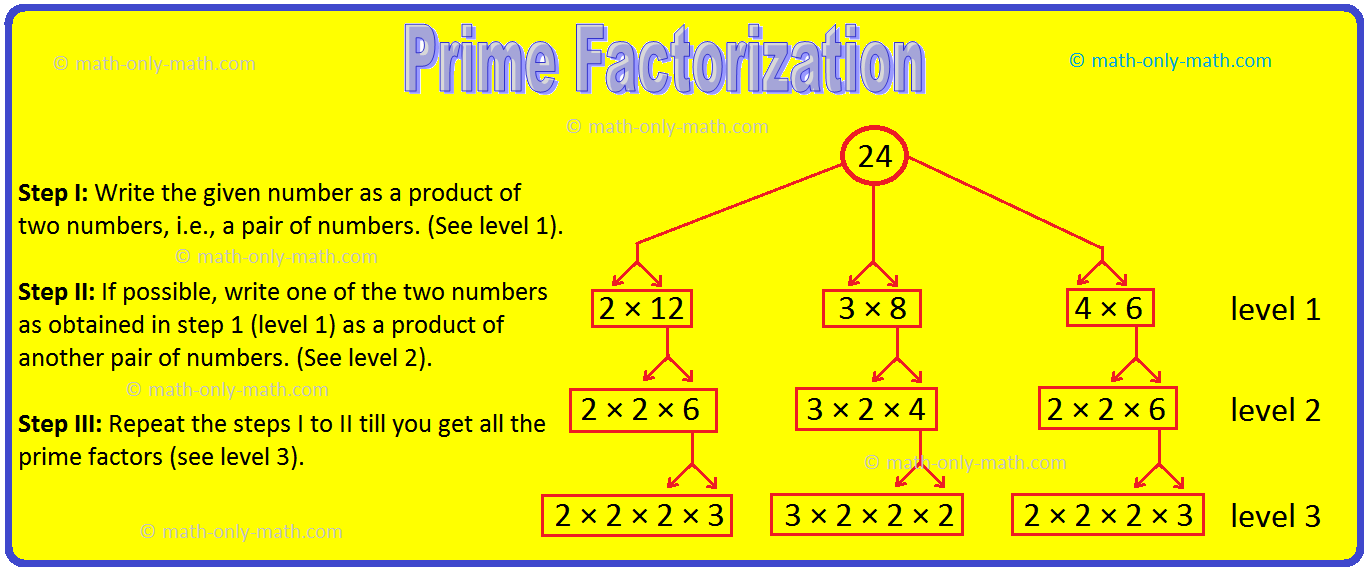
1. Let us check this process by making a factor tree for the number 24.
Working Rules to Find the Prime Factorization using Factor Tree Method:
Step I: Write the given number as a product of two numbers, i.e., a pair of numbers. (See level 1).
Step II: If possible, write one of the two numbers as obtained in step 1 (level 1) as a product of another pair of numbers. (See level 2).
Step III: Repeat the steps I to II till you get all the prime factors (see level 3).
We get the same factors in each box at the last level i.e, level 3
The factors 2 and 3 are thus prime numbers.
Prime Factorization Property: Every number greater than 1 has exactly one prime factorization.
Prime Factorization Working Rules:
Step I: Divide the number by the least (smallest) prime number.
Step II: Continue the process until a prime number is obtained as the remainder.
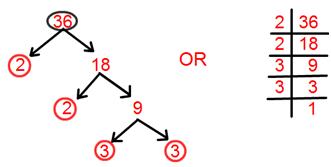
2. Find Prime Factorization of 36.
Prime factorisation of 36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3.
= 2² × 3².
[Here two ways to solve factorisation one is tree factorisation method and the other one is by dividing.]
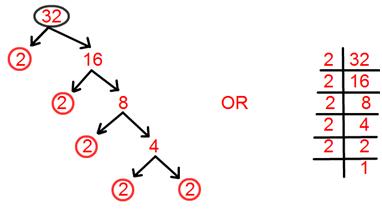
3. Find prime factorisation of 32.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 32 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
= 2⁵.
4. Find prime factorization of 51.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 51 = 3 × 17.
= 3¹ × 17¹
= 3 × 17.
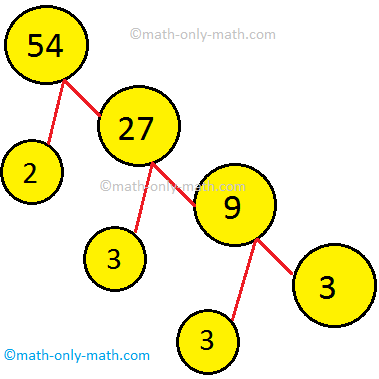
5. Draw a factor tree to show the prime factorization of 54.
Solution:
6. Find prime factorization of 57.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 57 = 3 × 19
= 3¹ × 19¹
= 3 × 19.
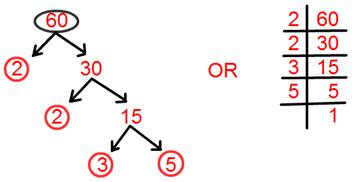
7. Find prime factorization of 60.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5.
= 2² × 3 × 5.
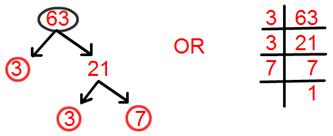
8. Find prime factorisation of 63.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 63 = 3 × 3 × 7.
= 3² × 7.
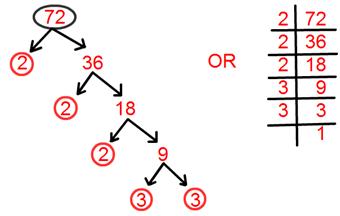
9. Find prime factorisation of 72.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3.
= 2³ × 3².
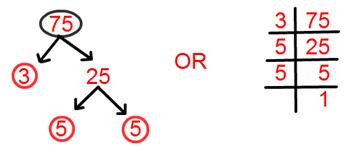
10. Find prime factorisation of 75.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 75 = 3 × 5 × 5.
= 3 × 5².
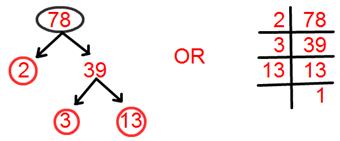
11. Find prime factorisation of 78.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 78 = 2 × 3 × 13.
12. Find prime factorisation of 93.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 93 = 3 × 31.
13. Find prime factorisation of 102.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 102 = 2 × 3 × 17.
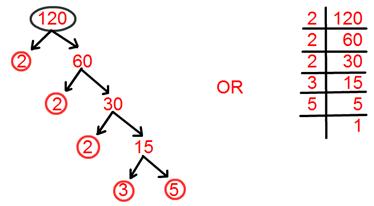
14. Find prime factorisation of 120.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5.
= 2³ × 3 × 5.
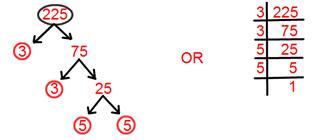
15. Find prime factorisation of 225.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 225 = 3 × 3 × 5 × 5.
= 3² × 5².
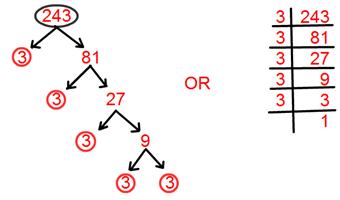
16. Find prime factorisation of 243.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 243 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3.
= 3⁵.
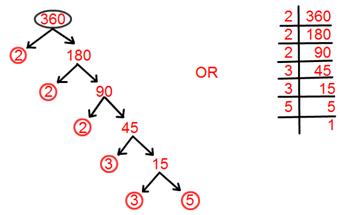
17. Find prime factorization of 360.
Solution:
Prime factorisation of 360 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5.
= 2³ × 3² × 5.
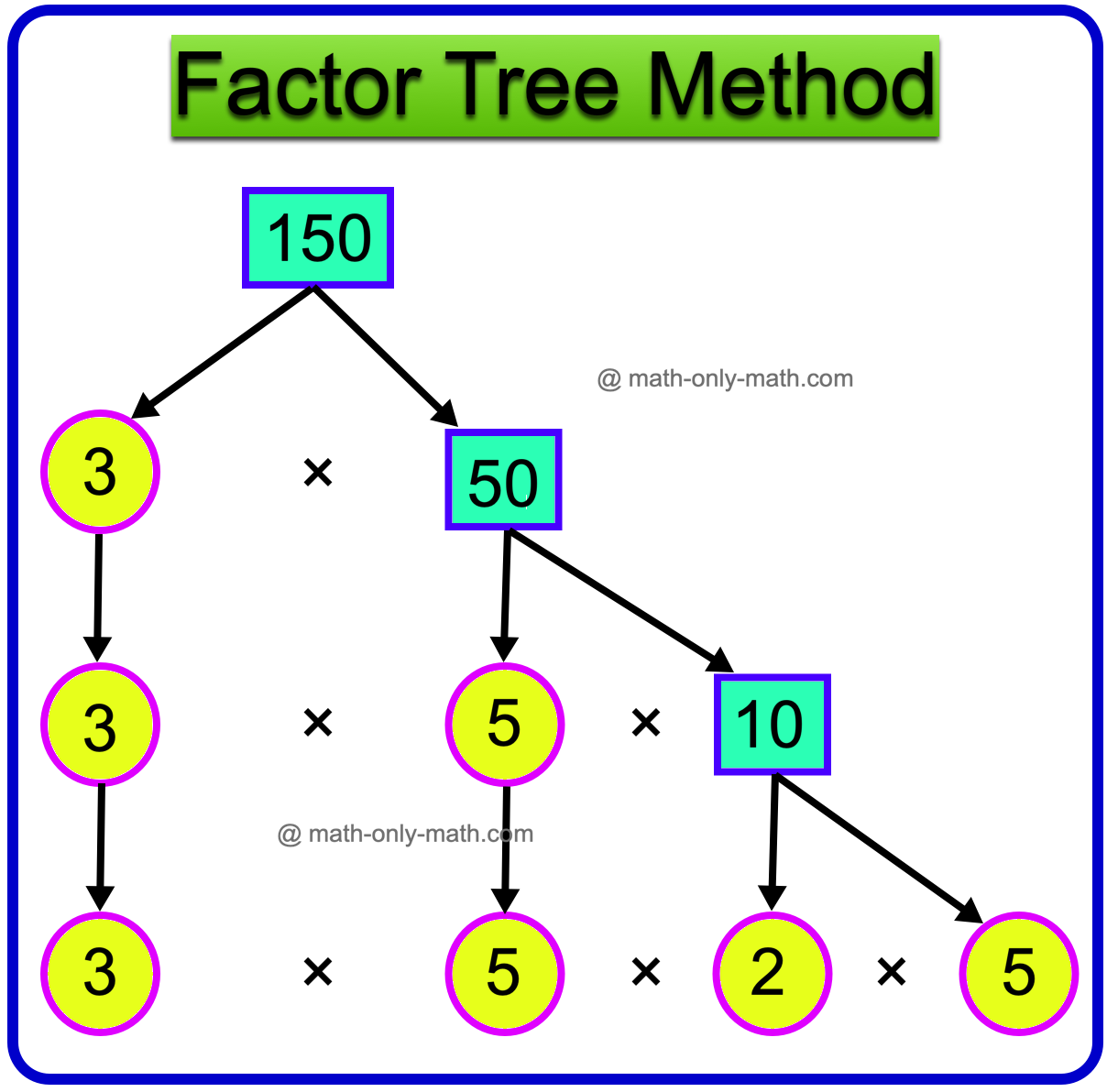
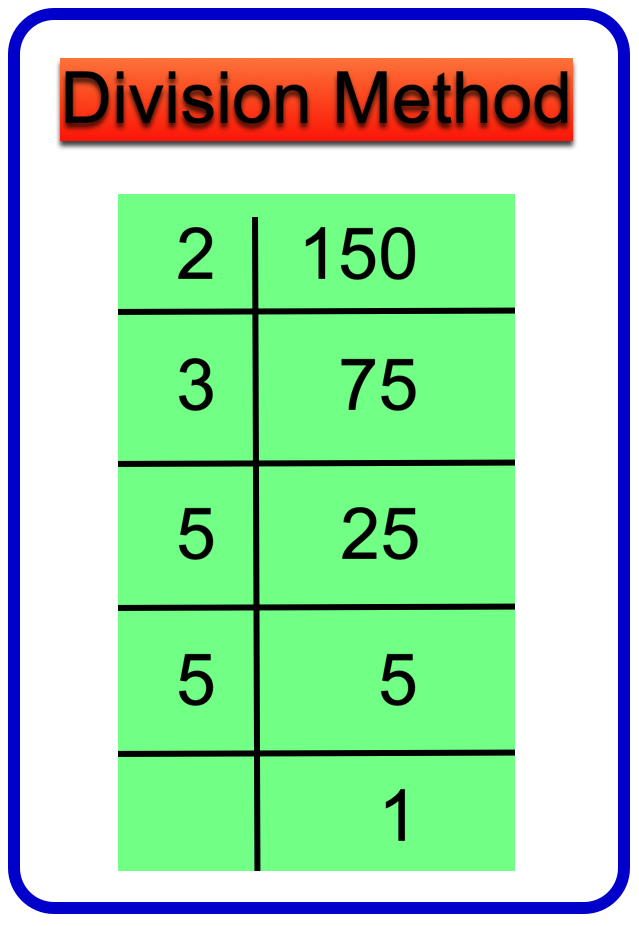
18. Write the prime factors of 150 by both the factor tree method and division method.
Solution:
Factor Tree Method:
Therefore, 150 = 3 × 5 × 2 × 5
Hence, the prime factors of 150 are 2, 3, 5.
Division Method:
Therefore, 150 = 2 × 3 × 5 × 5
Hence, the prime factors of 150 are 2, 3, 5.
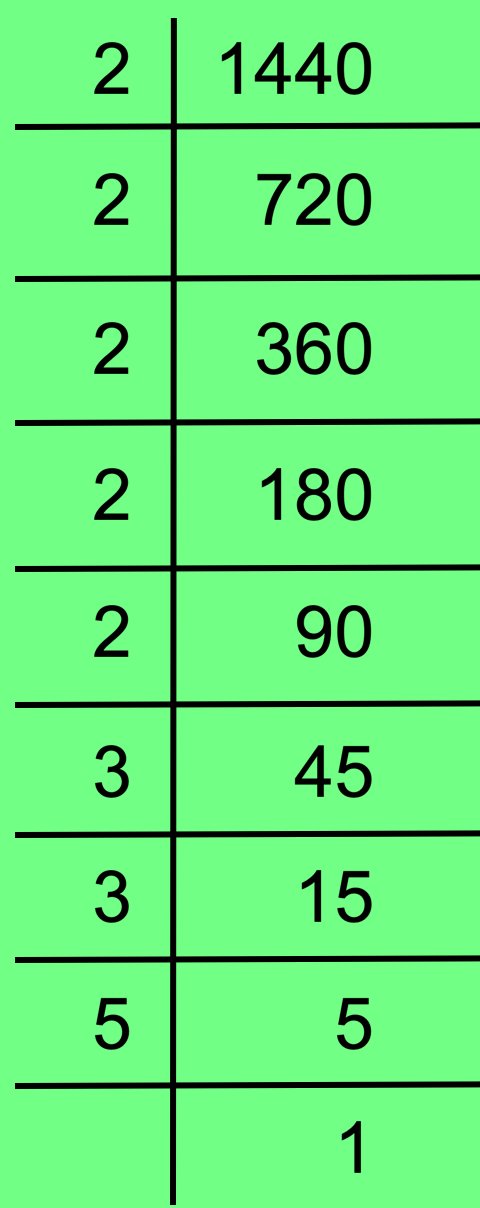
18. Find the prime factorisation of 1440 using division method.
Solution:
Therefore, 1440 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
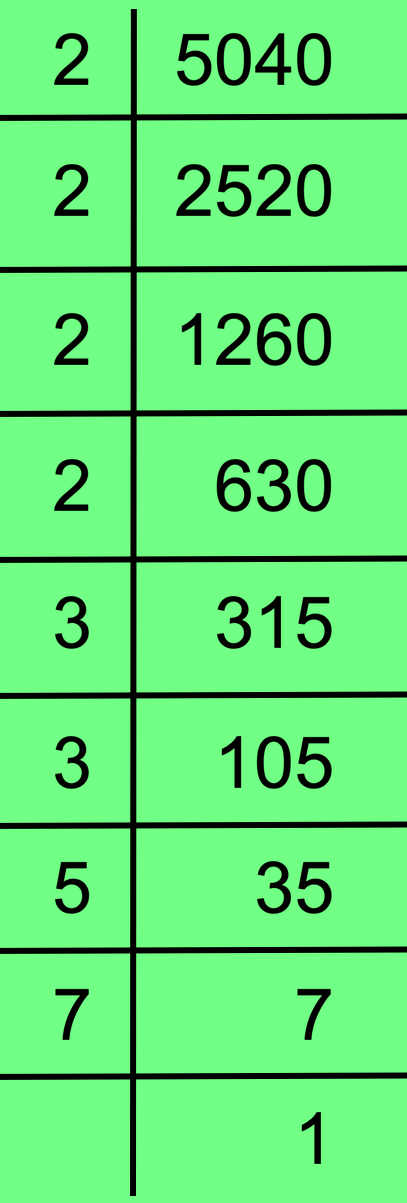
19. Find the prime factorisation of 5040 using division method.
Solution:
Therefore, 5040 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7
Prime Factorisation of 5040 Using Division Method Short Video:

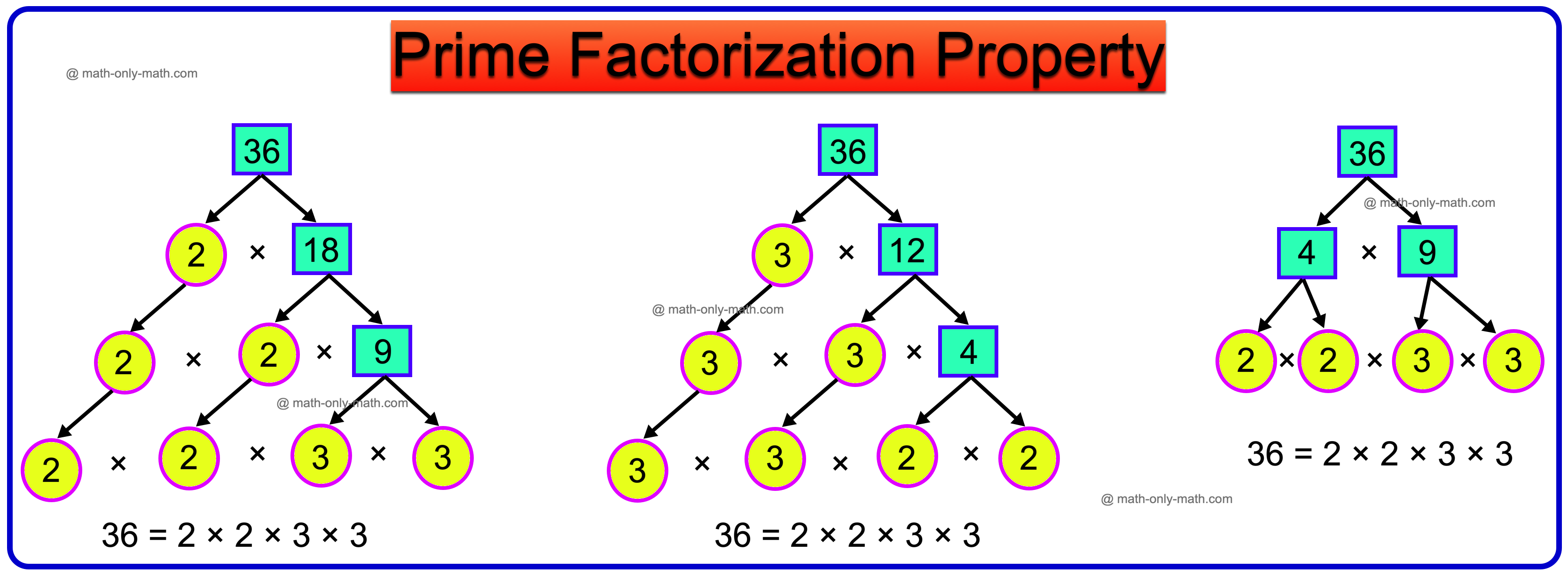
Prime Factorisation Property:
Let us find the prime factors of 36 by factor tree method.
From the above, we observe that the prime factors of 36 are the same in either factor tree method except for their order. Thus, the prime factorisation of 36 is unique. This property is called the prime factorisation property or the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. It states that:
Every composite number can be factorised into prime factors in one and only one way, except for the order of the prime factors.
Frequently asked questions on Prime Factorization:
1. What is Prime Factorization?
The factorization is a process by which a whole number is broken down (factorized) into factors and if each factor is a prime number, then such factorization of a number is called the prime factorization.
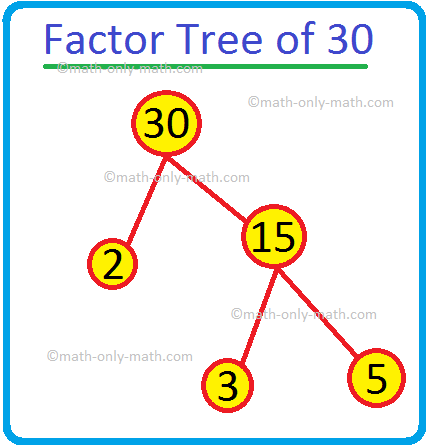
2. Prime Factorization of 30 is
(i) 2 × 15; (ii) 5 × 6; (iii) 6 × 5; (iv) 2 × 3 × 5
Solution:
30 = 2 × 3 × 5
Therefore, the option (iv) is the correct answer.
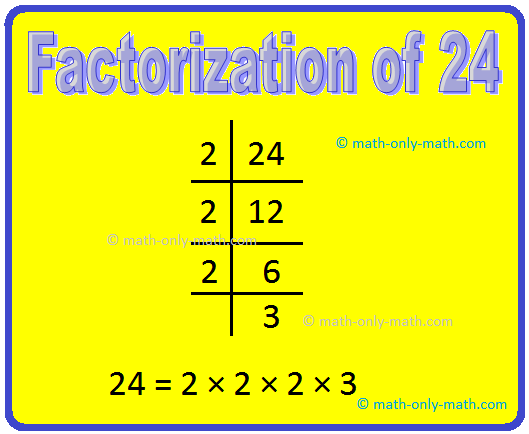
3. Find the prime factorization of 24 using Division Method.
Solution:
Hence, the prime factorization of 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3.
Worksheet on Prime Factorization:
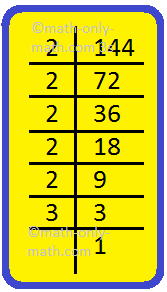
I. Find the prime factors of the given number through prime factorization. First one is shown as an example for you.
(i) 144
(ii) 81
(iii) 72
(iv) 48
(v) 100
(vi) 64
(vii) 108
(viii) 248
(ix) 256
1. What is prime factorisation?
1. What is prime factorisation?
Answer:
The method of finding all the prime factors of a number is called prime factorisation.
2. What are the methods of prime factorisation?
2. What are the methods of prime factorisation?
Answer:
To find the prime factors of a whole number, we apply the divisibility tests. We can divide the number successively by prime numbers 2, 3, 5, 7 and so on till the dividend is 1 and express them as a product of prime numbers. This method is known as division method. There is one another method known as factor tree method. The factor tree method is generally preferred when the number is large.
● Factors.
● Highest Common Factor (H.C.F).
● Examples on Highest Common Factor (H.C.F).
● Greatest Common Factor (G.C.F).
● Examples of Greatest Common Factor (G.C.F).
● To find Highest Common Factor by using Prime Factorization Method.
● Examples to find Highest Common Factor by using Prime Factorization Method.
● To find Highest Common Factor by using Division Method.
● Examples to find Highest Common Factor of two numbers by using Division Method.
● To find the Highest Common Factor of three numbers by using Division Method.
From Prime Factorization to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.