Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Side Angle Side Congruence
Conditions for the SAS - Side Angle Side congruence
Two triangles are said to be congruent if two sides and the included angle of one are respectively equal to the two sides and the included angle of the other.
Experiment to prove Congruence with SAS:
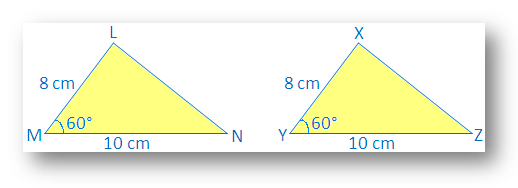
∆LMN with LM – 8 cm, MN – 10 cm, ∠M – 60°
Also, draw another ∆XYZ with XY = 8cm, YZ = 10cm, ∠Y= 60°.
We see that LM = XY, AC = ∠M = ∠Y and MN = YZ
Make a trace copy of ∆XYZ and try to make it cover ∆LMN with X on L, Y on M and Z on N.
We observe that: two triangle cover each other exactly.
Therefore ∆LMN ≅ ∆XYZ
Worked-out problems on side angle side congruence triangles (SAS postulate):
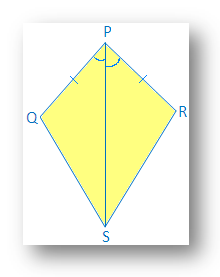
1. In the kite shown, PQ = PS and ∠QPR = ∠SPR.
(i) Find the third pair of corresponding parts to make ∆ PQR ≅ ∆PSR by SAS congruence condition.
(ii) Is ∠QRP = ∠SRP?
Solution:
(i) In ∆ PQR and ∆ PSR
PQ = PS → given
∠QPR = ∠SPR → given
PR = PR → common
Therefore, ∆PQR ≅ ∆PSR by SAS congruence condition
(ii) Yes, ∠QRP = ∠SRP (corresponding parts of congruence triangle).
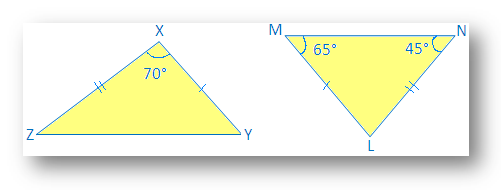
2. Identify the congruent triangle:
Solution:
In ∆LMN,
65° + 45° + ∠L = 180°
110° + ∠L = 180°
∠L = 180° - 110°
Therefore, ∠L = 70°
Now in ∆XYZ and ∆LMN
∠X = ∠L (given in the picture)
XY = LM (given in the picture)
XZ = NL (given in the picture)
Therefore, ∆XYZ ≅ ∆LMN by SAS congruence axiom
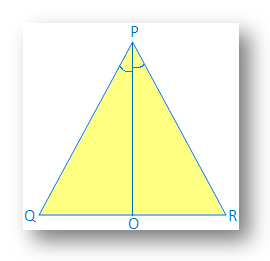
3. By using SAS congruency proof that, angles opposite to equal side of an isosceles triangle are equal.
Solution:
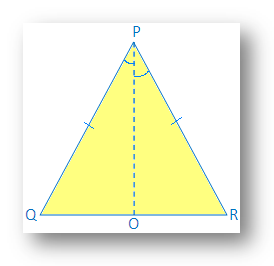
Given: ∆PQR is isosceles and PQ = PR
Construction: Draw PO, the angle bisector of ∠P, PO meets QR at O.
Proof: In ∆QPO and ∆RPO
PQ = PR (given)
PO = PO (common)
∠QPO = ∠RPO (by construction)
Therefore, ∆QPO ≅ ∆RPO (by SAS congruence)
Therefore, ∠PQO = ∠PRO (by corresponding parts of congruent triangle)
4. Show that bisector of the vertical angle of an isosceles triangle bisects the base at right angle.
Solution:
Given: ∆PQR is isosceles, and PO bisects ∠P
Proof: In ∆POQ and ∆POR
PQ = PR (isosceles triangle)
∠QPO = ∠RPO (PO bisects ∠P)
PO = PO (common)
Therefore, ∆ POQ ≅ ∆ POR (by SAS congruence axiom)
Therefore, ∠POQ = ∠POR (by corresponding parts of congruent triangle)
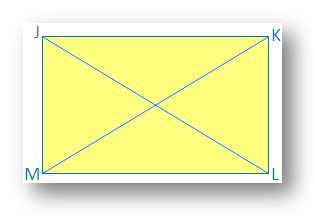
5. Diagonals of a rectangle are equal.
Solution:
In the rectangle JKLM, JL and KM are the two diagonals.
It is required to prove that JL = KM.
Proof: In ∆JKL and ∆KLM,
JK = ML [Opposite of a parallelogram]
KL = KL [Common side]
∠JKL = ∠KLM [Both are right angle]
Therefore, ∆JKL ≅ ∆KLM [By Side Angle Side Congruence]
Therefore, JL = KM [Corresponding parts of congruence triangle]
Note: Diagonals of a square are equal to one another.
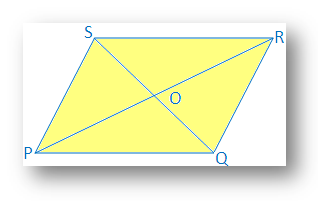
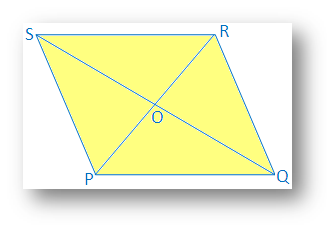
6. If two diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other, prove that the quadrilateral will be parallelogram.
Solution:
Two diagonals PR and QS of quadrilateral PQRS bisect each at point O.
Therefore, PO = OR and QO = OS
It is required to prove that PQRS is a parallelogram.
Proof: In ∆POQ and ∆ROS
PO = OR [Given]
QO = OS [Given]
∠POQ = ∠ROS
Therefore, ∆POQ ≅ ∆ROS [By Side Angle Side Congruence]
Therefore, ∠OPQ = ∠ORS [Corresponding angle of congruence triangle]
Since, PR joins PQ and RS, and two alternate angles are equal
Therefore, PQ ∥ SR
Similarly, it can be proved that, ∆POS ≅ ∆QOR and PS ∥ QR
Therefore, in quadrilateral PQRS,
PQ ∥ SR and PS ∥ QR
Therefore, PQRS is a parallelogram.
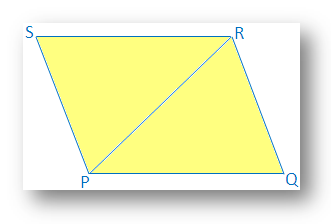
7. If a pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal and parallel, prove that it will be parallelogram.
Solution:
In a quadrilateral PQRS,
PQ = SR and
PQ ∥ SR.
It is required to prove that PQRS is parallelogram.
Construction: Diagonal PR is drawn.
Proof: In ∆PQR and ∆RSP
PQ = SR [Given]
∠QPR = ∠PRS [Since PQ ∥ SR and PR is transversal]
PR = PR [Common]
Therefore, ∆PQR ≅ ∆RSP [By SAS congruence condition]
Therefore, ∠QRP = ∠SPR [Corresponding parts of congruence triangle]
But PR joins QR and PS and two alternate angles are equal (∠QRP = ∠SPR).
Therefore, QR ∥ PS.
Therefore, in quadrilateral PQRS,
PQ ∥ SR [Given]
QR ∥ PS [Already proved]
Therefore, PQRS is a parallelogram.
Note: If a pair of line-segments are equal and parallel, so that line-segments formed by joining the end points, will be equal and parallel.
8. Two diagonals of a quadrilateral are unequal and bisect each other at right angle. Prove that the quadrilateral is a non square rhombus.
Solution:
Both the diagonals PR and QS of quadrilateral PQRS bisect each other at point O.
PO = OR; QO = OS; PR ≠ QS and PR ⊥ QS.
It is required to prove that PQRS is a rhombus.
Proof: The diagonals of a quadrilateral PQRS bisect each other.
Therefore, PQRS is a parallelogram.
Again, in ∆POS and ∆ROD,
PO = OR [By hypothesis]
OS = OS [Common side]
And ∠POs = ∠ROS [Since PR ⊥ QS]
Therefore, ∆POS ≅ ∆ROD, [By Side Angle Side Congruence]
Therefore, PS = RS [Corresponding sides of congruent triangle]
Similarly we can prove that PS = SR = RQ = QP
Therefore, Quadrilateral PQRS is a parallelogram whose four sides are equal and diagonals are unequal.
Therefore, PQRS is a rhombus, which cannot be a square.
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Side Angle Side Congruence to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.