Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Tetrahedron
What is tetrahedron?
A pyramid on a triangular base is called a tetrahedron. In other words, a tetrahedron is a solid bounded by four triangular faces. Evidently a tetrahedron is a triangular pyramid. If the base of a tetrahedron is an equilateral triangle and the other triangular faces are isosceles triangles then it is called a right tetrahedron. A tetrahedron is said to be regular when all its four faces are equilateral triangles. Clearly, these equilateral triangles are congruent to one another.
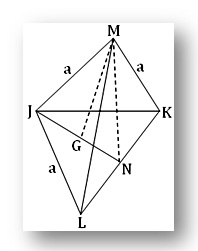
A regular tetrahedron has been shown in the given figure. M is the vertex and the equilateral triangle JLK is the base of the regular tetrahedron. JL, LK, KJ, MJ, ML and MK are its six edges and three lateral faces are congruent equilateral triangles LKM, KJM and JLM. If G be the centroid of the base JLK and N, the mid-point of the side LK then MG is the height and MN, the slant height of the regular tetrahedron.
Let a be the length of an edge of a regular tetrahedron. Then,
1. Area of the slant surface of the regular tetrahedron
= sum of the areas of three congruent equilateral triangles
= 3 ∙ (√3)/4 a² square units;
2. Area of the whole surface of the regular tetrahedron
= sum of the areas of four congruent equilateral triangles.
= 4 ∙ (√3)/4 a²
= √3 a² square units;
3. Volume of the regular tetrahedron
= 1/3 × area of the base × height
= (1/3) ∙ (√3)/4 ∙ a² × (√2)/(√3) a
= (√2/12) a³ cubic units.
Note:
In the plane ∆ JLK we have, JN ┴ LK
Therefore, JN² = JL² - LN² = a² - (a/2) ² = (3a²)/4
Now, JG = 2/3 ∙ JN
or, JG² = 4/9 ∙ JN²
or, JG² = (4/9) ∙ (3/4) a²
or, JG² = a²/3
Again, MG ┴ JG and JM = a
Hence, from the ∆ JGM we get,
MG² = JM² - JG²
or, MG² = a² - (a²/3)
or, MG² = (2a²)/3
Therefore, MG = (√2a)/√3 = height of the regular tetrahedron.
Worked-out problems in finding surface area and volume of a tetrahedron
1. Each edge of a regular tetrahedron is of length 6 metre. Find its total surface area and volume.
Solution:
A regular tetrahedron is bounded by four congruent equilateral triangles.
By question, each edge of the tetrahedron is of length 6 metre.
Therefore, the total surface area of the tetrahedron
= 4 × area of the equilateral triangle of side 6 metres
= 4 × (√3)/4 ∙ 6² square metre
= 36√3 square metre
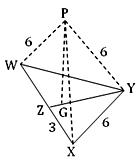
Let the equilateral triangle WXY be the base of the tetrahedron. If Z be the mid-point of WX, then YZ ┴ WX
Therefore, from the right - angled ∆ XYZ we get;
YZ² = XY² - XZ² = 6² - 3²
[Since, XY = 6 m. (given) and XZ = 1/2 ∙ WX = 3 m]
or, YZ² = 27
or, YZ 3√3
Let G be the centroid of the triangle WXY. Then,
YG = 2/3 ∙ YZ = 2/3 ∙ 3√3
Let PG be perpendicular to the plane of ∆ WXY at G. Then,
PG is the height of the tetrahedron.
Since, PG ┴ YG, hence from ∆ PYG we get,
PG² = PY² - YG² = 6² - (2√3)², [Since, PY = 6 m]
or, PG² = 36 - 12 = 24
or, PG = 2√6
Therefore, the required volume of the tetrahedron
= 1/3 × (area of ∆ WXY) × PG
= 1/3 ∙ (√3)/4 ∙ 6² ∙ 2√6 cubic metre.
= 18√2 cubic metre.
● Mensuration
- Formulas for 3D Shapes
- Volume and Surface Area of the Prism
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of Prism
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Right Pyramid
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Tetrahedron
- Volume of a Pyramid
- Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Problems on Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume of a Pyramid
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Practice Tetrahedron to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.