Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Formulas for 3D Shapes
Some of the useful math geometry formulas for 3D shapes are discussed below.
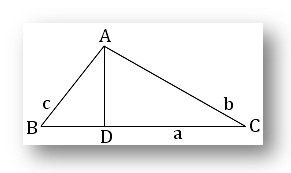
(i) Area of a Triangle: Let ABC be any triangle. If AD be perpendicular to BC and BC = a, CA = b, AB = c then the area of the triangle ABC (to be denoted by ⊿) is given by,
⊿ = ¹/₂ × base × altitude.
= ¹/₂ ∙ BC ∙ AD
(b) ⊿ = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Where 2x = a + b + c = perimeter of the ⊿ ABC.
(c) If the a be the length of a side of an equilateral triangle then its height = (√3/2) a and it’s area = (√3/4) a²
(ii) If a be the length and b, the breadth of a rectangle then its area = a ∙ b, length of its diagonal = √(a² + b² ) and its perimeter = 2 ( a + b).
(iii) If a be the length of a side of a square, then its area = a² length of its diagonal = a√2 and perimeter = 4a.
(iv) If the lengths of two diagonals of a rhombus be a and b respectively then its area = (1/2) ab and length of a side = (1/2) √(a² + b²)
(v) If a and b be the lengths of two parallel sides of a trapezium and h be the distance between the parallel sides then the area of the trapezium = (1/2) (a + b) ∙ h.
(vi) Area of a Regular Polygon: The area of a regular polygon of n sides = (na²/4) cot (π/n) where a is the length of a side of the polygon. In particular, if a be the length of a side of a regular hexagon then its area
= (6a²/4) ∙ cot (π/6) = (3√3/2) ∙ a²
(vii) The length of circumference of a circle of radius r is
2πr and
its area = πr²
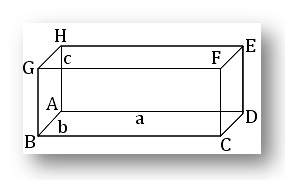
(viii) Rectangular Parallelopiped: If a, b and c be the length, breadth and height respectively of a rectangular parallelopiped then,
(a) the area of its surfaces = 2 ( ab + bc + ca)
(b) its volume = abc and
(c) the length of diagonal = √(a² + b² + c² ).
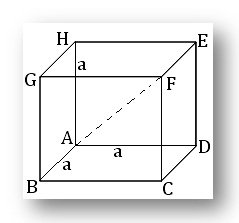
(ix) Cube: If the length of the side of a cube be a then,
(a) the area of its surfaces = 6a²,
(b) its volume = a³ and
(c) the length of the diagonal = √3a.
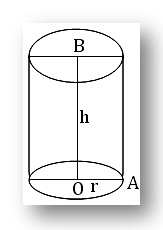
(x) Cylinder: Let r (= OA) be the radius of the base and h (=OB) be the height of a right circular cylinder ; then
(a) area of its curved surface = perimeter of base × height = 2πrh
(b) area of the whole surface = area of its curved surface + 2 × area of circular base
= 2πrh + 2πr²
= 2πr(h + r)
(c) volume of cylinder = area of base × height
= πr²h
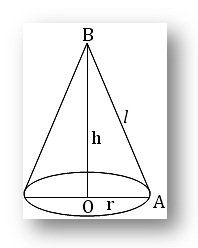
(xi) Cone: Let r (= OA) be the radius of the base, h (= OB), the height and I, the slant height of a right circular cone ; then
(a) l² = h² + r²
(b) area of its curved surface
= (1/2) × perimeter of the base × slant height =
(1/2)∙ 2πr ∙ l = πrl
(c) area of its whole surface = area of the curved surface + area of the circular base
= πrl + πr² = πrl + πr(l + r).
(d) volume of the cone = (1/3) × area of the base × height = (1/3)πr²h
● Mensuration
- Formulas for 3D Shapes
- Volume and Surface Area of the Prism
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of Prism
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Right Pyramid
- Volume and Whole Surface Area of Tetrahedron
- Volume of a Pyramid
- Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Problems on Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume and Surface Area of a Pyramid
- Worksheet on Volume of a Pyramid
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Formulas for 3D Shapes to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.