Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Congruent Triangles
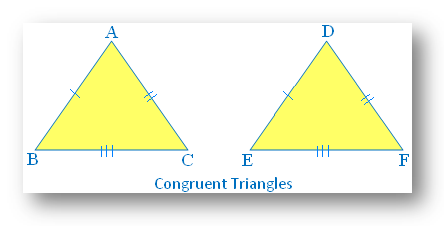
Congruent triangles are those two triangles which are said to be congruent if and only if one of them can be made to superpose on the other so as to cover it exactly.
Let ∆ABC and ∆DEF be two congruent triangles, then we can superpose ∆ABC on ∆DEF so as to cover it exactly. The vertices of ∆ABC fall on the vertices of ∆DEF in the following order A ↔ D, B ↔ E, C ↔ F.
Thus, the order in which vertices match automatically determines the correspondence between the sides and angles of the triangle. Corresponding parts are also called matching parts of triangles.
So, we have six equalities
Corresponding sides are congruent: AB = DE BC = EF CA = FD
Corresponding angles are congruent: ∠A = ∠D ∠B = ∠E ∠C = ∠F
In the congruent triangles we will observe six correspondences between their verities. The symbol used to denote correspondence is ‘↔’
A ↔ D B ↔ E C ↔ F written as ABC ↔ DEF
A ↔ E B ↔ F C ↔ D written as ABC ↔ EFD
A ↔ F B ↔ D C ↔ E written as ABC ↔ FDE
A ↔ D B ↔ F C ↔ E written as ABC ↔ DFE
A ↔ E B ↔ D C ↔ F written as ABC ↔ EDF
A ↔ F B ↔ E C ↔ D written as ABC ↔ FED
Therefore, ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF
Note:
The order of letters in the name of two triangles will indicated the correspondence between the vertices of two triangles. Thus, two triangles are congruent only if there exist a correspondence between their vertices such that the correspondence sides and correspondence angles of two triangles are equal.
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Congruent Triangles to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.