Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Symmetric Difference using Venn Diagram
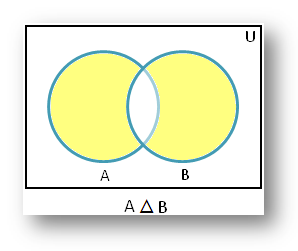
The symmetric difference using Venn diagram of two subsets A and B is a sub set of U, denoted by A △ B and is defined by
A △ B = (A – B) ∪ (B – A)
Let A and B are two sets. The symmetric difference of two sets A and B is the set (A – B) ∪ (B – A) and is denoted by A △ B.
Thus, A △ B = (A – B) ∪ (B – A) = {x : x ∉ A ∩ B}
or, A △ B = {x : [x ∈ A and x ∉ B] or [x ∈ B and x ∉ A]}
The shaded part of the given Venn diagram represents A △ B.
A △ B is
the set of all those elements which belongs either to A or to B but not to
both.
A △ B is also expressed by (A ∪ B) - (B ∩ A).
It follows that A △ ∅ = A for all subset A,
A △ A = ∅ for all subset A
Properties of symmetric difference:
(i) A △ B = B △ A; [Commutative property]
(ii) A △ (B △ C) = (A △ B) △ C [Associative property]
Example to find the symmetric difference using Venn diagram:
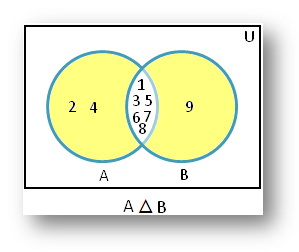
1. If A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} and B = {1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, then A – B = {2, 4}, B – A = {9} and A △ B = {2, 4, 9}.
Therefore, the shaded part of the Venn diagram represents A △ B = {2, 4, 9}.
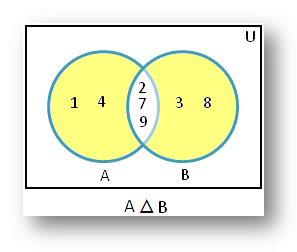
2. If A = {1, 2, 4, 7, 9} and B = {2, 3, 7, 8, 9} then A △ B = {1, 3, 4, 8}
Therefore, the shaded part of the Venn diagram represents A △ B = {1, 3, 4, 8}.
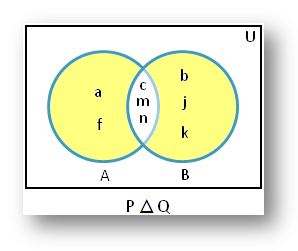
3. If P = {a, c, f, m, n} and Q = {b, c, m, n, j, k} then P △ Q = {a, b, f, j, k}
Therefore, the shaded part of the Venn diagram represents P △ Q = {a, b, f, j, k}.
● Set Theory
● Sets
● Subset
● Practice Test on Sets and Subsets
● Problems on Operation on Sets
● Practice Test on Operations on Sets
● Venn Diagrams in Different Situations
● Relationship in Sets using Venn Diagram
● Practice Test on Venn Diagrams
● Symmetric Difference using Venn Diagram
8th Grade Math Practice
From Symmetric Difference using Venn Diagram to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.