Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Word problems on Pythagorean Theorem
Learn how to solve different types of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem.
Pythagoras Theorem can be used to solve the problems step-by-step when we know the length of two sides of a right angled triangle and we need to get the length of the third side.
Three cases of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem:
Case 1: To find the hypotenuse where perpendicular and base are given.
Case 2: To find the base where perpendicular and hypotenuse are given.
Case 3: To find the perpendicular where base and hypotenuse are given.
Word problems using the Pythagorean Theorem:
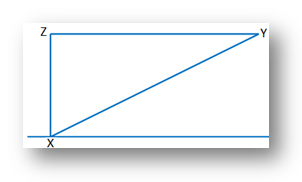
1. A person has to walk 100 m to go from position X in the north of east
direction to the position B and then to the west of Y to reach finally at
position Z. The position Z is situated at the north of X and at a distance of
60 m from X. Find the distance between X and Y.
|
Solution: Let XY = x m Therefore, YZ = (100 – x) m
In ∆ XYZ, ∠Z = 90° Therefore, by Pythagoras theorem XY2 = YZ2 + XZ2⇒ x2 = (100 – x)2 + 602 ⇒ |
⇒ 200x = 10000 + 3600
⇒ 200x = 13600
⇒ x = 13600/200
⇒ x = 68
Therefore, distance between X and Y = 68 meters.
Solution:
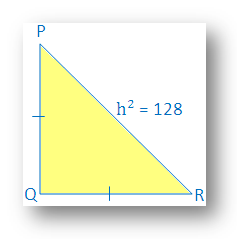
Let the two equal side of right angled isosceles triangle, right angled at Q be k cm.
Given: h2 = 128
So, we get
PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
h2 = k2 + k2
⇒ 128 = 2k2
⇒ 128/2 = k2
⇒ 64 = k2
⇒ √64 = k
⇒ 8 = k
Therefore, length of each side is 8 cm.
Using the formula solve more word problems on Pythagorean Theorem.
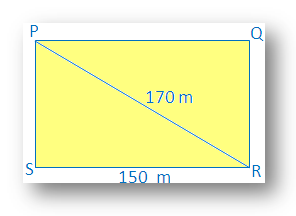
3. Find the perimeter of a rectangle whose length is 150 m and the diagonal is 170 m.
Solution:
In a rectangle, each angle measures 90°.
Therefore PSR is right angled at S
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get
⇒ PS2 + SR2 = PR2⇒ PS2 + 1502 = 1702
⇒ PS2 = 1702 – 1502
⇒ PS2= (170 + 150) (170 – 150), [using the formula of a2 - b2 = (a + b) (a - b)]
⇒ PS2= 320 × 20
⇒ PS2 = 6400
⇒ PS = √6400
⇒ PS = 80
Therefore perimeter of the rectangle PQRS = 2 (length + width)
= 2 (150 + 80) m
= 2 (230) m
= 460 m
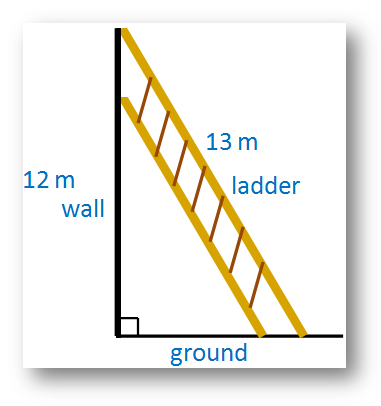
4. A ladder 13 m long is placed on the ground in such a way that it touches the top of a vertical wall 12 m high. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the bottom of the wall.
Solution:
Let the required distance be x meters. Here, the ladder, the wall and the ground from a right-angled triangle. The ladder is the hypotenuse of that triangle.
According to Pythagorean Theorem,
x2 + 122 = 132⇒ x2 = 132 – 122
⇒ x2 = (13 + 12) (13 – 12)
⇒ x2 = (25) (1)
⇒ x2 = 25
⇒ x = √25
⇒ x = 5
Therefore, distance of the foot of the ladder from the bottom of the wall = 5 meters.
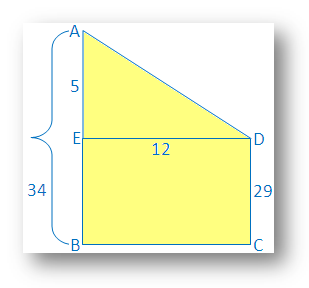
5. The height of two building is 34 m and 29 m respectively. If the distance between the two building is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
Solution:
The vertical buildings AB and CD are 34 m and 29 m respectively.
Draw DE ┴ AB
Then AE = AB – EB but EB = BC
Therefore
AE = 34 m - 29 m = 5 m
Now, AED is right angled triangle and right angled at E.
Therefor,
AD2 = AE2 + ED2⇒ AD2 = 52 + 122
⇒ AD2 = 25 + 144
⇒ AD2 = 169
⇒ AD = √169
⇒ AD = 13
Therefore the distance between their tops = 13 m.
The examples will help us to solve various types of word problems on Pythagorean Theorem.
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Word problems on Pythagorean Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.