Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Proof of Pythagorean Theorem
The proof of Pythagorean Theorem in mathematics is very important.
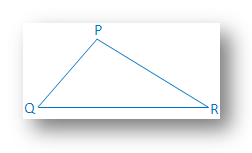
In a right angle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
States that in a right triangle that, the square of a (a2) plus the square of b (b2) is equal to the square of c (c2).
In short it is written as: a2 + b2 = c2
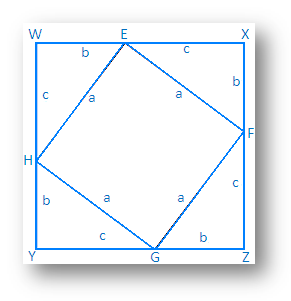
Let QR = a, RP = b and PQ = c. Now, draw a square WXYZ of side (b + c). Take points E, F, G, H on sides WX, XY, YZ and ZW respectively such that WE = XF = YG = ZH = b.
Then, we will get 4 right-angled triangle, hypotenuse of each of
them is ‘a’: remaining sides of each of them are band c. Remaining part of the
figure is the
Now, we are sure that square WXYZ = square EFGH + 4 ∆ GYF
or, (b + c)2 = a2 + 4 ∙ 1/2 b ∙ c
or, b2 + c2 +
or, b2 + c2 = a2
Proof of Pythagorean Theorem using Algebra:
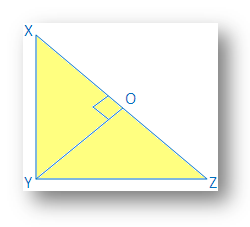
Given: A ∆ XYZ in which ∠XYZ = 90°.To prove: XZ2 = XY2 + YZ2
Construction: Draw YO ⊥ XZ
Proof: In ∆XOY and ∆XYZ, we have,
∠X = ∠X → common
∠XOY = ∠XYZ → each equal to 90°
Therefore, ∆ XOY ~ ∆ XYZ → by AA-similarity
⇒ XO/XY = XY/XZ
⇒ XO × XZ = XY2 ----------------- (i)In ∆YOZ and ∆XYZ, we have,
∠Z = ∠Z → common
∠YOZ = ∠XYZ → each equal to 90°
Therefore, ∆ YOZ ~ ∆ XYZ → by AA-similarity
⇒ OZ/YZ = YZ/XZ
⇒ OZ × XZ = YZ2 ----------------- (ii)From (i) and (ii) we get,
XO × XZ + OZ × XZ = (XY2 + YZ2)
⇒ (XO + OZ) × XZ = (XY2 + YZ2)
⇒ XZ × XZ = (XY2 + YZ2)
⇒ XZ 2 = (XY2 + YZ2)
Conditions for the Congruence of Triangles
Right Angle Hypotenuse Side congruence
Converse of Pythagorean Theorem
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Proof of Pythagorean Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.