Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Angle Side Angle Congruence
Conditions for the ASA - Angle Side Angle congruence
Two triangles are said to be congruent if two angles and the included side of the one are respectively equal to the two angles and the included side of the other.
Experiment to prove Congruence with ASA:
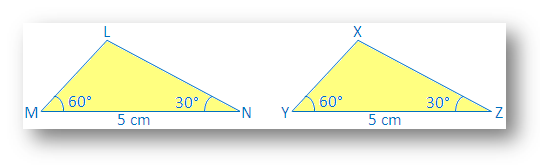
Draw a ∆LMN with ∠M = 60°, MN = 5 cm, ∠N = 30°.
Also, draw another ∆XYZ with ∠Y = 60°, YZ = 5cm, ∠Z = 30°.
We see that ∠M = ∠Y, MN = YZ and ∠N = ∠Z.
Make a trace copy of ∆XYZ and try to make it cover ∆LMN with X on L, Y on M and Z on N.
We observe that: two triangles cover each other exactly.
Therefore ∆LMN ≅ ∆XYZ
Worked-out problems on angle side angle congruence triangles (ASA postulate):
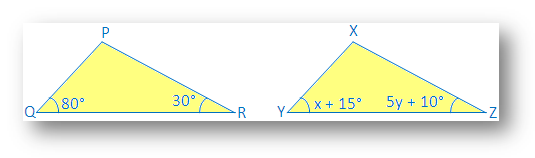
1. ∆PQR ≅ ∆XYZ by ASA congruence condition. Find the value of x and y.
Solution:
WE know ∆ PQR ≅ ∆XYZ by ASA congruence.
Therefore ∠Q = ∠Y i.e., x + 15 = 80° and ∠R = ∠Z i.e., 5y + 10 = 30°.
Also, QR = YZ.
Since, x + 15 = 80°
Therefore x = 80 – 15 = 65°
Also, 5y + 10 = 30°
So, 5y = 30 – 10
Therefore, 5y = 20
⇒ y = 20/5
⇒ y = 4°
Therefore, the value of x and y are 65° and 4°.
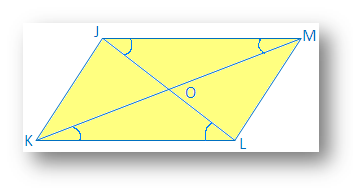
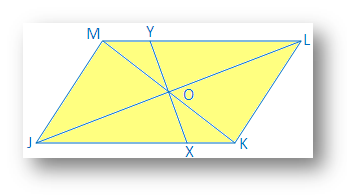
2. Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
In a parallelogram JKLM, diagonal JL and KM intersect at O
It is required to prove that JO = OL and KO = OM
Proof: In ∆JOM and ∆KOL
∠OJM = ∠OLK [since, JM ∥ KL and JL is the transversal]
JM = KL [opposite sides of a parallelogram]
∠OMJ = ∠OKL [since, JM ∥ KL and KM is the transversal]
Therefore, ∆JOM and ∆KOL [Angle-Side-Angel]
Therefore, JO = OL and KO = OM [Sides of congruent triangle]
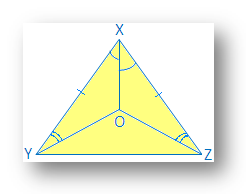
3. ∆XYZ is an equilateral triangle such that XO bisects ∠X.
Also, ∠XYO = ∠XZO. Show that ∆YXO ≅ ∆ZXO
Solution:
∆ XYZ is an equilateral
Therefore, XY = YZ = ZX
Given: XY bisects ∠X.
Therefore, ∠YXO = ∠ZXO
Given: ∠XYO = ∠XZO
Given: XY = XZ
Therefore, ∆YXO ≅ ∆ZXO by ASA congruence condition
4. The straight line drawn through the intersection of the two diagonals of a parallelogram divide it into two equal parts.
Solution:
O is the point of intersection of the two diagonals JL and KM of the parallelogram JKLM.
Straight line XOY meets JK and LM at the point X and Y respectively.
It is required to prove that quadrilateral JXYM equal to quadrilateral LYXK.
Proof: In ∆JXO and ∆LYO, JO = OL [diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other]
∠OJX= alternate ∠OLY
∠JOX = ∠LOY
Therefore, ∆ JOX ≅ ∆ LOY [by angle side angle congruence]
Therefore, JX = LY
Therefore, KX = MY [since, JK = ML]
Now in quadrilaterals JXYM and LYXK, JX = LY; XY = YX, YM = XK and MJ = KL and ∠MJX = ∠KLY
Hence it is proved that in the two quadrilaterals the sides are equal to each other and the included angles of two equal sides are also equal.
Therefore, quadrilateral JXYM equal to quadrilateral XKLY.
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Angle Side Angle Congruence to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.