Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Place Value and Face Value
FACE VALUE AND PLACE VALUE OF A DIGIT IN A NUMERAL
Face Value: The face value of a digit in a numeral is the actual value of a digit at whatever place it may be.
Place Value: The place value of a digit in a numeral depends on the position it occupies in a numeral.
Let us consider the numeral 675:
Arrange the digits of 675 in the place value chart as shown below:
H
T
O
6
7
5
From the place value chart, we have:
The place value of 6 = 6 hundreds
= 600; the face value of 6 = 6,
The place value of 7 = 7 tens
= 70; the face value of 7 = 7,
The place value of 5 = 5 ones
= 5; the face value of 5 = 5.
Note:
The place value of 0 is always zero, irrespective of its place in the numeral. For example, the place value of 0 in 609 and 805 is 0 in each case.
Let us look at the digits 1 and 2.
We know that digit 2 is greater than the digit 1 or 2 > 1.
With the digits 1 and 2 we can make the numbers 12 and 21.
Face value is the value of a digit in a number.
So, the digit 1 has the same face value in both the numbers `12 and 21.
Similarly, the digit 2 has the same face value in the numbers 12 and 21.
Therefore, the face value of a digit always remains the same.
Face Value of a Number Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
We write 12 and 21 by using ones and tens as:
In the number 12, the value of 2 (i.e., 2 ones) is less than the value of 1 (i.e., 1 ten)
In the number 21, the value of 2 (i.e., 2 tens) is greater than the value of 1 (i.e., 1 one)
In both the numbers 12 and 21 there value is different this is because of its place value.
Place value of a digit is the value of a digit because of its place in a number.
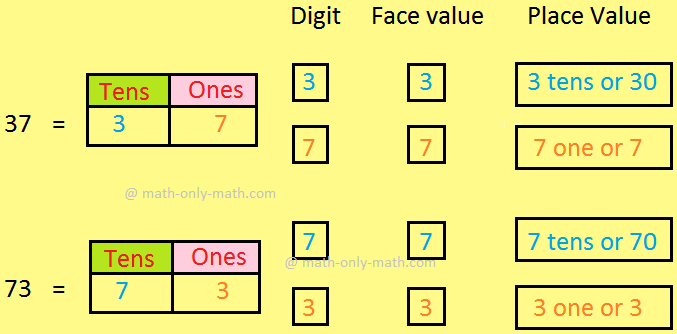
Similarly, the digit 3 and 7 can be used to make the number 37 and 73.
Place Value of a Number Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
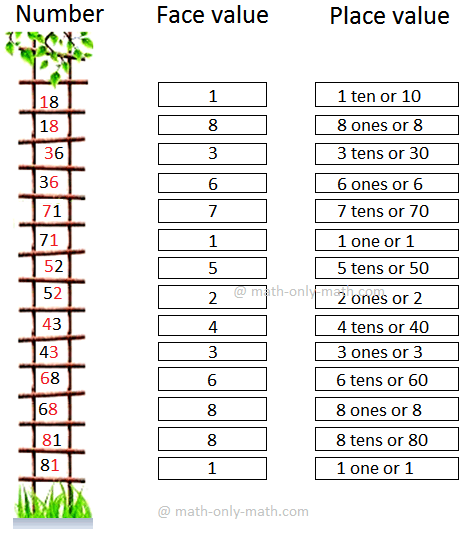
Let us look at the example to understand the difference of face value and place value.
Face value and place value of the digits are coloured in red.
|
Number 18 18 36 36 71 71 52 52 43 43 68 68 81 81 |
Face value Place value 1 1 ten or 10 8 8 ones or 8 3 3 tens or 30 6 6 ones or 6 7 7 tens or 70 1 1 one or 1 5 5 tens or 50 2 2 ones or 2 4 4 tens or 40 3 3 ones or 3 6 6 tens or 60 8 8 ones or 8 8 8 tens or 80 1 1 one or 1 |
Learn the easiest way to understand the basic concept on place value and face value in the second grade.
Suppose we write a number in figures 435 in words we write four hundred thirty five.
Thus,
435 means 4 hundreds 3 tens and 5 ones
= 400 + 30 + 5
We write the expanded form of the numbers as
435 = 400 + 30 + 5
Hence, in the number 435, the place value of 4, 3 and 5 are 400, 30 and 5 respectively.
In place value and face value let us first understand the concept of place value of the concerned digits by following the examples.
(i) 350 means: 3 hundreds 5 tens and 0 ones
= 300 + 50 + 0
350 = 300 + 50 + 0
In the number 350, the place value of 3, 5 and 0 are 300, 50 and 0 respectively.
(ii) 602 means: 6 hundreds 0 tens and 2 ones
= 600 + 00 + 2
602 = 600 + 00 + 2
In the number 602, the place value of 6, 0 and 2 are 600, 00 and 2 respectively.
(iii) 278 means: 2 hundreds 7 tens and 8 ones
= 200 + 70 + 8
278 = 200 + 70 + 8
In the number 278, the place value of 2, 7 and 8 are 200, 70 and 8 respectively.
(iv) 777 means: 7 hundreds 7 tens and 7 ones
= 700 + 70 + 7
777 = 700 + 70 + 7
In the number 777, the place value of 7, 7 and 7 are 700, 70 and 7 respectively.
(v) 63 means: 0 hundreds 6 tens and 3 ones
= 000 + 60 + 3
63 = 000 + 60 + 3
In the number 63, the place value of 0, 6 and 3 are 000, 60 and 3 respectively.
Therefore, the place value of a digit in a number is the value of the place which it has in the number.
In the number 549, the place value of 5 is 500, of 4 is 40 and 9 is 9 as 5 occupies the place of hundreds, 4 occupies the place of tens and 9 occupies the place of ones or unit in the given number 549.
We know the digit in a number occupy the place of ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc. from extreme right to left and have the value of that place.
The original value of a digit is called its face value.
In the number 385;
the place value of 3 is 300 and its face value is 3,
the place value of 8 is 80 and its face value is 8,
the place value of 5 is 5 and its face value is 5.
Therefore, in any number its important to know the place value and face value of a concerned digit.
Place Value and Face Value of a Number Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Worksheet on Place Value and Face Value
Questions and Answers on Place Value and Face Value:
1. Fill in the blanks. One has been done for you.
(i) 1 ten = 10 ones
(ii) 2 tens = __________
(iii) 3 tens = __________
(iv) 4 tens = __________
(v) 5 tens = __________
(vi) 6 tens = __________
(vii) 7 tens = __________
(viii) 8 tens = __________
(ix) 9 tens = __________
Word Problem on Face Value Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
2. Write the place value of all the digits in the following numbers.
|
|
Number |
Face Value |
Place Value |
3. Write the place value of the coloured digits. One has been done for you.
|
(i) |
725 |
2 tens or 20 |
|
(ii) |
425 |
_______________ |
|
(iii) |
806 |
_______________ |
|
(iv) |
219 |
_______________ |
|
(v) |
423 |
_______________ |
|
(vi) |
990 |
_______________ |
|
(vii) |
341 |
_______________ |
|
(viii) |
889 |
_______________ |
Word Problems on Combination of Place Value and Face Value Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
4. Write the face value of each digit in the numeral 785:
(i) Face value of 7 = _____
(i) Face value of 8 = _____
(i) Face value of 5 = _____
From Place Value and Face Value to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.

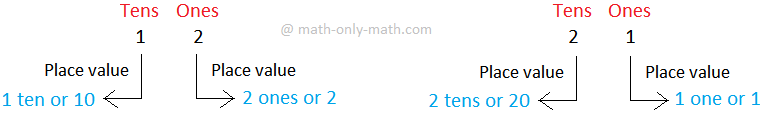


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.