Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Representing Decimals on Number Line
Representing decimals on number line shows the intervals between two integers which will help us to increase the basic concept on formation of decimal numbers.
We have learnt to represent fraction on the number line.
Representing a decimal and a fraction on the number line is one and the same thing. In other words, we represent decimal on a number line too.
Working Rules for Representing Decimals on Number Line:
Step I: Draw or number line and mark the whole numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, etc. on it.
Step II: Divide the portion between the whole numbers (like 0 and 1, 1 and 2, 2 and 3 etc..) into equal 2 parts or 3 parts or 4 parts or any other parts as per requirement.
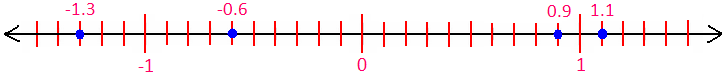
1. Represent the following decimals 0.9, -1.3, -0.6 and 1.1 on a number line.
Since, 0.9 = \(\frac{9}{10}\), -1.3 = -\(\frac{13}{10}\), -0.6 = -\(\frac{6}{10}\) and 1.1 = \(\frac{11}{10}\)
Divide the space between every pair of consecutive integers (on the number line) in 10 equal parts. Each part so obtained will represent the fraction \(\frac{1}{10}\) i.e., decimal 0.1 and the number line obtained will be of the form:
To mark 0.9; move nine parts on the right-side of zero.
To mark -1.3; move thirteen parts on the left-side of zero.
To mark -0.6; move six parts on the left-side of zero.
To mark 1.1; move eleven parts on the right-side of zero.
The following diagram shows markings of decimals 0.9, -1.3, -0.6 and 1.1 on a number line.
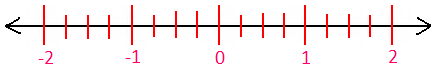
2. Represent the decimals: 0.3, 0.7, -0.4 and -1.2 on a number line.
Since, 0.3 = \(\frac{3}{10}\), 0.7 = \(\frac{7}{10}\), -0.4 = -\(\frac{4}{10}\) and -1.2 = -\(\frac{12}{10}\)
Divide the space between every pair of consecutive integers (on the number line) in 10 equal parts. Each part so obtained will represent the fraction \(\frac{1}{10}\) i.e., decimal 0.1 and the number line obtained will be of the form:
To mark 0.3; move three parts on the right-side of zero.
To mark 0.7; move seven parts on the right-side of zero.
To mark -0.4; move four parts on the left-side of zero.
To mark -1.2; move twelve parts on the left-side of zero.
The
following diagram shows markings of decimals 0.3, 0.7, -0.4 and -1.2 on a
number line.
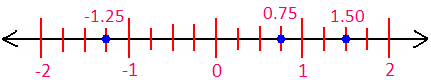
3. Draw a number line to represent decimals: 0.75, 1.50 and -1.25
Since, 0.75 = \(\frac{75}{100}\), 1.50 = \(\frac{150}{100}\) and -1.25 = -\(\frac{125}{100}\)
Divide the space between every pair of consecutive integers (on the number line) in 4 equal parts. Each part so obtained will represent the fraction \(\frac{1}{25}\) i.e., decimal 0.25 and the number line obtained will be of the form:
To mark 0.75; move three parts on the right-side of zero.
To mark 1.50; move six parts on the right-side of zero.
To mark -1.25; move five parts on the left-side of zero.
The following diagram shows markings of decimals 0.75, 1.50 and -1.25 on a number line.
4. Represent the following decimals on the number line.
(i) 0.5
(ii) 1.8
(iii) 2.3
Solution:
(i) We know that 0.5 is more than zero but less than 1. There are 5 tenths in 0.5. Divide the unit length between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts and take 5 parts as shown in figure at A.
Thus, point A shows 10 or 0.5
(ii) The decimal 1.8 has 1 as whole number and 8 tenths. Therefore, the point lies between 1 and 2. Divide the unit length between 1 and 2 into 10 equal parts and take 8 parts as shown in the figure at B. 18
Thus, point B shows \(\frac{18}{10}\) or 1.8.
(iii) In 2.3, the whole number part is 2 and decimal part is 3.
Therefore, it lies between 2 and 3. Divide the unit length between 2 and 3 into 10 equal parts and take 3 part as shown in the figure at C.
Thus, point C shows \(\frac{23}{10}\) or 2.3.
Thus, we have learnt how to represent and draw any decimal points on the number line.
From Representing Decimals on Number Line to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.