Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Volume of a Pyramid
To calculate volume of a pyramid, formula is used to solve the problems on pyramid using step-by-step explanation.
Worked-out examples on volume of a pyramid:
1. The base of a right pyramid is a rectangle of length 12 meters and breadth 9 meters. If each of the slant edges of the pyramid is 8.5 meters, find the volume of the pyramid.
Solution:
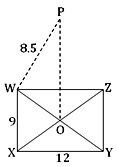
Let the rectangle WXYZ be the base of the right pyramid and its diagonal WY and XZ intersect at O. If OP be perpendicular to the plane of the rectangle at O then OP is the height of the right pyramid.
Join PW .
Then according to the question,
WX = 9 m, XY = 12 m. and PW = 8.5 m
Now, from the plane right angled ∆ WXY we get,
WY² = WX² + XY²
or, WY² = 9² + 12²
or, WY² = 81 + 144
or, WY² = 225
or, WY = 15²
Therefore, WY =15;
Hence, WO = 1/2 WY = 1/2 × 15 = 7.5
Since PO is perpendicular to the plane of rectangle WXYZ at O, hence PO ┴ OW
Therefore, from the right angled triangle POW we get;
OW² + OP² = PW²
or, OP² = PW² - OW²
or, OP² = (8.5)² - (7.5)²
or, OP² = 16
or, OP = √16
Therefore, OP = 4
i.e., the height of the pyramid = 4 m.
Therefore, the required volume of the pyramid
= 1/3 × (area of rectangle WXYZ) × OP
= 1/3 × 12 × 9 × 4 cubic metre.
= 144 cubic metre.
2. OX, OY , OZ are three mutually perpendicular line segments in space; if OX = OY = OZ = a,
Find the area of the area of the triangle XYZ and the volume of pyramid formed.
Solution:
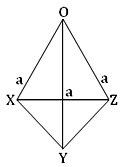
According to the question, OX = OY = OZ = a
Again, OX ┴ OY;
Hence, from ∆ OXY we get,
XY² = OX² + OY²
or, XY² = a² + a²
or, XY² = 2a²
Therefore, XY = √2 a
Similarly, from triangle OYZ we get, YZ = √2 a (Since, OY ┴ OZ)
And from ∆ OZX we get, ZX = √2 a (Since, OZ ┴ OX).
Thus, XYZ is an equilateral triangle of side √2 a.
Therefore, the area of the triangle XYZ is
(√3)/4 ∙ XY²
= (√3)/4 ∙ (√2 a)² = (√3/2) a² square units
Let Z be the vertex of the pyramid OXYZ; then the base of the pyramid is the triangle OXY.
Thus, the area of the base of the pyramid
= area of ∆ OXY
= 1/2 ∙ OX ∙ OY , (Since, OX ┴ OY) = 1/2 a ∙ a = 1/2 a²
Again, OZis perpendicular to both OX and OY at their at their point of intersection O.
Therefore, the height of the pyramid is OZ.
Therefore, the required volume of the pyramid OXYZ
= 1/3 × (area of ∆ XOY) × OZ
= 1/3 ∙ 1/2 a² ∙ a
= 1/6 a³ cubic units
3. The base of a right pyramid is a regular hexagon whose area is 24√3 square cm. If the area of a side face the pyramid is 4√6 square cm what should be its volume?
Solution:
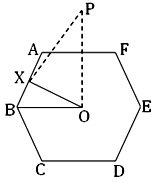
Let the regular hexagon ABCDEF of side a cm. be the base of the right pyramid. Then the area of the base of the pyramid = area of the hexagon ABCDEF
= (6 a²/4) cot (π/6), [using the formulae (na²/4) cot (π/n), for the area of the regular polygon of n sides]
= (3√3/2) a² square cm.
According to the question,
(3√3/2) a² = 24√3
or, a² = 16
or, a = √16
or, a = 4 (Since, a > 0)
Let OP be perpendicular to the plane of the base of the pyramid at O, the centre of the hexagon; then OP is the slant height of the pyramid.
Draw OX ┴ AB and join OB and PX.
Clearly, X is the mid-point of AB;
Hence, PX is the slant height of the pyramid.
According to the question, the area of ∆ PAB = 4√6
or, 1/2 ∙ AB ∙ PX = 4√6, (Since, PX ┴ AB)
or, 1/2 ∙ 4 ∙ PX = 4√6, (Since, AB = a = 4)
or, PX= 2√6
Again , OB = length of a side of the hexagon = 4
And BX = 1/2 ∙ AB = 2.
Therefore from right- angled ∆ BOX we get,
OX² + BX² = OB²
or, OX² = 4² – 2²
or, OX² = 16 – 4
or, OX² = 12
or, OX = √12
or, OX = 2√3
Again, OP ┴ OX;
hence, from the right – angled ∆ POX we get,
OP² + OX² = PX²
or, OP² = PX² – OX²
or, OP² = (2√6)² - (2√3)²
or, OP² = 24 – 12
or, OP² = 12
or, OP = √12
or, OP = 2√3
Therefore, the required volume of the pyramid
= 1/3 × area of the base × OP.
= 1/3 × 24√3 × 2√3 cubic cm.
= 48 cubic cm.
● Mensuration
- Formulas for 3D Shapes
- Volume and Surface Area of the Prism
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of Prism
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Right Pyramid
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Tetrahedron
- Volume of a Pyramid
- Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Problems on Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume of a Pyramid
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Volume of a Pyramid to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.