Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Distance Formula
We will discuss here how to find the distance between two points in a plane using the distance formula. As, we know the coordinates of two points in a plain fix the positions of the points in the plane and also the distance between them. The distance and the coordinates of the two points are related by an algebraic relation which can be deduced as shown below.
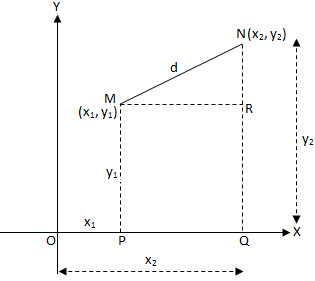
Let M (x\(_{1}\), y\(_{1}\)) and N (x\(_{2}\), y\(_{2}\)) are the two points in the plane. OX and OY being the rectangular axes of reference. Let MN = d. Draw MP ⊥ OX, NQ ⊥ OX and MR ⊥ NQ
According to the definition of the co-ordinates,
OP = x\(_{1}\), MP = y\(_{1}\), OQ = x\(_{2}\), NQ = y\(_{2}\)
From geometry, MR = PQ = OQ - OP = x\(_{2}\) - x\(_{1}\), and
NR = NQ - RQ = NQ - MP = y\(_{2}\) - y\(_{1}\).
In the right-angled triangle MRN,
MN\(^{2}\) = MR\(^{2}\) + NR\(^{2}\)
or, d\(^{2}\) = (x\(_{2}\) - x\(_{1}\))\(^{2}\) + (y\(_{2}\) - y\(_{1}\))\(^{2}\)
Therefore, d = \(\sqrt{(x_{2} - x_{1})^{2} + (y_{2} - y_{1})^{2}}\)
The distance between two points (x\(_{1}\), y\(_{1}\)) and (x\(_{2}\), y\(_{2}\)) = \(\sqrt{(x_{2} - x_{1})^{2} + (y_{2} - y_{1})^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{(difference of x-coordinates)^{2} + (difference of y-coordinates)^{2}}\)
The above formula is known as the distance formula.
Solved example to find the distance between two points in a plane:
Find the distance between the two points (2, 3) and (-1, -1).
= \(\sqrt{(-1 - 2)^{2} + (-1 - 3)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{(-3)^{2} + (-4)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{9 + 16}\)
= \(\sqrt{25}\)
= 5
That is 5 units.
Note:
(i) The distance between two points is always positive.
(ii) The distance of a point (x, y) from the origin (0, 0) = \(\sqrt{(x - 0)^{2} + (y - 0)^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{x^{2} + y^{2}}\)
(iii) The distance formula d\(^{2}\) = (x\(_{2}\) - x\(_{1}\))\(^{2}\) + (y\(_{2}\) - y\(_{1}\))\(^{2}\) should be understood as an algebraic relation between five variables x\(_{1}\), y\(_{1}\), x\(_{2}\), y\(_{2}\) and d. Given any four of them, the fifth variable can be known.
● Distance and Section Formulae
- Distance Formula
- Distance Properties in some Geometrical Figures
- Conditions of Collinearity of Three Points
- Problems on Distance Formula
- Distance of a Point from the Origin
- Distance Formula in Geometry
- Section Formula
- Midpoint Formula
- Centroid of a Triangle
- Worksheet on Distance Formula
- Worksheet on Collinearity of Three Points
- Worksheet on Finding the Centroid of a Triangle
- Worksheet on Section Formula
10th Grade Math
From Distance Formula to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.