Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are the fractions having the same value. Same fraction can be represented in many ways. Let us take the following example.
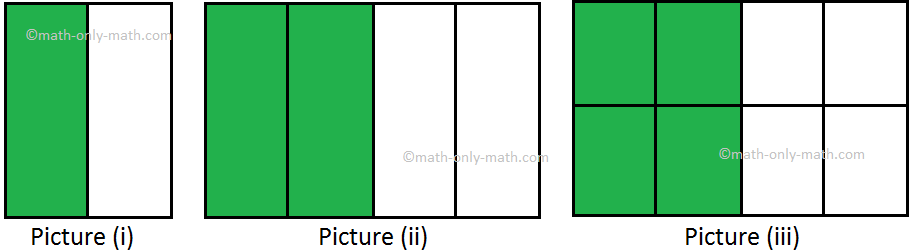
In picture (i) the shaded part is represented by fraction \(\frac{1}{2}\).
The shaded part in picture (ii) is represented by fraction \(\frac{2}{4}\). In picture (iii) the same part is represented by fraction \(\frac{4}{8}\). SO, the fraction represented by these shaded portions are equal. Such fractions are called equivalent fractions.
We say that \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Hence, for a given fraction there can be many equivalent fractions.
Fractions that have the same value or represent the same part of a whole are called equivalent fractions.
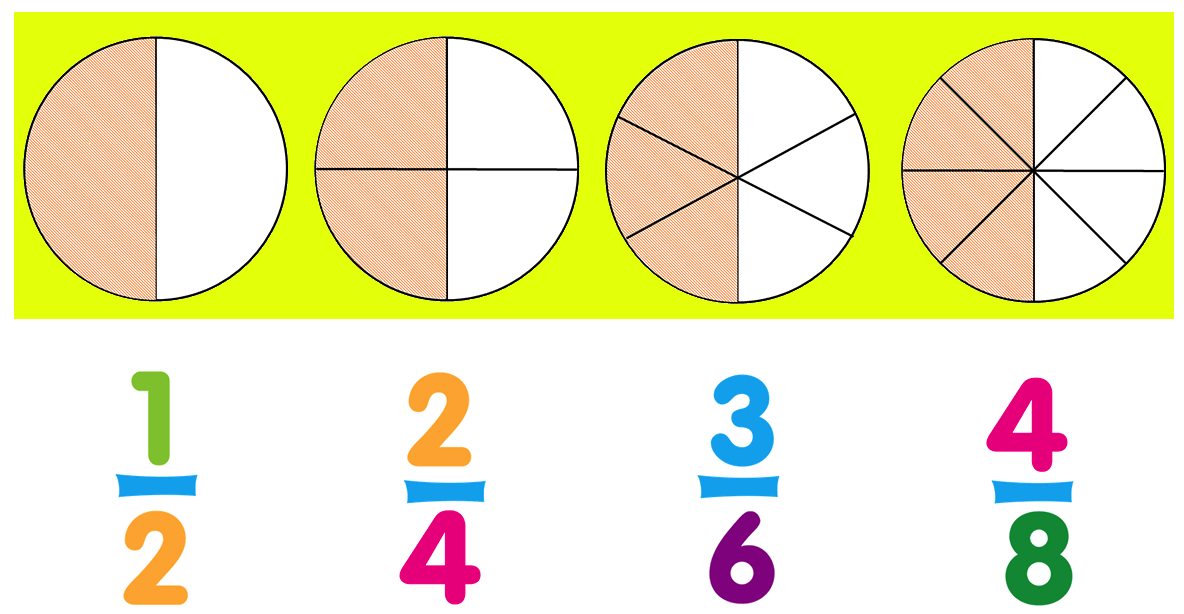
Look at the figures given below:
The shaded parts of all figures are equal, i.e., \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
So, \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{6}\) and \(\frac{4}{8}\) are equivalent fractions.
To get a fraction equivalent to a given fraction we divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number.
For example:
\(\frac{10}{15}\) = \(\frac{10 ÷ 5}{15 ÷ 5}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Hence, the fraction \(\frac{2}{3}\) is equivalent to the fraction \(\frac{10}{15}\).
An equivalent fraction has an infinite number of equivalent fractions.
Making Equivalent Fractions:
We have seen in the above example that \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{4}\) and \(\frac{4}{8}\) are equivalent fractions.
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{2}\) can be written as \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 2}{2 × 2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 3}{2 × 3}\) = \(\frac{1 × 4}{2 × 4}\) and so on.
Hence, an equivalent fraction of any given fraction can be obtained by multiplying its numerator and denominator by the same number.
Same way, when the numerator and denominator of a fraction are divided by the same number, we get its equivalent fractions.
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 ÷ 1}{2 ÷ 1}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{2 ÷ 2}{4 ÷ 2}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{3 ÷ 3}{6 ÷ 3}\)
We have,
2/4 = (1 × 2)/(2 × 2)We observe that 2/4, 3/6 and 4/8 are obtained by multiplying the numerator and denominator of 1/2 by 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
3/6 = (1 × 3)/(2 × 3)
4/8 = (1 × 4)/(2 × 4)
Thus, an equivalent fraction of a given fraction can be obtained by multiplying its numerator and denominator by the same number (other than zero).
2/4 = (2÷ 2)/(4 ÷ 2) = 1/2
3/6 = (3÷ 3)/(6 ÷ 3) = 1/2
4/8 = (4 ÷ 4)/(8 ÷ 4) = 1/2
We observe that if we divide the numerators and denominators of 2/4, 3/6 and 4/8 each by their common factor 2, we get an equivalent fraction 1/2.
Thus, an equivalent fraction of a given fraction can be obtained by dividing its numerator and denominator by their common factor (other than 1), if ant.
Note:
(ii) Dividing its numerator (top) and denominator (bottom) by their common factor (other than 1).
For Example:
1. Write three equivalent fraction of 3/5.
Equivalent fractions of 3/5 are:
(3 × 2)/(5× 2) = 6/10,
(3 × 3)/(5 × 3) = 9/15,
(3 × 4)/(5 × 4) = 12/20
Therefore, equivalent fractions of 3/5 are 6/10, 9/15 and 12/20.
2. Write next three equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{3}\).
We multiply the numerator and the denominator by 2.
We get, \(\frac{2 × 2}{3 × 2}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Next, we multiply the numerator and the denominator by 3. We get
\(\frac{2 × 3}{3 × 3}\) = \(\frac{6}{9}\).
Next, we multiply the numerator and the denominator by 4. We get
\(\frac{2 × 4}{3 × 4}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\).
Therefore, equivalent fractions of \(\frac{2}{3}\) are \(\frac{4}{6}\), \(\frac{6}{9}\) and \(\frac{8}{12}\).
3. Write three equivalent fraction of 1/4.
Equivalent fractions of 1/4 are:
(1× 2)/(4× 2) = 2/8,
(1 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 3/12,
(1× 4)/(4× 4) = 4/16
Therefore, equivalent fractions of 1/4 are 2/8, 3/12 and 4/16.
4. Write three equivalent fraction of 2/15.
Equivalent fractions of 2/15 are:
(2× 2)/(15 × 2) = 4/30,
(2 × 3)/(15 × 3) = 6/45,
(2× 4)/(15 × 4) = 8/60
Therefore, equivalent fractions of 2/15 are 4/30, 6/45 and 8/60.
5. Write three equivalent fraction of 3/10.
Equivalent fractions of 3/10 are:
(3× 2)/(10× 2) = 6/20,
(3 × 3)/(10 × 3) = 9/30,
(3× 4)/(10× 4) = 12/40
Therefore, equivalent fractions of 3/10 are 6/20, 9/30 and 12/40.
To get a fraction equivalent to a given fraction we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number.
For example:
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{4 × 2}{5 × 2}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{8 × 3}{10 × 3}\) = \(\frac{24}{30}\).
Hence, the fractions \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{24}{30}\) are equivalent to the fraction \(\frac{4}{5}\).
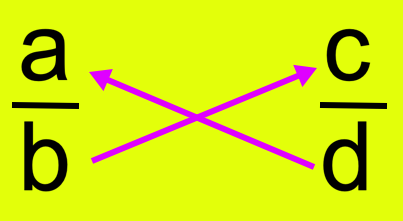
To check whether two fractions are equivalent or not, we cross multiply as follows:
Let \(\frac{a}{b}\) and \(\frac{c}{d}\) be two fractions. Then:
If the cross products are equal, i.e., the product of the numerator of first fraction and the denominator of the second is equal to the product of the denominator of the first and the numerator of the second, the two fractions are equivalent.
Thus, ad = bc.
6. Write an equivalent fraction of \(\frac{9}{15}\) with denominator 5.
Solution:
We have, \(\frac{9}{15}\) = \(\frac{□}{5}\)
⟹ 15 × ⯀ = 9 × 5 ; [By cross multilication]
⟹ 5 × 3 × ⯀ = 3 × 3 × 5
⟹ ⯀ = 3
Hence, \(\frac{3}{5}\) is the required equivalent fraction.
7. Write the three equivalent fractions of \(\frac{3}{7}\).
Solution:
\(\frac{3}{7}\) = \(\frac{3 × 2}{7 × 2}\) = \(\frac{3 × 3}{7 × 3}\) = \(\frac{3 × 4}{7 × 4}\) = \(\frac{6}{14}\) = \(\frac{9}{21}\) = \(\frac{12}{28}\)
Hence, \(\frac{6}{14}\), \(\frac{9}{21}\) and \(\frac{12}{28}\) are three equivalent fractions of \(\frac{3}{7}\).
8. Check whether \(\frac{4}{9}\) and \(\frac{16}{36}\) are equivalent or not.
Solution:
To check whether two fractions are equivalent, we cross multiply as:
The cross products are: 4 × 36 = 144 and 9 × 16 = 144.
SInce both the products are equal, hence the fractions \(\frac{4}{9}\) and \(\frac{16}{36}\) are equivalent.
● Fraction
Representations of Fractions on a Number Line
Conversion of Mixed Fractions into Improper Fractions
Conversion of Improper Fractions into Mixed Fractions
Interesting Fact about Equivalent Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Like Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Unlike Fractions
Inserting a Fraction between Two Given Fractions
From Equivalent Fractions to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.