Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Proof of Compound Angle Formula
sin (α + β)
We will learn step-by-step the proof of compound angle formula sin (α + β). Here we will derive formula for trigonometric function of the sum of two real numbers or angles and their related result. The basic results are called trigonometric identities.
The expansion of sin (α + β) is generally called addition formulae. In the geometrical proof of the addition formulae we are assuming that α, β and (α + β) are positive acute angles. But these formulae are true for any positive or negative values of α and β.
Now we will prove that, sin (α + β) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β; where α and β are positive acute angles and α + β < 90°.
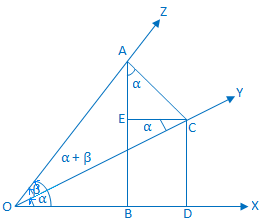
Let a rotating line OX rotate about O in the anti-clockwise direction. From starting position to its initial position OX makes out an acute ∠XOY = α.
Again, the rotating line rotates further in the same
direction and starting from the position OY makes out an acute ∠YOZ
= β.
Thus, ∠XOZ = α + β < 90°.
We are suppose to prove that, sin (α + β) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β.
|
Construction: On the bounding line of the compound angle (α + β) take a point A on OZ, and draw AB and AC perpendiculars to OX and OY respectively. Again, from C draw perpendiculars CD and CE upon OX and AB respectively. |
Proof: From triangle ACE we get, ∠EAC = 90° - ∠ACE = ∠ECO = alternate ∠COX = α.
Now, from the right-angled triangle AOB we get,
sin (α + β) = \(\frac{AB}{OA}\)
= \(\frac{AE + EB}{OA}\)
= \(\frac{AE}{OA}\) + \(\frac{EB}{OA}\)
= \(\frac{AE}{OA}\) + \(\frac{CD}{OA}\)
= \(\frac{AE}{AC}\) ∙ \(\frac{AC}{OA}\) + \(\frac{CD}{OC}\) ∙ \(\frac{OC}{OA}\)
= cos ∠EAC sin β + sin α cos β
= sin α cos β + cos α sin β, (since we know, ∠EAC = α)
Therefore, sin (α + β) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β. Proved.
1. Using the t-ratios of 30° and 45°, evaluate sin 75°
Solution:
sin 75°
= sin (45° + 30°)
= sin 45° cos 30° + cos 45° sin 30
= \(\frac{1}{√2}\) ∙ \(\frac{√3}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{√2}\) ∙ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{√3 + 1}{2√2}\)
2. From the formula of sin (α + β) deduce the formulae of cos (α + β) and cos (α - β).
Solution:
We know that, sin (α + β) = sin α cos β + cos α sin β …….. (i)
Replacing α by (90° + α) on both sides of (i) we get,
sin (90° + α + β)
= sin {(90° + α) + β} = sin (90° + α) cos β + cos (90° + α) sin β, [Applying the formula of sin (α + β)]
⇒ sin {90° + (α + β)} = cos α cos β - sin α sin β, [since sin (90° + α) = cos α and cos (90° + α) = - sin α]
⇒ cos (α + β) = cos α cos β - sin α sin β …….. (ii)
Again, replacing β by (- β) on both sides of (ii) we get,
cos (α - β) = cos α cos (- β) - sin α sin (- β)
⇒ cos (α - β) = cos α cos β + sin α sin β, [since cos (- β) = cos β and sin (- β) = - sin β]
3. If sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\), cos y = -\(\frac{12}{13}\) and x, y both lie in the second quadrant, find the value of sin (x + y).
Solution:
Given, sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\), cos y = -\(\frac{12}{13}\) and x, y both lie in the second quadrant.
We know that cos\(^{2}\) x = 1 - sin\(^{2}\) x = 1 - (\(\frac{3}{5}\))\(^{2}\) = 1 - \(\frac{9}{25}\) = \(\frac{16}{25}\)
⇒ cos x = ± \(\frac{4}{5}\).
Since x lies in the second quadrant, cos x is – ve
Therefore, cos x = -\(\frac{4}{5}\).
Also, sin\(^{2}\) y = 1 - cos\(^{2}\) y = 1 - (-\(\frac{12}{13}\))\(^{2}\) = 1 - \(\frac{144}{169}\) = \(\frac{25}{169}\)
⇒ sin y = ± \(\frac{5}{13}\)
Since y lies in the second quadrant, sin y is + ve
Therefore, sin y = \(\frac{5}{13}\)
Now, sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y
= \(\frac{3}{5}\) ∙ (- \(\frac{12}{13}\)) + (- \(\frac{4}{5}\)) ∙ \(\frac{5}{13}\)
= - \(\frac{36}{65}\) - \(\frac{20}{65}\)
= - \(\frac{56}{65}\)
4. If m sin (α + x) = n sin (α + y), show that, tan α = \(\frac{n sin y - m sin x}{m cos x - n cos y}\)
Solution:
Given, m sin (α + x) = n sin (α + y)
Therefore, m (sin α cos x + cos α sin x) = n (sin α cos y+ cos α sin y), [Applying the formula of sin (α + β)]
m sin α cos x + m cos α sin x = n sin α cos y + n cos α sin y,
or, m sin α cos x - n sin α cos y = n cos α sin y - m cos α sin x
or, sin α (m cos x - n cos y) = cos α (n sin y - m sin x)
or, \(\frac{sin α}{cos α}\) = \(\frac{n sin y - m sin x}{m cos x - n cos y}\).
or, tan α = \(\frac{n sin y - m sin x}{m cos x - n cos y}\). Proved.
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula sin (α + β)
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula sin (α - β)
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula cos (α + β)
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula cos (α - β)
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula sin 22 α - sin 22 β
- Proof of Compound Angle Formula cos 22 α - sin 22 β
- Proof of Tangent Formula tan (α + β)
- Proof of Tangent Formula tan (α - β)
- Proof of Cotangent Formula cot (α + β)
- Proof of Cotangent Formula cot (α - β)
- Expansion of sin (A + B + C)
- Expansion of sin (A - B + C)
- Expansion of cos (A + B + C)
- Expansion of tan (A + B + C)
- Compound Angle Formulae
- Problems using Compound Angle Formulae
- Problems on Compound Angles
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Proof of Compound Angle Formula sin (α + β) to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.